Difference between cytokines and chemokines
Cytokines are small proteins released by cells, the function of which is “cell-signaling“.
Chemokines are small cytokines, which functions as a “chemo-attractant“.
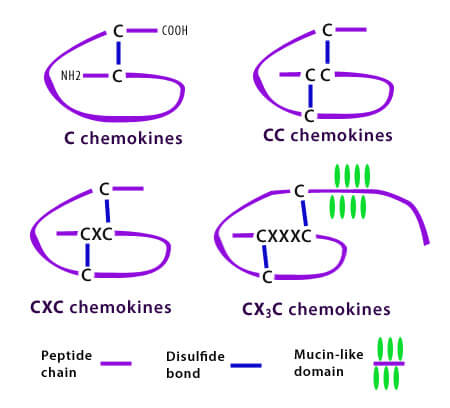
Types of Chemokines
When you go through the structural classification of chemokines, you come accross various arrangements of letter:
- C: denotes cysteine
- X: denotes other amino acids
CXC (alpha chemokines): Acts on NEUTROPHILS.
- Example: IL-8
C-C (beta chemokines): Acts on ALL LEUKOCYTES EXCEPT NEUTROPHILS
- Monocyte Chemoattractant protein – 1 (MCP-1)
- Regulated and Normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES)
- Eotaxin
C (gamma chemokines): Acts on LYMPHOCYTES
- Example: Lymphotaxin
CX3C (d-chemokine): Acts on Monocytes and T-lymphocytes
- Only example: Fractalkaline
Mnemonic:
Just remember the timeline of cells during inflammation:
- First to appear: Neutrophil
- Then appears: Monocyte-macrophages (Remember as other leukocytes)
- Then in chronic inflammation: Lymphocytes
In the order of decreasing “letters” in the subfamily of chemokines:
- CXC = Alpha chemokines
- CC = Beta chemokines
- C = Gamma chemokines
CXC = Acts on neutrophils (IL-8)
CC = Acts on other leukocytes (MCP-1, RANTES, Eotaxin)
C = Acts on Lymphocytes (Lymphokines)
CX3C = Unique (Fractalkaline)

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.