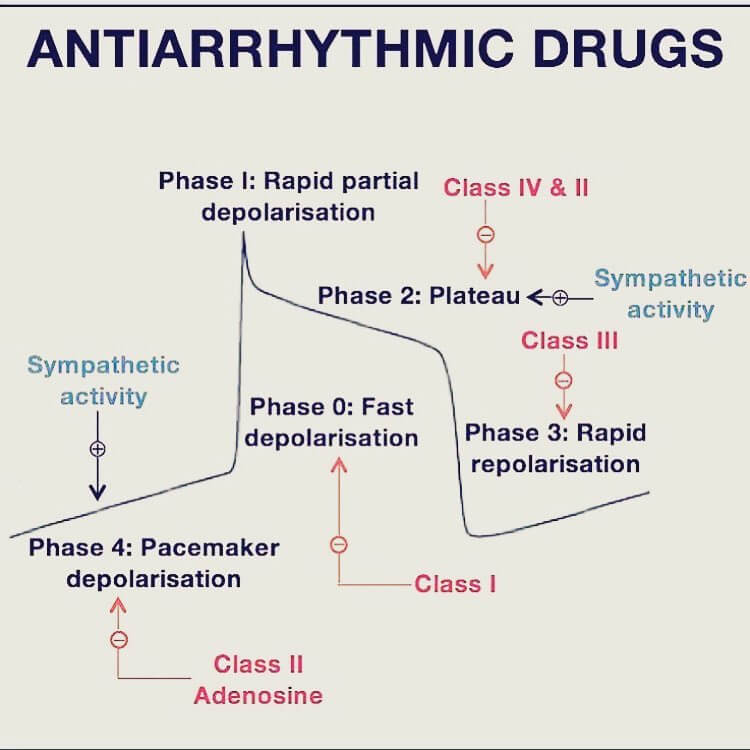
Understand the conducting system of heart, cardiac action potential and pacemaker action potential. Mnemonic to remember Vaughan Williams classification for anti-arrhythmic – Some Block Potassium Channel DAAM! Mnemonic Class Mechanism of action Comments Example Use Some IA Sodium channel blocker (moderate)Intermediate action Moderate ↓ phase 0 slope↑ EFR & AP…
Tag: Pharmacology
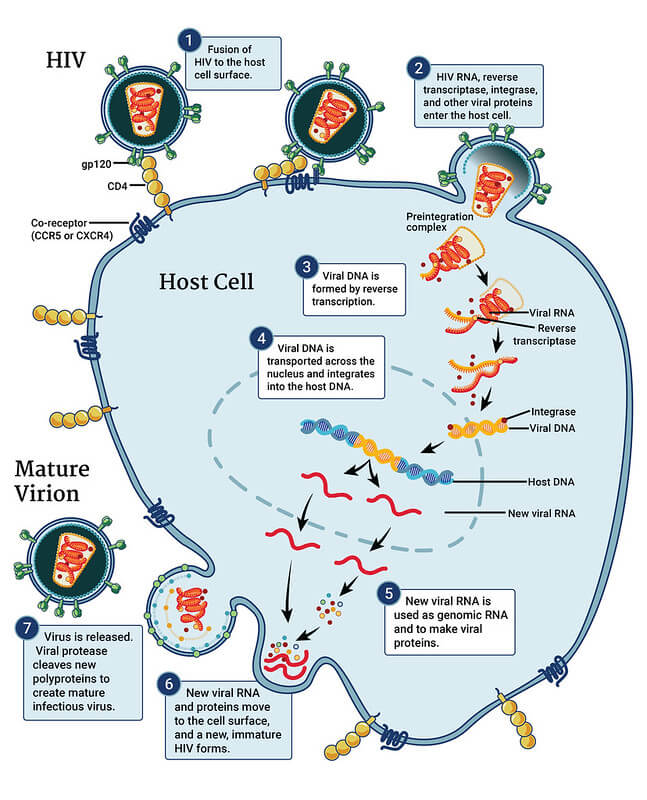
HIV Replication and Antiretroviral Drugs
HIV Replication and Antiretroviral Mechanism of Action Mnemonic: AFRITAB 1. Attachment (to CD4 cells) 2. Fusion (enters CD4 cells and dump it’s contents – RNA and reverse transcriptase) 3. Reverse transcription (1 strand RNA becomes 2 strand DNA) 4. Integration (HIV DNA integrates into human’s CD4 cell’s DNA) 5. Transcription…

The Science of Cannabinoids: Exploring the Health-Boosting Compounds in Cannabis Seeds
Cannabinoids are compounds that can be found in cannabis plants. There are many different cannabinoids and the ones that Marijuana plant are called Tetrahydrocannabinol or THC, which gives off a “high” feeling. Cannabis plants that are grown for their medicinal and therapeutic properties are called hemp and they contain a…
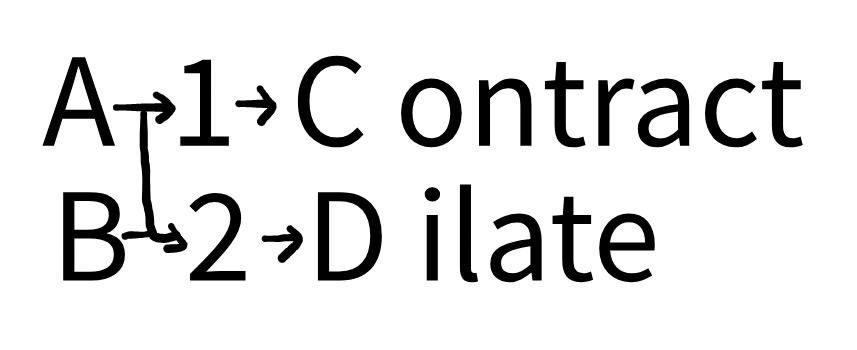
Alpha and Beta Adrenergic Receptors : Mnemonics
Location Alpha = Arteries and smooth muscles Beta = Beats or Breaths Types and Action 1 = Contract 2 = Dilate Receptors Alpha 1: Alpha 2: Beta 1: Mnemonic: We have 1 HEART Beta 2: Mnemonic: We have 2 LUNGS Beta 3: Mnemonic: 3 = Triglyceride

4 Reasons Why You May Be Required to Take a Travel Nurse Drug Test
Drug testing is important for travel nurses serving a crucial role in guaranteeing patient safety and preserving the reputation of healthcare institutions. Detecting substance abuse issues promptly enables healthcare facilities to intervene and verify that travel nurses are fully capable of delivering optimal patient care. 1. Pre-Employment Drug Testing Drug…

What Are Prescription Opioids? [Effects, Dangers & Treatment]
It’s no new that while prescription opioids can effectively alleviate pain, they can also be highly addictive. For this reason, the first thing you want to do after being prescribed these medications is to learn as much about them as possible. This way, you know what to expect and how…
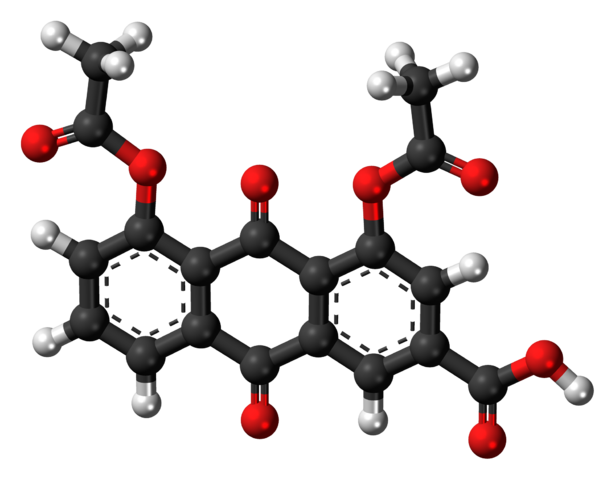
Diacerin : Mnemonic
Diacerin is a DMOAD (Diseases Modifying Osteoarthritis Drug) – D – Diarrhea (not recommended in >65 years – more vulnerable to diarrhea) I – IL-1 Inhibition A – Anthraquinone C – Chondroprotective effects E – Eczema R – Rashes I – Increase in hepatic enzymes (contraindicated in patients with history…

Methotrexate : Mnemonic
Methotrexate is a dihydrofolate reductase (DHFRase) inhibitor which inhibits DNA repair, synthesis and cellular replication. Actively proliferating tissues such as malignant cells, bone marrow, fetal cells, buccal and intestinal mucosa, and cells of the urinary bladder are in general more sensitive to its effect. A convenient regimen for Low Dose…