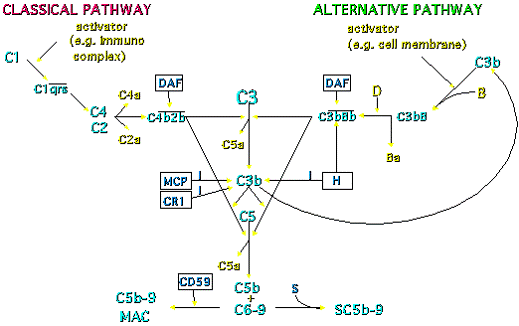
The complement system is composed of about 20 different proteins released into the blood after production in the liver. They interact in coordinated and regulated way to produce biologically active protein products. ACTIVATION OF COMPLEMENT CASCADE The complement cascade can be activated in 3 ways: C3 and C3 CONVERTASE All of…
Tag: Pathology
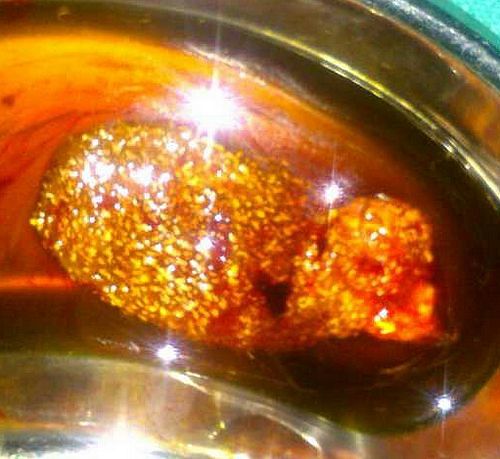

Strawberry Gallbladder (Cholesterolosis)
Synonyms: Strawberry gallbladder is also known as hyperplastic cholecystoses. Hyperplastic cholecystoses are a spectrum of non-neoplastic proliferative disorders caused by deposition of cholesterol-laden macrophages within the wall of the gall bladder. The cholecystose range from abnormalities of the gallbladder wall (adenomyomatosis and strawberry gall bladder) to gallbladder polyps extending into…

Mendelian Inheritance : Basis of Genetics
Some important terminologies Gene: a functional part of the DNA molecule of a chromosome which directs the synthesis of a specific polypeptide chain. Allele (allelomorph): alternative form of a gene found at the same locus on a pair of homologous chromosomes. Homozygous: the presence of two identical alleles at a…
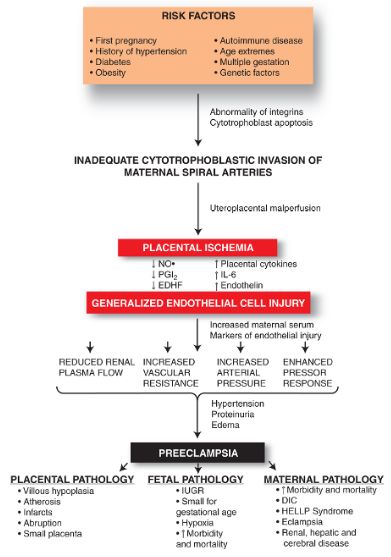
Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy – Basics
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy is a term that encompass wide range of blood pressure related disorders during pregnancy like gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, etc. Blood pressure in Normal Pregnancy: During middle trimester, due to the reduction in Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) and Arterio-venous (AV) shunting within the uterus and intervillous…
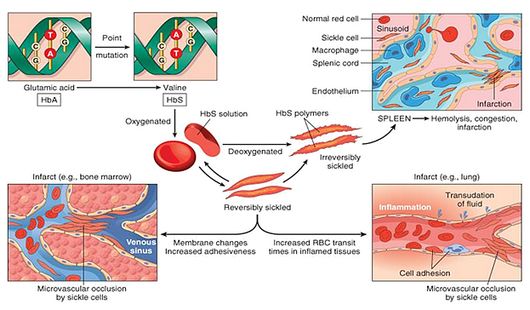
Salmonella Osteomyelitis in Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a hereditary disorder of hemoglobin synthesis caused by a mutation in the globin gene that changes the sixth amino acid from glutamic acid to valine resulting in abnormal sickling (rigid, inflexibled and sickle-shaped) of Red Blood Cells (RBCs) under low oxygen conditions. Sickle cell anemia…
Leprosy: Etiopathogenesis, Classification and Complications
Synonyms: Hansen’s disease, Kushta roga, Mezels Definition: Leprosy is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium leprae which affects prinicpally the skin and peripheral nerves. Other commonly affected sites are the cooler parts of the body like mucosa of upper respiratory tract, anterior chamber of eyes and testes. The cooler…
Pathology Spotters: Instruments
Pathology Spotter Series: Instruments Level: Undergraduate (MBBS) A) Spotter 1: Instrument: Paraffin Block Use: Tissue embedding – After adding fixative, biopsies are embedded in paraffin/wax to support the tissue so that thin sections or slices can be cut and placed on a microscope slide. B) Spotter 2: Instrument: Lumbar Puncture…