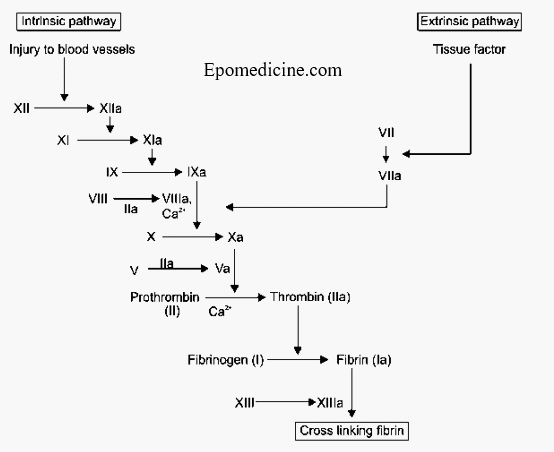
In medical school, coagulation cascade might be a pain to learn and teach as well. Plenty of roman numerals with arrows going here and there – is this the reason you hate coagulation cascade? I will pretty much try to simplify the whole thing with essential clinical correlation here. I…
Tag: Pathology
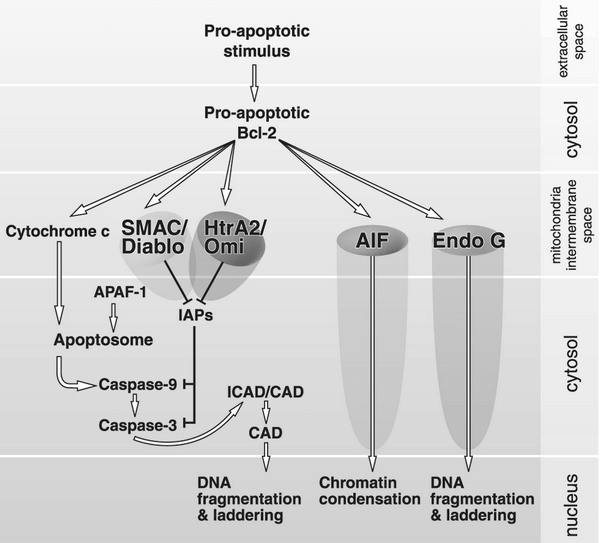
Apoptosis (Caspases and Genes) : Mnemonics
Caspases (Pro-apoptotics) Initiator caspases: Executioner caspases: 3 and 7 Pro-apoptotic genes Mnemonic: “B” followed by a vowel Anti-apoptotic genes Mnemonic: Contains “L” or “XL” Other: Inhibitor of Apoptosis (XIAP) How all these genes and molecules work together to complete apoptosis? Find it here.
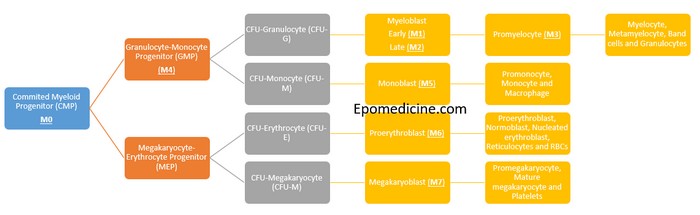
Concept of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) FAB Classification
There is no need of mnemonics to remember the FAB classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML); just remember the process myeloid differentiation. A simple schematic diagram with few intermediate processes and stimulating factors eliminated will meet our purpose here. The cells belonging to the myeloid lineage are: Granulocytes: Neutrophils, Eosinophils…
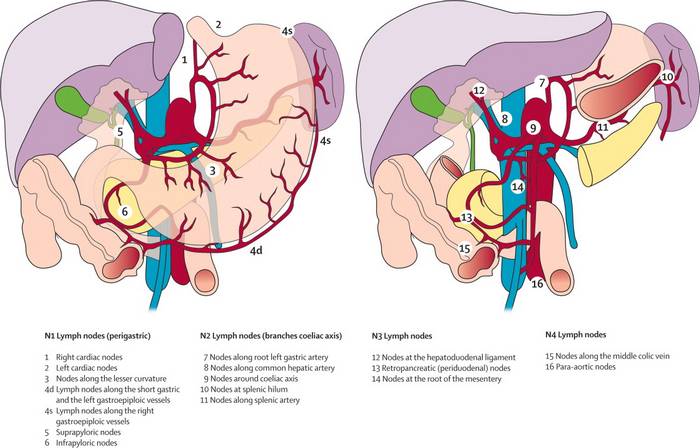
TNM and Staging of Gastric Carcinoma Simplified
Unique features of stomach in relation to TNM cancer classification 1. Cancer penetrates the muscular propria and invades the ligaments (gastrohepatic and gastrocolic, i.e. lesser and greater omentum respectively) subserosally without breeching the serosa. Gastric cancer invasion of the lesser and greater omentum is T3, not T4. Perforation of the…
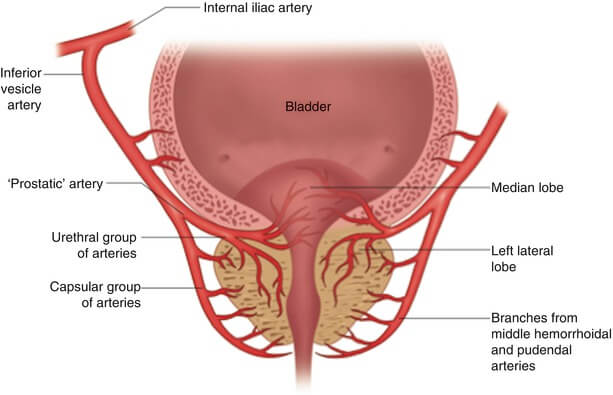
Prostate Anatomy – Clinical correlate
Anatomy of Prostate The embryology and detailed gross and microscopic anatomy of the prostate has already been discussed earlier. Read the anatomy of prostate. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Occurs exclusively in transition zone (progressively enlarges with age). Median lobe of the gland enlarges upward and encroaches sphincter vesicae, located at…
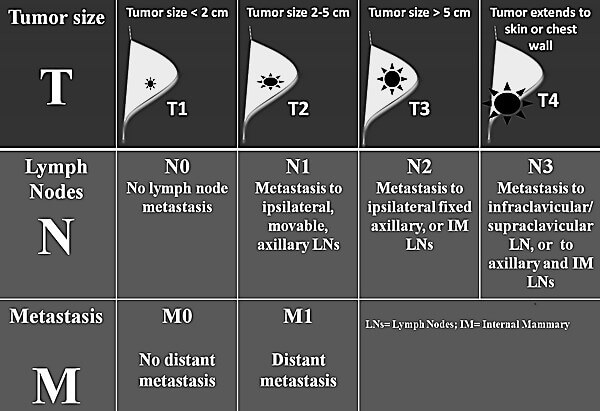
TNM and Staging of Breast Cancer Simplified
TNM Classification for Breast Cancer Primary Tumor (T) T1: ≤2 cm (20 mm) mi: ≤1 mm a: 1-5 mm b: 5-10 mm c: 10-20 mm T2: 2-5 cm T3: >5 cm T4: Direct extension to chest wall and/or skin a: Chest wall (exclude only pectoralis muscle adherence/invasion) b: Ipsilateral ulceration, satellite nodules…
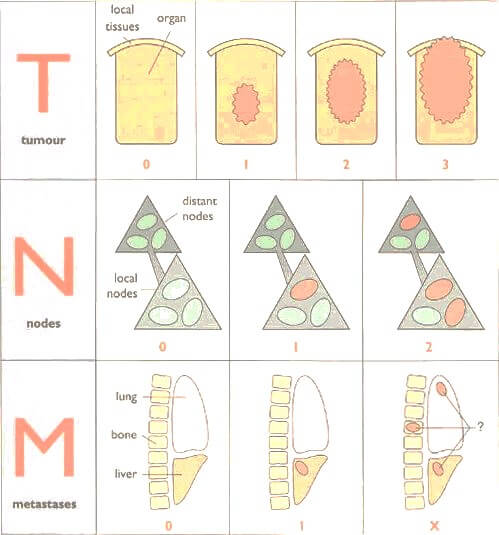
TNM Classification and Cancer Staging Simplified
You must be asking yourself – “how to remember the TNM staging system?” and looking here and there for mnemonics only to find nowhere. Understanding the oncoanatomy helps to understand the staging system of the cancers. Tumor Status (T) T1 T2 T3 T4 Depth of invasion Solid organs Confined Capsule,…
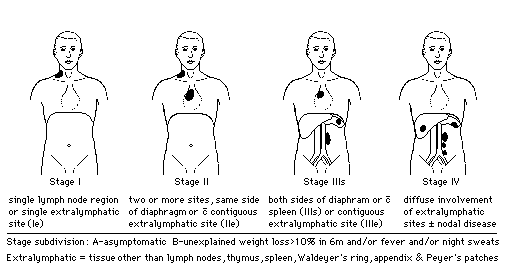
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – Staging and Prognostic Factors
Costwold Modified Ann-Arbor Staging I: 1 Lymph Node (LN) region (I) or 1 Extralymphatic site (IE) II: On the same side of diaphragm – ≥2 LN region (II) or Localized Extralymphatic extension + ≥1 LN region (IIE) III: On both the sides of diaphragm – LN regions (III) ± Spleen involvement (IIIS) ± Localized…