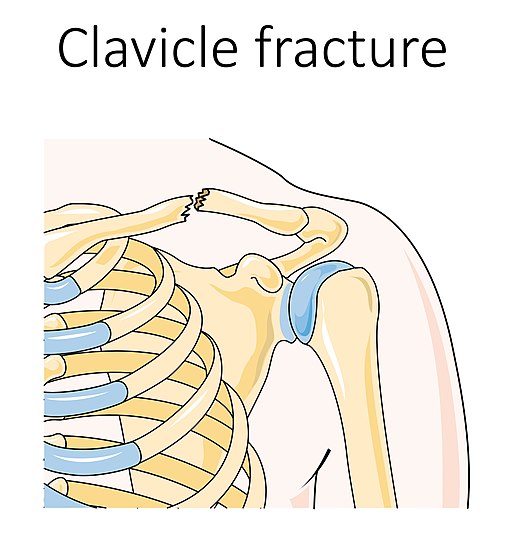
1. 80-85% are mid-shaft fractures (other 10-15% are lateral 3rd and 5% are medial 3rd fractures) because of: 2. Deforming forces: 3. X-ray views: 4. Allman classification: Dameron and Rockwood classification for lateral 1/3 pediatric fractures: Type I: Mild strains of ligaments or periosteal tears Type II: Complete disruption of…
Tag: Musculoskeletal system
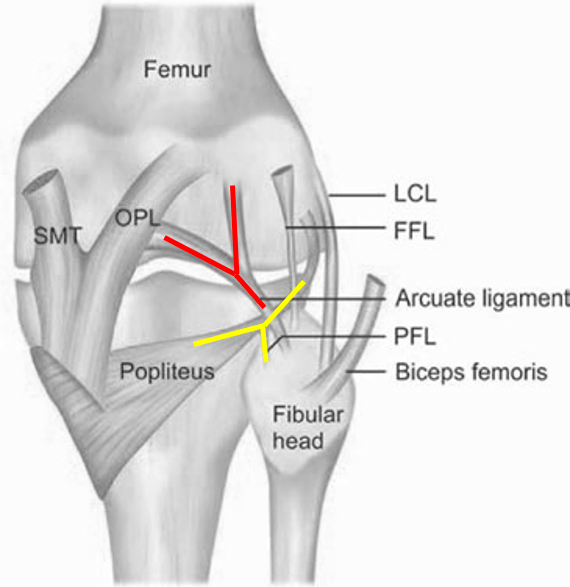
Posterolateral corner (PLC) of knee
Anatomy of PLC 3 major static stabilizers of PLC Lateral collateral ligament Popliteus tendon Popliteofibular ligament Other static stabilizers of PLC Lateral capsule thickening Arcuate ligament Fabellofibular ligament Dynamic stabilizers of PLC Biceps femoris Popliteus muscle Iliotibial band (ITB) Lateral head of gastrocnemius There are 2 “Y” shaped structures in…
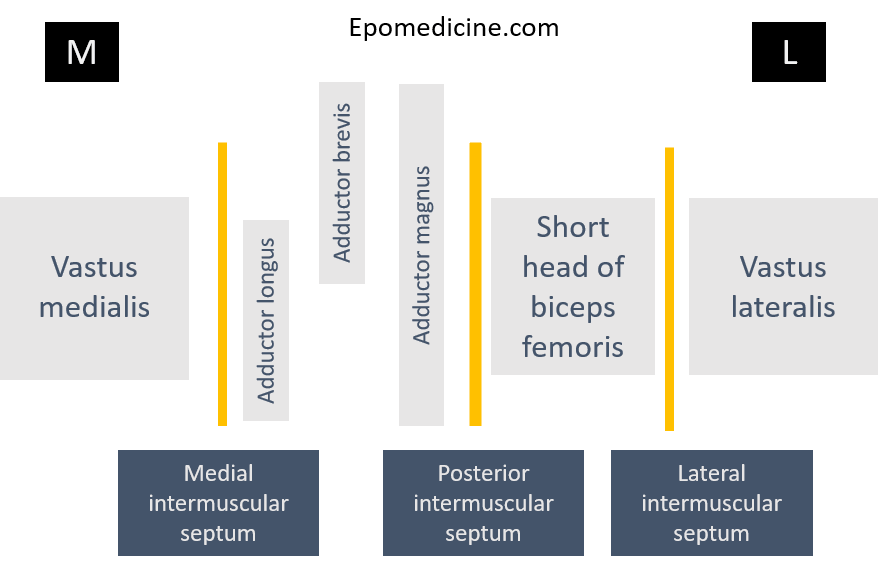
Linea Aspera
Linea aspera is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of femur which serves as a site for attachment of muscles and intermuscular septum. The various structures attached to linea aspera can be remembered using few mnemonics: Mnemonic 1#: 1, 2, 3 It gives attachment…
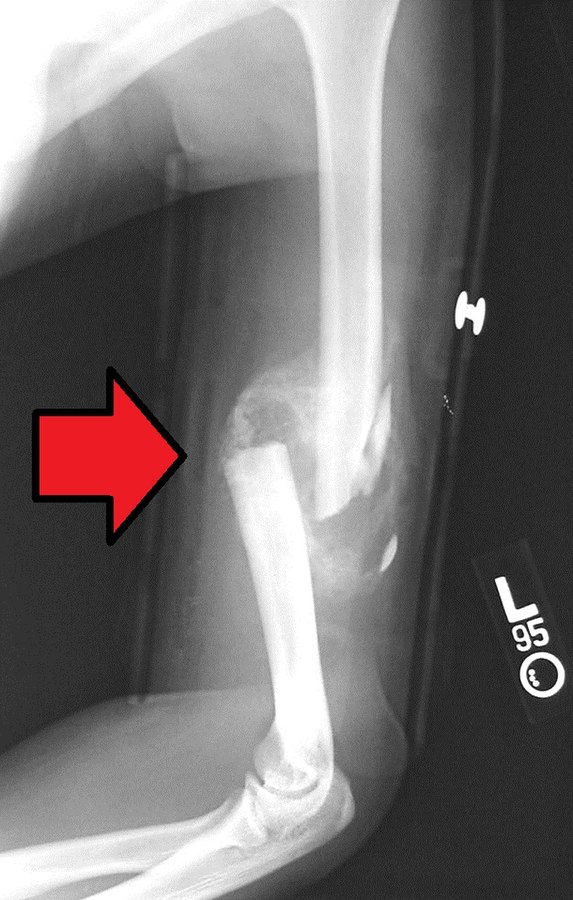
Perkin’s Timetable for Fracture Healing
One needs to understand the difference between bone union and consolidation first Union Consolidation Definition Partial/Incomplete repair Full/Complete repair Callus Calcified Ossified Attempted angulation Painful Painless Fracture line in X-ray Still visible Obliterated and crossed by bony trabeculae Full weight bearing Cannot be undertaken Can be undertaken Reference: Physiotherapy in…

AO fracture classification made easy
It is an alpha-numeric system of classification developed by Muller and colleagues. Step 1: 1st digit specifies bone Step 2: 2nd digit specifies segment of bone Square definition: Proximal and distal segments are defined by a square whose sides = length of widest part of epiphysis Exceptions of square definition:…
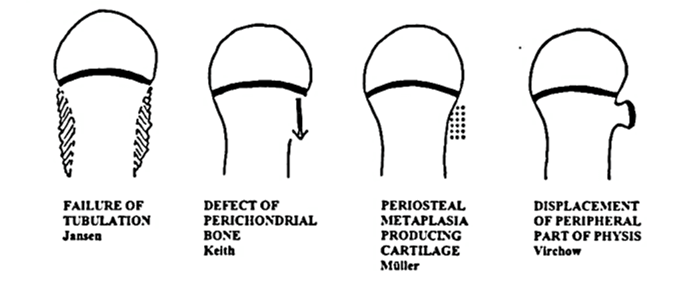
Osteochondroma : Mnemonics
Features of Osteochondroma Mnemonic: Six “C” Commonest benign bone tumor Continue to grow until Closure of physis Cartilage cap (appears larger clinically than in X-ray) Continuous with native bone (cortex and medullary canal) Cane (pedunculated/stalked points away from joint and sessile/broad based have higher risk of malignant degeneration) Change (mutation)…
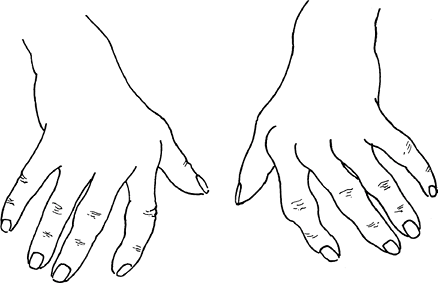
Rheumatoid hand
Ulnar drift or deviation of fingers Normal anatomical factors contributing to ulnar drift of fingers at MCP joint: Normal mechanical advantage of ulnar intrinsic muscles Asymmetry and ulnar slope of metacarpal heads of index and middle fingers Greater ulnar deviation permitted by radial collateral ligament when MCP joint is flexed…
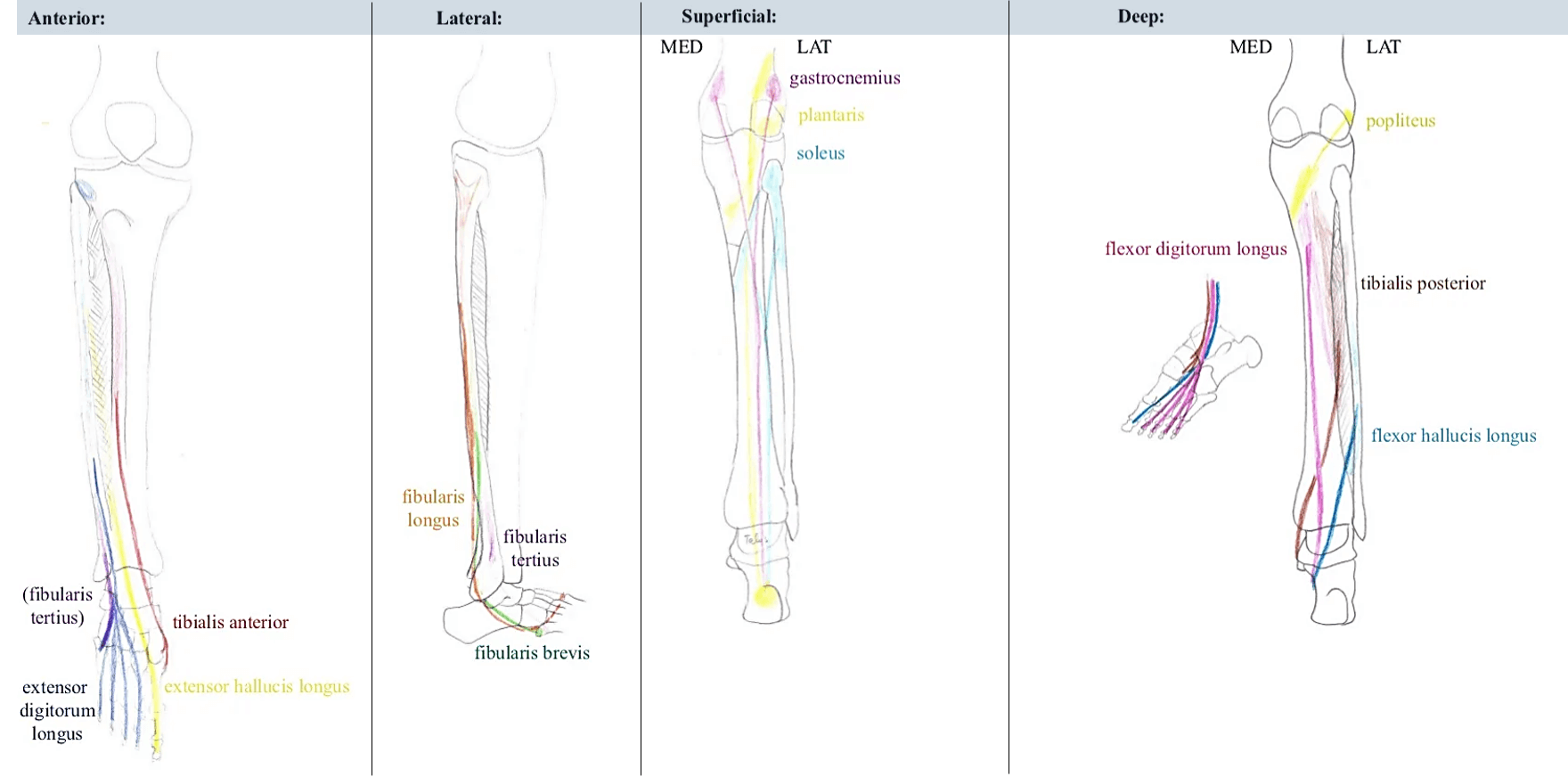
Compartments, Muscles and Fasciotomy of the leg
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Anterior compartment 1. Tibialis anterior (TA) Superior 2/3 lateral surface of tibia Medial cuneiform, 1st metatarsal Dorsiflexion, foot inversion Deep peroneal nerve (L5) 2. Extensor digitorum longus (EDL) Superior 2/3 of fibula and interosseous membrane Middle and distal phalanx, lateral 4 toes Dorsiflexion, toe extension…