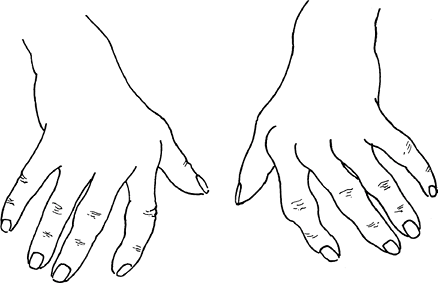
Ulnar drift or deviation of fingers
Normal anatomical factors contributing to ulnar drift of fingers at MCP joint:
- Normal mechanical advantage of ulnar intrinsic muscles
- Asymmetry and ulnar slope of metacarpal heads of index and middle fingers
- Greater ulnar deviation permitted by radial collateral ligament when MCP joint is flexed
- Ulnar forces applied during pinch and grasp
- Flexor tendons enter fibrous sheath at an angle, exerting ulnar and palmar pull that is resisted in normal hand
- Greater strength of abductor digiti quinti and flexor digiti quinti than of 3rd palmar interossei (adductor)
Pathological factors contributing to ulnar drift of fingers at MCP joint:
- Z mechanism: Carpal collapse can cause radial deviation of the carpi leading to compensatory MCP joint ulnar deviation
- Dorsoradial ligament damage from MCP synovitis:
- Radial sagittal bands: Ulnar subluxation of extensor tendon
- Accessory collateral ligament: Ulnar displacement of flexor tendons within their tunnels
- Collateral ligament: Volar displacement of proximal phalanges
- ECU dysfunction (Caput ulnae): Increased mobility of 4th and 5th metacarpals
Management:
- Synovectomy, extensor tendon centralization, and intrinsic release arthroplasty
- Crossed intrinsic transfer: division of the intrinsics on the ulnar side of the wrist and transfer to the radial side
- Silicon MCP arthroplasty (for late disease)
Swan neck and Boutonniere deformity
Caput Ulna Syndrome (Wrist)
Pathoanatomy:
Synovitis in the DRUJ → ECU subsheath stretching → ECU subluxation → supination of the carpal bones away from the head of the ulna → volar subluxation of the carpus away from the ulna → increased pressure over the extensor compartments → tendon rupture
Treatment:
- Early synovectomy
- Manifest caput ulnae syndrome:
- Resection of ulnar head with dorsal wrist stabilization
- Arthrodesis of DRUJ with segmental resection of ulna or arthroplasty (Sauve-Kapandji)
Mannerfelt lesion
Pathoanatomy: Rupture of FPL due to abrasion (attritional rupture) over scaphoid osteophyte
Treatment: Exploration of carpal tunnel + Flexor tenosynovectomy +/- Excision of osteophyte + FPL advancement and pull through/FDS4 to FPL tendon transfer/tendon graft/Arthrodesis of IP joint
Vaughan Jackson Syndrome
Definition: Ulnar to radial progression of extensor tendon rupture
Pathoanatomy: Tenosynovitis (synovial infiltration + diminished vascular supply) and Caput ulnae → Attrition over prominent ulna → Rupture of EDQ and EDC of little finger → sequential rupture of the EDC tendons of the ring, long, and index fingers
EPL is commonly ruptured due to attrition over Lister’s tubercle.
Treatment: Treat caput ulnae + Tendon repair or transfers (EIP to EDC or FDS if multiple ruptures)
Rheumatoid thumb
Nalebuff classification
| Type | CMC joint | MP joint | IP joint | Treatment |
| I (Boutonniere) | – | Flexed | Hyperextended | MCPJ synovectomy + EPL re-routing; Arthrodesis, Arthroplasty |
| II (Boutonniere with CMCJ involvement) | Flexed & Adducted | Flexed | Hyperextended | Block arthrodesis to restore metacarpal adduction (+/- CMC arthrodesis); Capsulodesis, Arthrodesis |
| III (Swan neck with CMCJ subluxation) | Subluxed, Flexed & Adducted | Hyperextended | Flexed | Same as in II |
| IV (Gamekeeper thumb) | Flexed & Adducted | Hyperextended, UCL unstable | – | MCP stabilization, UCL reconstruction and Z-plasty for adduction contracture |
| V (Swan neck without CMCJ disease) | +/- involvement | Hyperextension, volar plate unstable | Flexed | MCPJ capsulodesis or fusion; Volar plate advancement |
| VI (Arthritis mutilans) | Bone loss at any level | Bone loss at any level | Bone loss at any level | Arthrodesis |
Rheumatoid arthritis diagnostic criteria have been discussed here with mnemonics: Rheumatoid Arthritis Criteria Mnemonics | Epomedicine