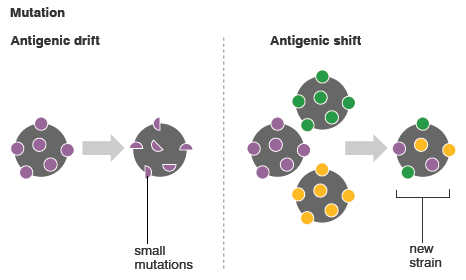
Antigenic Drift Nature of antigenic variation: Minor Mechanism: Gradual accumulation of amino acid substitutions due to point mutation in the hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) genes. As mutations accumulate, antibodies generated by exposure to previous strains do not neutralize current strains to the same extent, resulting in only limited or…
Tag: Microbiology

Bedside Cold Agglutinin Test for Mycoplasma
Definition of Cold Agglutinin Cold agglutinins are polyclonal IgM that have specificity against the I-antigen on red cells, and often there is light chain restriction, with kappa being predominant. The infections associated with cold agglutinins are: Mycoplasma pneumoniae Epstein Barr virus Cytomegalovirus HIV Rubella Steps for Bedside Cold Agglutinin Test…
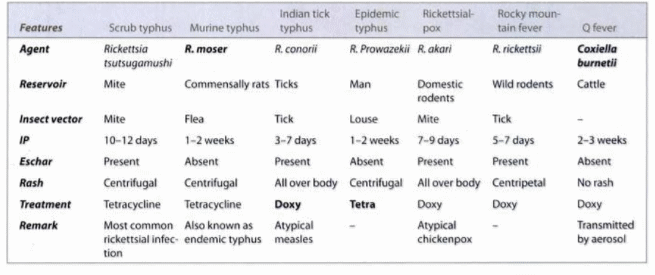
Rickettsial Diseases Made Easy
Important features of Rickettsia and Rickettsial Diseases Obligate intracellular parasites like Chlamydia – can survive only in host cells Cannot produce their own ATP, so they utilize the ATP of a host cell Gram negative coccobacillia, and short bacilli that grow strictly in eukaryotic cells (unable to grow in cell…
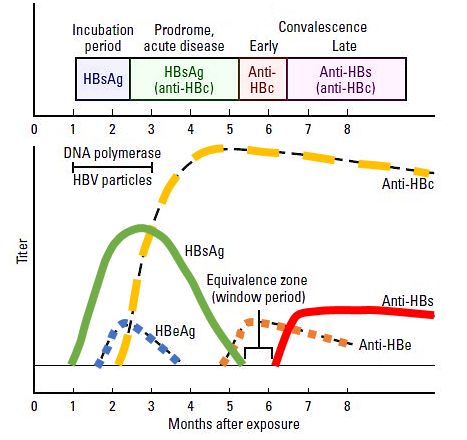
Interpreting Hepatitis B Serology in 5 Easy steps
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) Appears during incubation period (1-6 months), 2-7 weeks prior to symptoms. Peaks when the patient is most ill. Becomes undetectable in 3-6 months. Indicates infection – recent or chronic. Hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs or HBsAb) Arises once the acute disease has resolved. Sometimes, not…
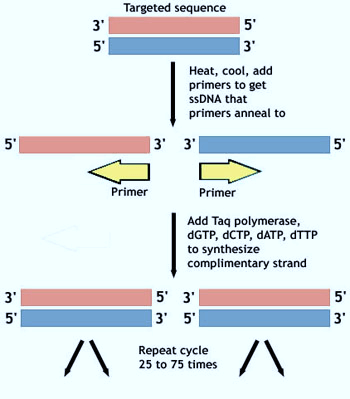
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Made Easy
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction ? It is a process of artificial DNA replication (amplification of a selected part of DNA). As the name suggests: Polymerase: It requires DNA polymerase for extending the added primers to complete DNA replication. Chain Reaction: PCR is run in cycles. The number of molecules…
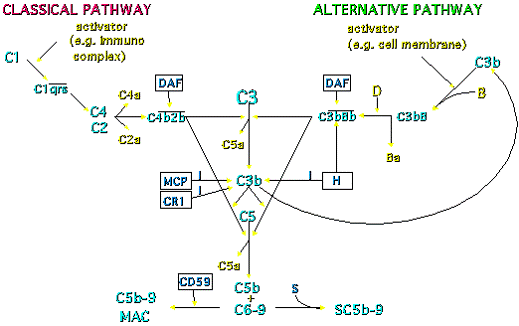
Complement Pathway – Explained
The complement system is composed of about 20 different proteins released into the blood after production in the liver. They interact in coordinated and regulated way to produce biologically active protein products. ACTIVATION OF COMPLEMENT CASCADE The complement cascade can be activated in 3 ways: C3 and C3 CONVERTASE All of…