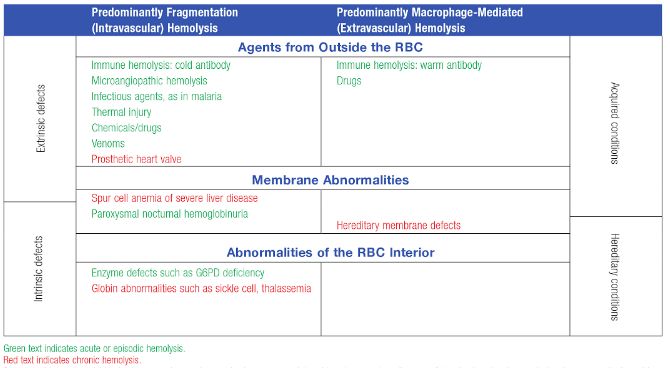
Although, we classify as intravascular and extravascular hemolysis, “diseases” don’t read the book. These disorders may be described as causing extravascular hemolysis, but your case may be the uncommon exception with intravascular hemolysis that was not mentioned. Diseases may cause anemia by both intravascular and extravascular hemolysis. Extravascular hemolysis typically…
Tag: Hematology
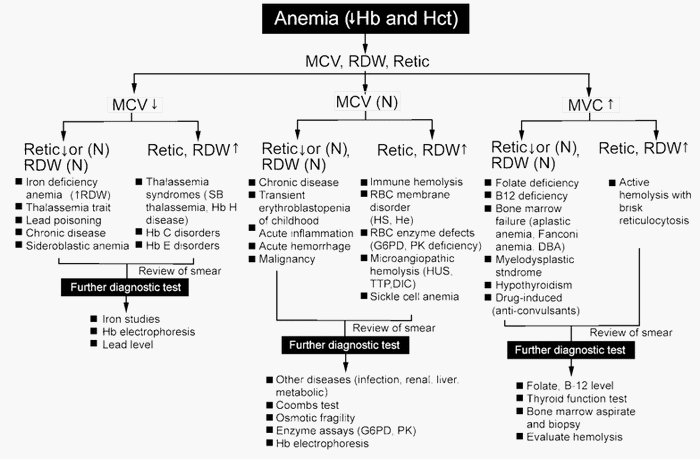
Understanding Red cell indices
Rule of 3s The measured hemoglobin concentration is 3 times the RBC count, and the calculated hematocrit is 3 times the Hb level. A significant deviation means artifacts in the value estimated or the RBCs are smaller or larger than the normal. HCt = 3 X Hb RBC count =…
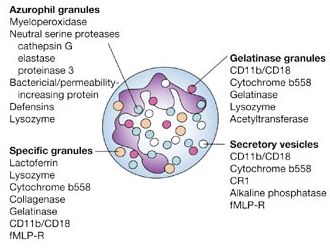
Granular contents of Neutrophils and Platelets
Neutrophil Granules Azurophilic (Primary) Granules These are lysosomes that occur in all granulocytes, as well as in lymphocytes and monocytes. In addition to expected lysosomal hydrolases, they also contain peroxidases (used to demonstrate azurophilic granules chemically). Develop earlier than specific granules. Stains blue/purple by Romanowsky stain. Mnemonic: ABCDE MnOP Acid hydrolase…
Tissue Specific and Named Macrophages
Subtle differences in the morphology and functions of macrophages develop as a result of the influence of a particular microenvironment. Appearance of macrophages to histologists have been described as a kind of mythological Proteus, “a creature who had the power of changing his appearance at will”. The life-span of these fixed…
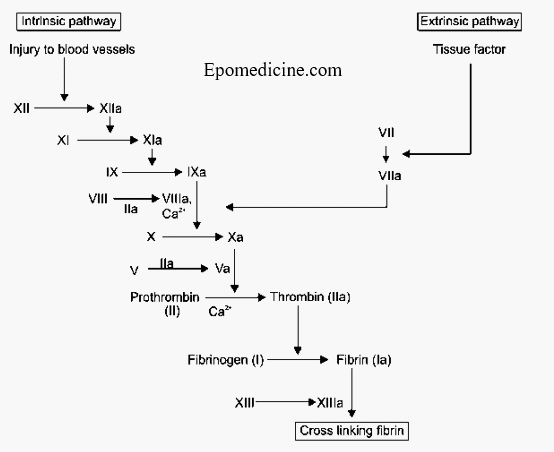
Simple Coagulation Cascade with Mnemonics
In medical school, coagulation cascade might be a pain to learn and teach as well. Plenty of roman numerals with arrows going here and there – is this the reason you hate coagulation cascade? I will pretty much try to simplify the whole thing with essential clinical correlation here. I…
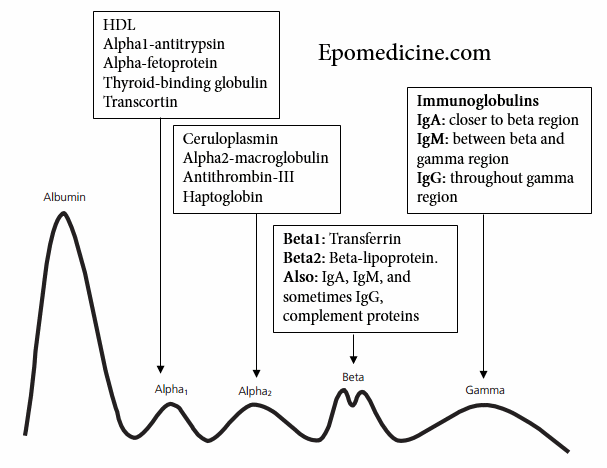
M-spike
Synonyms: Monoclonal spike, M-protein spike, Monoclonal band, Monoclonal gammopathy Tests showing M-spike Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP) Urine Protein Electrophoresis (UPEP) Normal SPEP or UPEP Electrophoresis is a method of separating proteins based on their physical properties. Albumin – the largest peak, lies closest to the positive electrode and the next five…
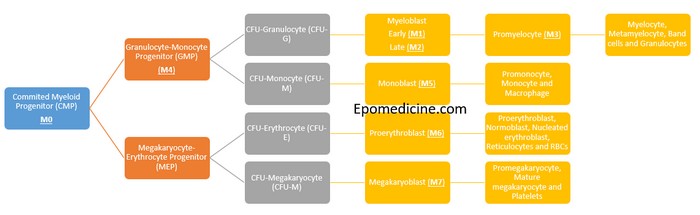
Concept of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) FAB Classification
There is no need of mnemonics to remember the FAB classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML); just remember the process myeloid differentiation. A simple schematic diagram with few intermediate processes and stimulating factors eliminated will meet our purpose here. The cells belonging to the myeloid lineage are: Granulocytes: Neutrophils, Eosinophils…
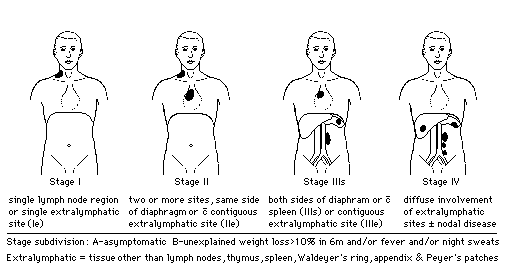
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – Staging and Prognostic Factors
Costwold Modified Ann-Arbor Staging I: 1 Lymph Node (LN) region (I) or 1 Extralymphatic site (IE) II: On the same side of diaphragm – ≥2 LN region (II) or Localized Extralymphatic extension + ≥1 LN region (IIE) III: On both the sides of diaphragm – LN regions (III) ± Spleen involvement (IIIS) ± Localized…