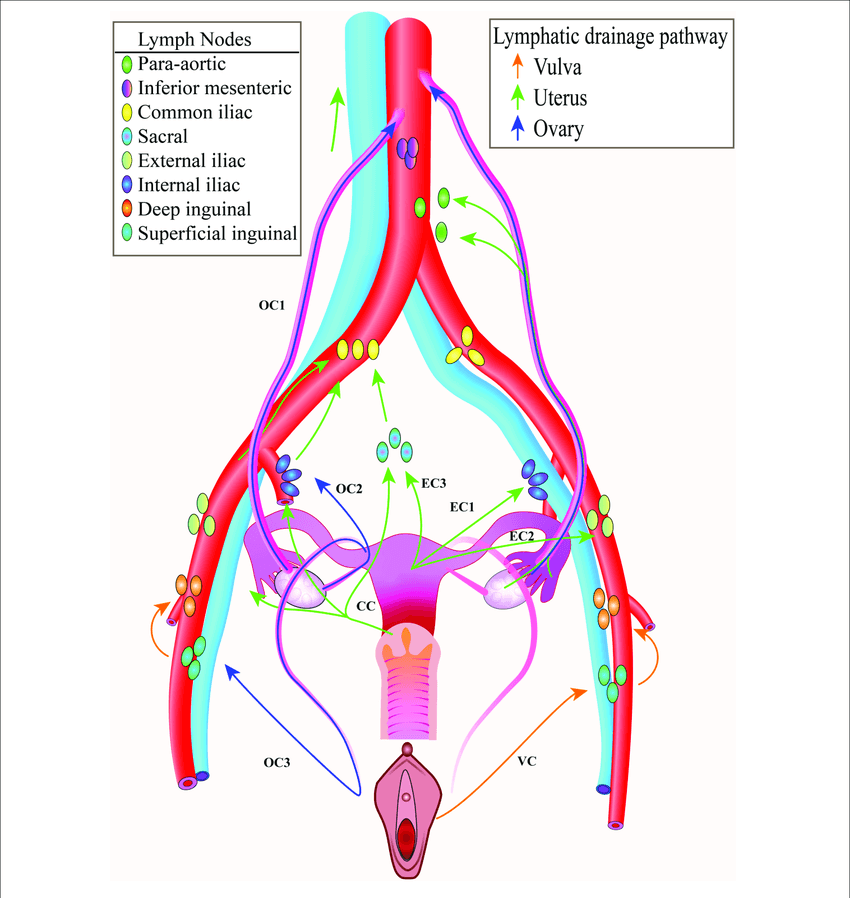
1. Para-aortic (lumbar) nodes: Gonads (derive blood supply from kidneys) 2. Inferior mesenteric nodes: As of blood supply – to the structures derived from hindgut 3. Common iliac nodes: Receives external and internal iliac nodes; Drains into para-aortic nodes 4. Superficial inguinal nodes: Everything that can be touched with fingers…
Tag: Anatomy
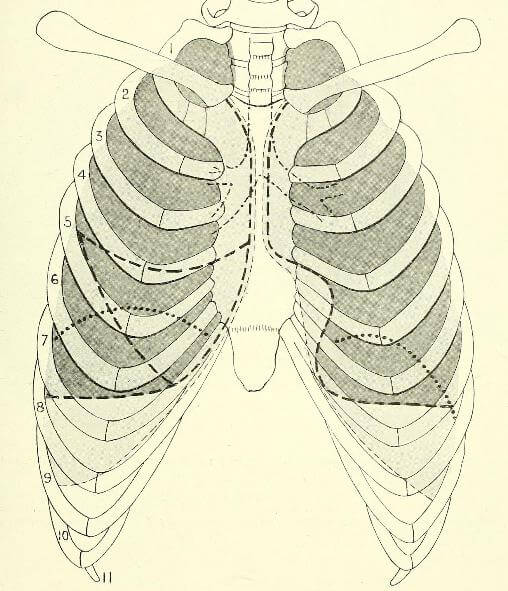
Surface Anatomy of Pleura and Lung
Surface Anatomy of Pleura Mnemonic: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 rule 1. Starts about 2 cm above the midpoint of medial 1/3 of clavicle. 2. Meet in the midline at rib 2. 3. Left side reaches sternal line at rib 4 (to make room for heart). 4. Right side…
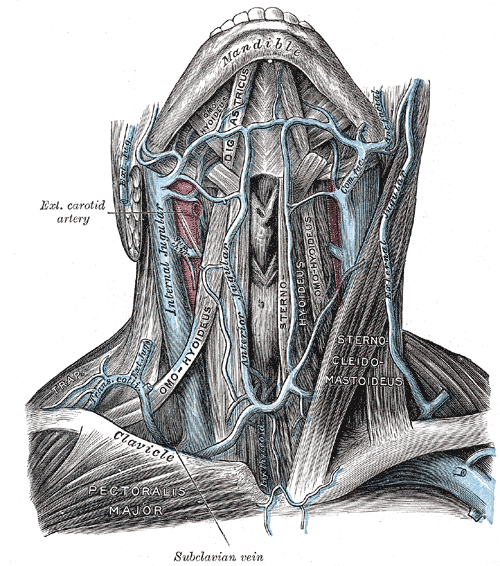
Internal and External Jugular Veins with Mnemonics
Jugular veins are the veins that take blood from the head to the heart via Superior Venacava (SVC). Internal Jugular Vein (IJV) External Jugular Vein (EJV) Formation (Drains from) Inferior petrosal sinus + Sigmoid sinus (At or just distal to Jugular foramen) Posterior div. of retromandibular vein + Posterior auricular…
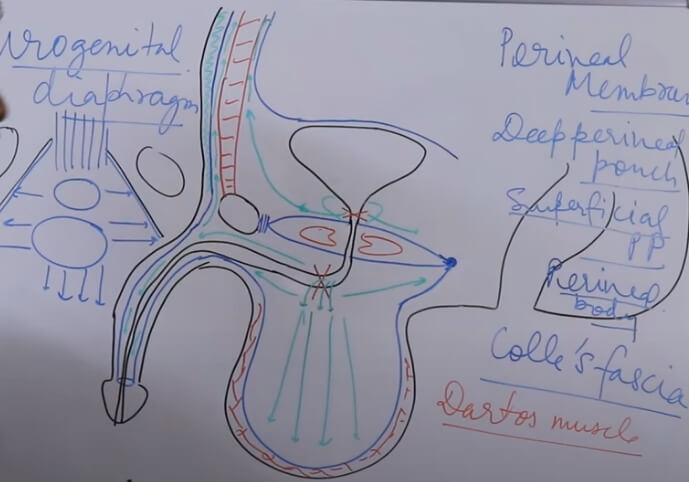
Male Reproductive Anatomy : Mnemonics
Penile Layers Mnemonic: ABCD (from inside to outside) 1. Albuginea (tunica albuginea): Envelopes 3 corporal bodies (2 cavernosa and 1 spongiosum) 2. Buck’s fascia: Separates corpora cavernosa from corpus spongiosum; separates superficial and deep dorsal veins of the penis 3. Colle’s fascia: Continuous with Scarpa’s fascia of abdomen and Dartos…
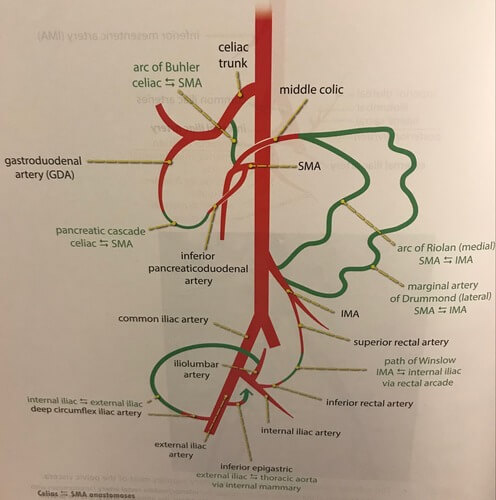
Branches of Celiac trunk, Superior and Inferior mesenteric arteries and veins
Celiac trunk (T12) Mnemonic: LHS (Left Hand Side) Supplies Foregut (Upto opening of bile duct in 2nd part of duodenum) 1. Left gastric artery 2. Hepatic artery (common) 3. Splenic artery Superior Mesenteric Artery (L1) Mnemonic: IMRIS Supplies Midgut (Upto proximal 2/3 of transverse colon) 1. Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery 2….
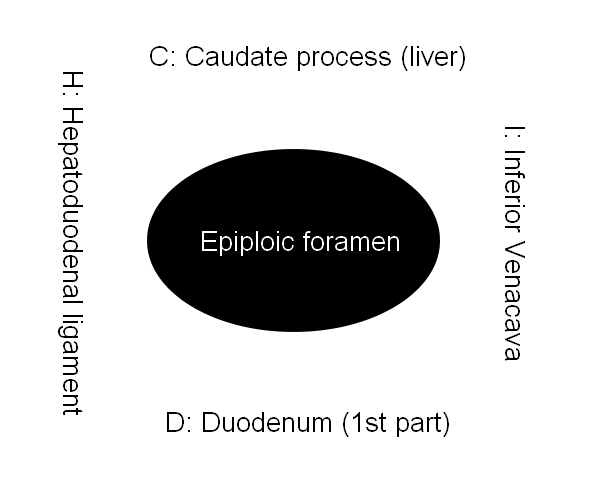
Epiploic foramen of Winslow : Mnemonic
Epiploic foramen is a vertical opening through which lesser sac (omental bursa) communicates with the greater sac (peritoneal cavity proper). It is at the level of T12 vertebra. Boundaries Mnemonic: Epiploic foramen is located between CD and HI. Superior: Caudate process of liver Inferior: Duodenum (1st part) Anterior: Hepatoduodenal ligament…
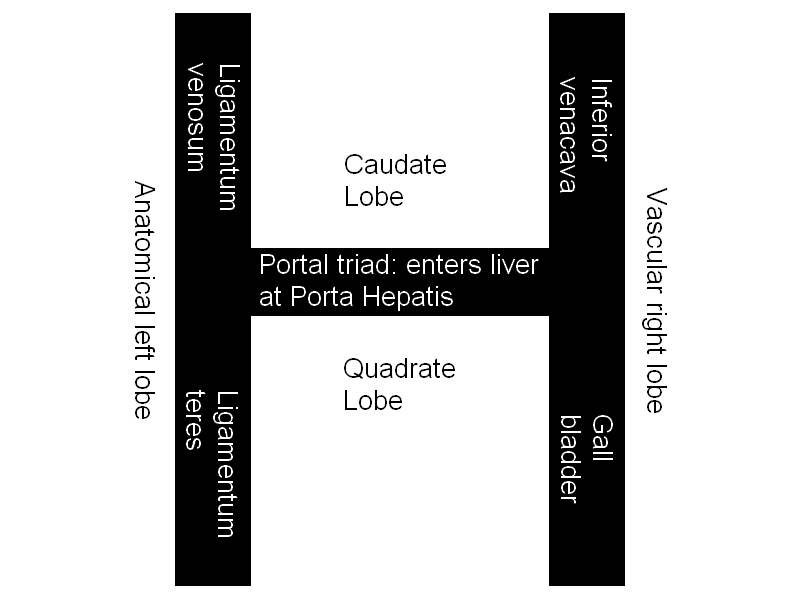
Liver Anatomy : Mnemonics
Ligaments Mnemonic: TV TFCL 1. True ligaments: 2. False ligaments (Peritoneal folds): Posteroinferior (Visceral) Surface of Liver Anatomical halves are separated by Ligamentum venosum and Ligamentum teres. Vascular halves are separated by IVC and Gall bladder. Caudate lobe and Quadrate lobe: Mnemonic: IVC are in one line Mnemonic: LGBTQ are…
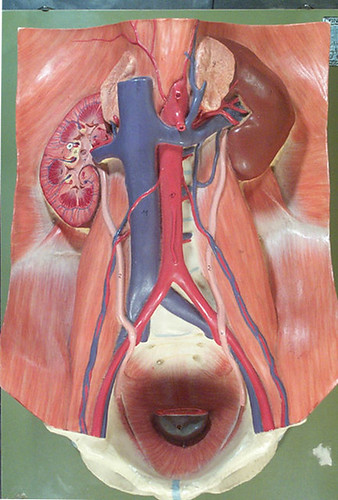
Inferior Venacava (IVC) Tributaries and Abdominal Aorta Branches : Mnemonic
Inferior Venacava (IVC) Tributaries Mnemonic: I Like To Rise So Incredibly High 1. common Iliac veins (L5) – Origin or Formation 2. Lumbar veins (L1-L5) 3. Testicular/gonadal veins – right (L2) 4. Renal veins (L1) 5. Suprarenal veins – right (L1) 6. Inferior phrenic veins (T8) 7. Hepatic veins (T8)…