Chronic paronychia is an inflammatory recalcitrant disorder affecting the nail folds. It can be defined as an inflammation lasting for more than 6 weeks and involving one or more of the three nail folds (one proximal and two lateral).
Surgical management is only indicated in cases of chronic paronychia, which does not respond to medical management and proper use of general measures. Surgical treatment is required in such cases to remove the chronically inflamed tissue, which aids in effective penetration of topical as well as oral medications and regeneration of the cuticle.
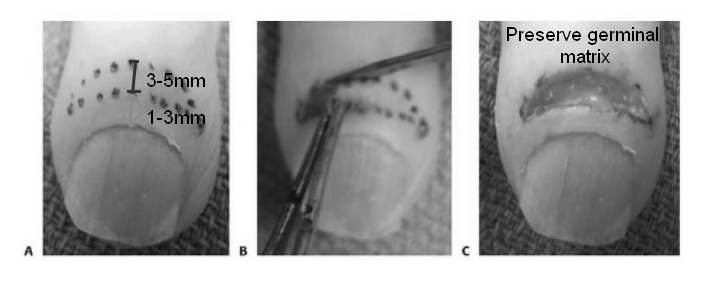
Technique of Eponychial Marsupialization
Anesthesia: Digital nerve block
Incision: Make a crescent shaped incision 1-3mm proximal to the eponychial fold, extending 3-5 mm proximally (at its largest point) and extending to edge of each nail fold
Excision: Excise the tissue, taking care not to damage the underlying germinal matrix
Nail plate removal: Should only be done when there is concurrent nail irregularities.
- Eponychial marsupialization only drains the dorsal surface of the dorsal roof of germinal matrix
- Nail removal more thoroughly debrides the entire nail fold by permitting drainage of the volar portion of the dorsal roof as well as the ventral floor
Dressing: Irrigate and dress the wound appropriately. Allow the wound to heal by secondary intention.
This procedure exteriorizes the infected and obstructed nail matrix and allows its drainage. Epithelialization of the excised defect occurs over the next 2-3 weeks.