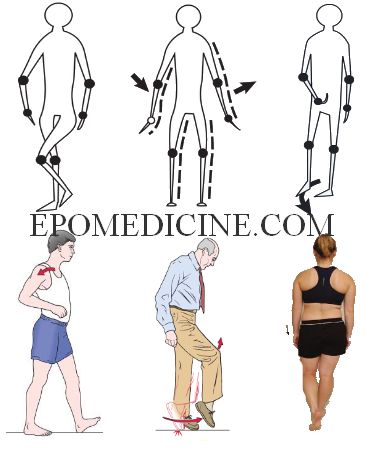
Definitions Gait: Gait is the cyclical pattern of musculoskeletal motion that carries the body forwards. It involves a cyclic loss and regaining of balance by a shift of the line of gravity in relation to the center of gravity. Normal gait is smooth, symmetrical and ergonomically economical. Gait cycle: The…

Examination of Facial Nerve (7th Cranial Nerve)
The anatomy of facial nerve has already been discussed in detail earlier. It is essential to have proper knowledge of anatomy to understand this section of clinical examination of facial nerve. A) Inspection: Observe: Face at rest for any facial asymmetry Any facial tics, symmetry of eye blinking or eye…
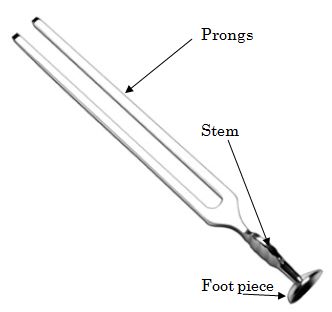
Hearing tests with Tuning fork
Tuning fork Parts of a tuning fork 1. Foot piece 2. Stem 3. Prongs How to use tuning fork? Hold the stem of the tuning fork between the index finger and thumb of your right hand without touching the prongs. Strike the junction of superior 1/3 and inferior 2/3 of the…
Should I study MBBS ?
When little, you would ink pages with your thoughts hovering around your dream of wearing a white coat and hanging up a stethoscope; you wouldn’t wait a second to think before you answer that the ambition of your life is to become a doctor. But no one ever said being…
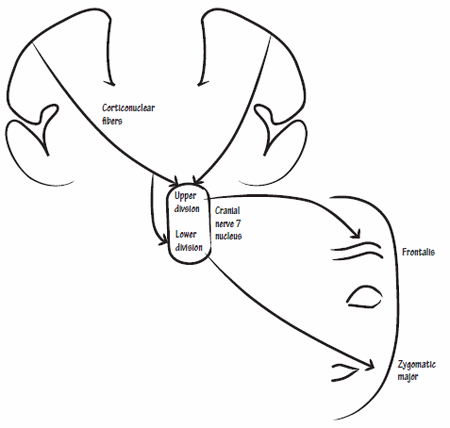
Facial Nerve Anatomy
SYNONYMS: Cranial nerve seven (VII), Nervus facialis Supranuclear pathways 1. Somatomotor cortex: controlling motor component of facial nerve lies in precentral gyrus (Broadmann area 4,6,8) 2. Volitional component: Corticonuclear tracts descend and cross to supply both ipsilateral and contralateral facial (mainly to the contralateral side) nucleus i.e. frontal branch components…
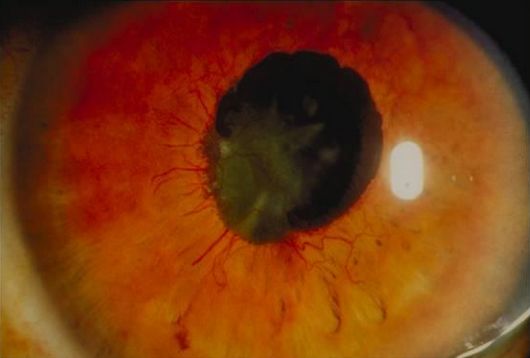
Ophthalmology spot diagnosis : Rubeosis Iridis
Definition: Neovascularization of iris Pathophysiology: Causes that lead to retinal hypoxia triggers release of vasoproliferative factors include vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and others Etiology: 1. Diabetic Retinopathy 2. Retinal Vascular Occlusive Diseases Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) Ischaemic Hemiretinal Vein Occlusion 3. Ocular Ischaemic Syndrome Carotid…
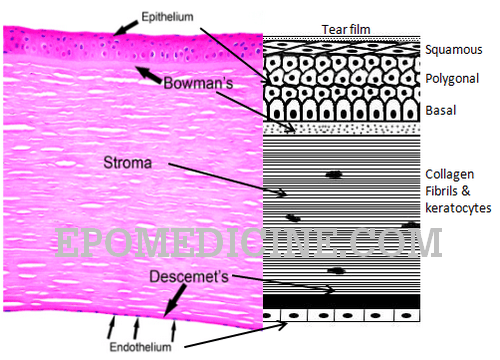
Histology of Cornea and Corneal Dystrophies
Prefix: kerat- Definition: The cornea is a transparent, avascular, watch-glass like structure which forms anterior one-sixth of the outer fibrous coat of the eyeball and covers iris, pupil and anterior chamber. Histology: It consists of 5 distinct layers which can be remembered using the mnemonic “ABCDE“:
Uses of Fluorescein strips
Content: 1-2% fluorescein dye impregnated Method of use: Explain the procedure to the patient Ask the patient to look up Moisten the strip with a small amount of normal saline or anesthetic drops, without touching the dye impregnated end of the strip with dropper Gently touch the inside of the…