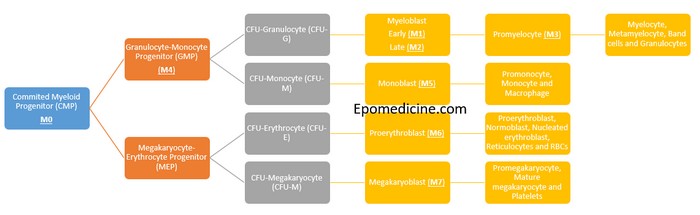
There is no need of mnemonics to remember the FAB classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML); just remember the process myeloid differentiation. A simple schematic diagram with few intermediate processes and stimulating factors eliminated will meet our purpose here. The cells belonging to the myeloid lineage are: Granulocytes: Neutrophils, Eosinophils…
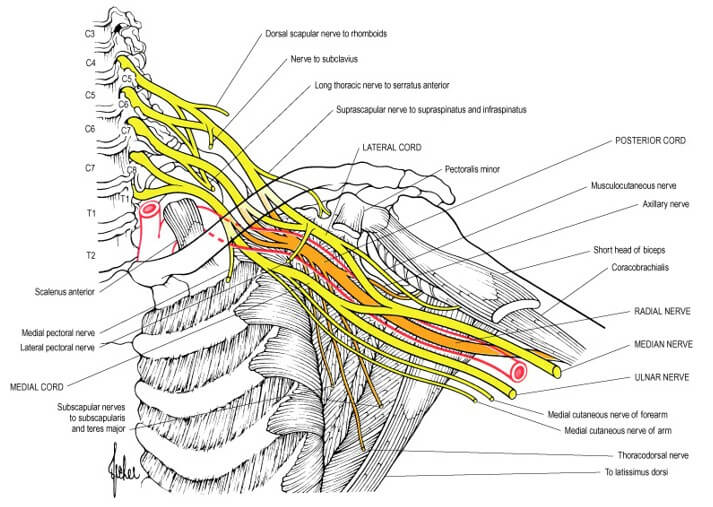
Brachial Plexus Simplified with Mnemonics
Components of Brachial Plexus Mnemonic: Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beer From proximal to distal, brachial plexus consists of: How are the roots formed? From the Ventral Rami of C5 to T1 spinal nerves. Extent and course: Intervertebral foramina to Transverse process to Interscalene triangle (bounded by anterior scalene and middle…
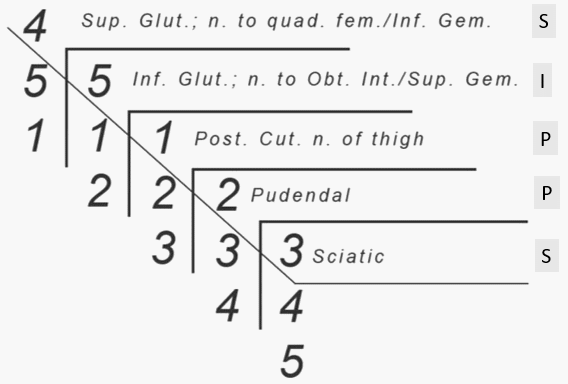
Lumbosacral Plexus Simplified
While everyone is busy talking about the brachial plexus – lumbosacral plexus (the origin of nerves that supplies everything below the umbilicus) seems to be bit under-rated. Formation of Lumbosacral Plexus Ventral rami of L1-S4; has 2 components – Lumbar plexus (L1-L4) – forms within psoas major anterior to lumbar…
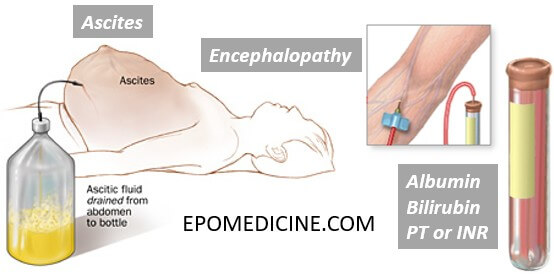
Child Pugh Score: Mnemonic and Explanation
The Child-Pugh-Turcot (CTP) score consists of 5 clinical features and is used to assess the prognosis of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Mnemonic: A BEAP Albumin (gm/dl) Bilirubin (mg/dl) Encephalopathy (Based on West Haven Criteria) Ascites Prothrombin Time (PT) Prolonged or INR Child-Pugh-Turcot Score Factor 1 point 2 points 3…
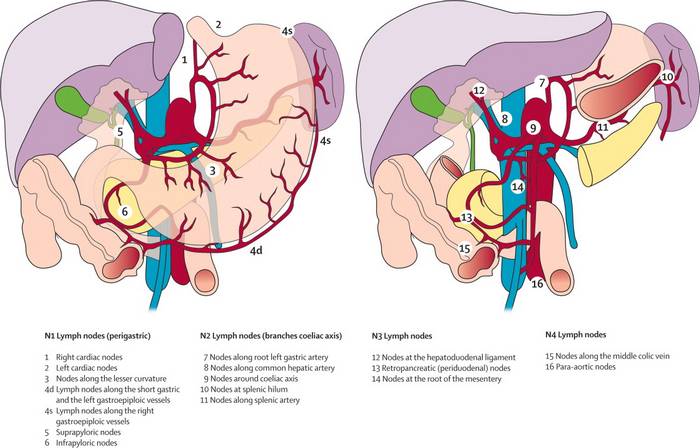
TNM and Staging of Gastric Carcinoma Simplified
Unique features of stomach in relation to TNM cancer classification 1. Cancer penetrates the muscular propria and invades the ligaments (gastrohepatic and gastrocolic, i.e. lesser and greater omentum respectively) subserosally without breeching the serosa. Gastric cancer invasion of the lesser and greater omentum is T3, not T4. Perforation of the…
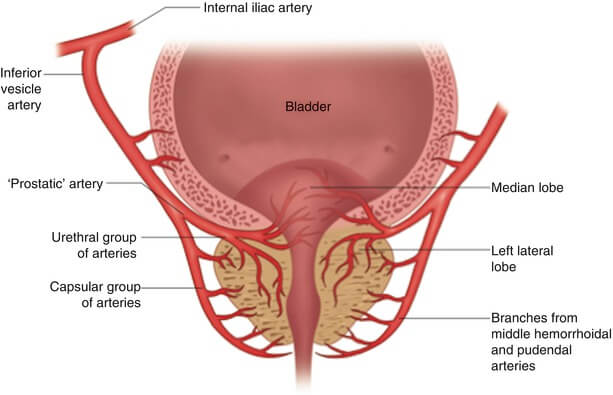
Prostate Anatomy – Clinical correlate
Anatomy of Prostate The embryology and detailed gross and microscopic anatomy of the prostate has already been discussed earlier. Read the anatomy of prostate. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Occurs exclusively in transition zone (progressively enlarges with age). Median lobe of the gland enlarges upward and encroaches sphincter vesicae, located at…
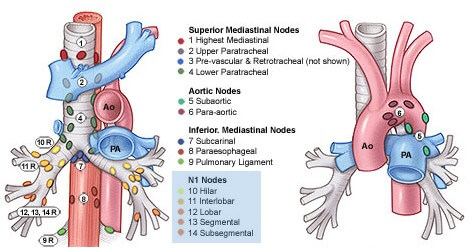
TNM and Staging of Lung Cancer Simplified
The current staging system is recommended for the classification of both non–small cell and small cell lung carcinomas and for carcinoid tumors of the lung . TNM Staging of Lung Cancer Primary Tumor (T) The “T” staging of bronchogenic carcinoma is a bit complex compared to others. Five things must…
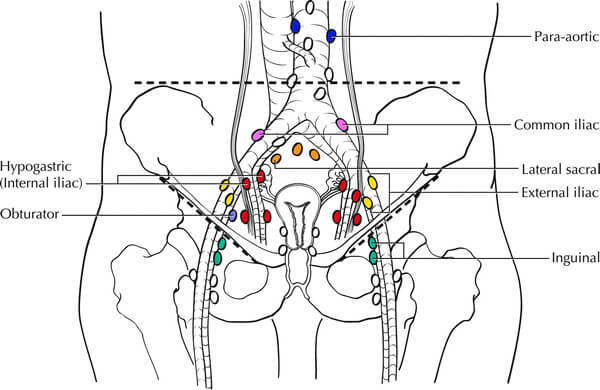
TNM and FIGO Staging of Ovarian Carcinoma Simplified
FIGO has published a new classification for ovarian cancer. These new cancer staging rules will be incorporated into the 8th Edition of the UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, which is thought to be effective from 2017. Cancer of the ovary has 3 major stages (I, II and III) and…