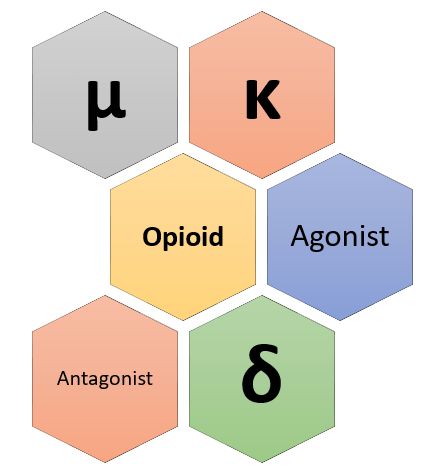
Opioid receptors are a group of inhibitory G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. Mu (µ) Receptor (MOP) Mnemonic: MU CARDS Miosis eUphoria Constipation Analgesia (Supraspinal + Spinal) Respiratory depression Rigidity (truncal) Dependency Sedation µ1 mediates supraspinal analgesia, and most of other effects including spinal analgesia is mediated by µ2. Kappa…
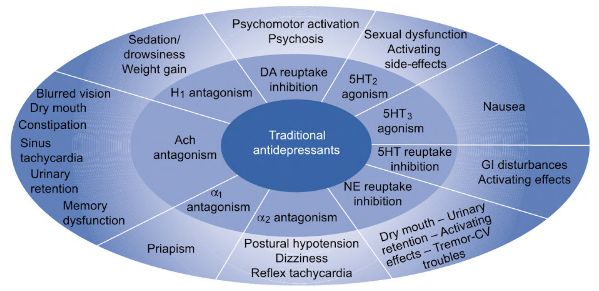
Antidepressants Made Easy
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCA) Mnemonic: -pramine, -triptyline, -pin Secondary amines: predominantly norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors Nor-triptyline Desi-pramine Tertiary amines: Ami-triptyline Imi-pramine Clomi-pramine Doxe-pin Irreversible MAO Inhibitors Mnemonic: TIPS Non-selective MAO inhibitors: Tranylcypromine Isocarboxazid Phenelzine Selective MAO-B inhibitor: Selegiline (transdermal patch) Reversible Inhibitor of MAO-A (RIMA) Moclobemide Tolaxatone Tetracyclic Antidepressants Nonselective inhibitor of…
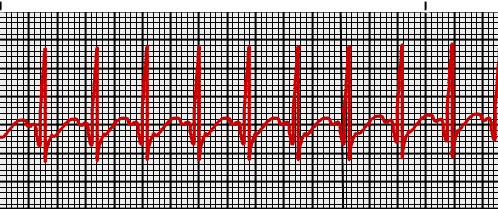
Supraventricular Tachycardia vs Sinus Tachycardia
Yesterday, I had encountered a tachycardic patient with heart rate 160/min. Somewhere in medical school, I was taught that the sinus tachycardia with heart rate >160/min must be considered as a Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). With such misinformation, it was easier for me to overlook the fact that the patient was…
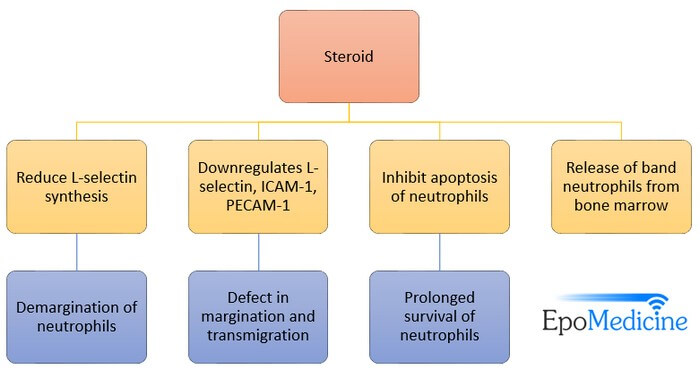
Steroid Induced Leukocytosis
Mechanism of Steroid Induced Leukocytosis There are 3 major mechanisms responsible for corticosteroid induced granulocytosis: 1. Demargination of neutrophils from endothelial cells (60% of the rise): Recall the leukocyte adhesion cascade in the chapter of inflammation. L-selectins are present in leukocytes that mediates their rolling on the endothelial lining of…
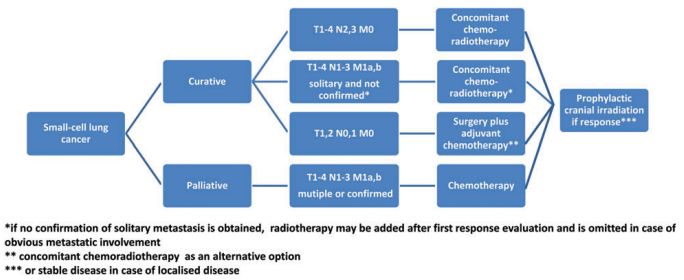
Extensive Small Cell Lung Cancer
Short Case Summary 74 years old smoker, male patient presented with significant weight loss, productive cough and abdominal discomfort of short duration. Patient was icteric with stable vitals. On examination of chest, there was decreased air entry over right lung field. On examination of abdomen, liver was palpable with hard,…
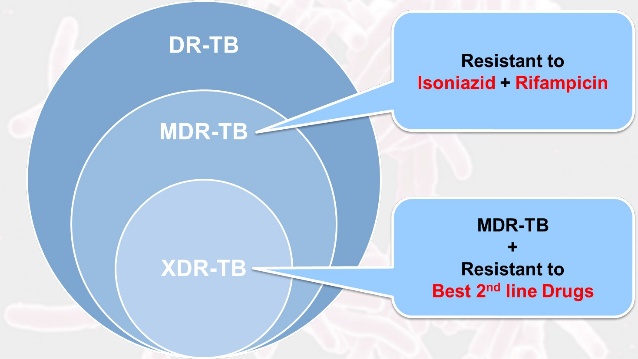
Drug Resistance TB Management Summary
Antitubercular drug symbols H = Isoniazid R = Rifampicin Z = Pyrazinamide E = Ethambutol S = Streptomycin Km = Kanamycin Cm = Capreomycin Lfx = Levofloxacin Ofx = Ofloxacin Mfx = Moxifloxacin Eto = Ethionamide PAS = Para-aminosalicylic acid Cs = Cycloserine Amx/Clv = Amoxicillin-Clavulanate Bdq = Bedaquiline Lzd…
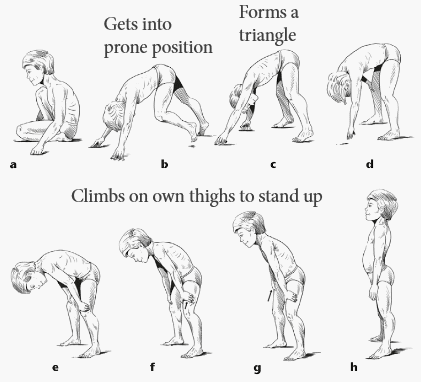
Gower’s sign
Synonyms: Gower’s maneuver, Myopathic walking, Butt-first maneuver Identifying Gower’s sign To check for Gower’s sign, place the patient in the supine position and ask him to rise. A positive Gower’s sign – an inability to lift the trunk without using the hands and arms to brace and push – indicates…

Substance abuse vs Substance dependence
Both of these substance use disorders are maladpative patterns of substance use, leading to clinically significant impairment/distress but defined by separate criteria. Substance abuse ≥1 of the following occurring within a 12 month period: Mnemonic: 4 Rs Role failure: Recurrent use resulting in failure to fulfill role obligation Risky behavior:…