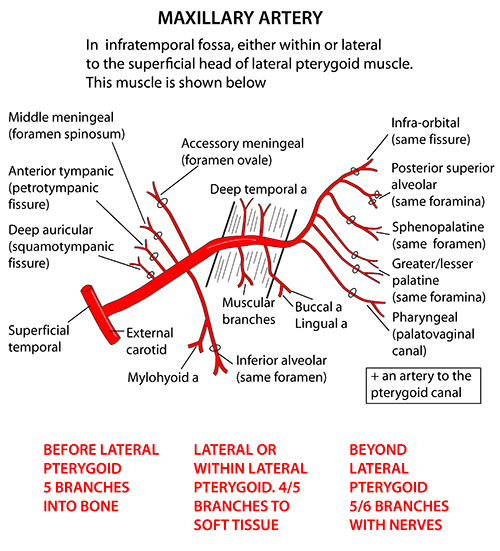
Origin of Maxillary artery: Terminal branch of External Carotid Artery (ECA) Derived from: 1st Arch Divisions of Maxillary artery: 3 parts by lateral pterygoid Branches of Maxillary artery Remember: Branches from 1st part Branches from the 2nd part Mnemonic: They supply muscles of mastication which are also derivatives of the…
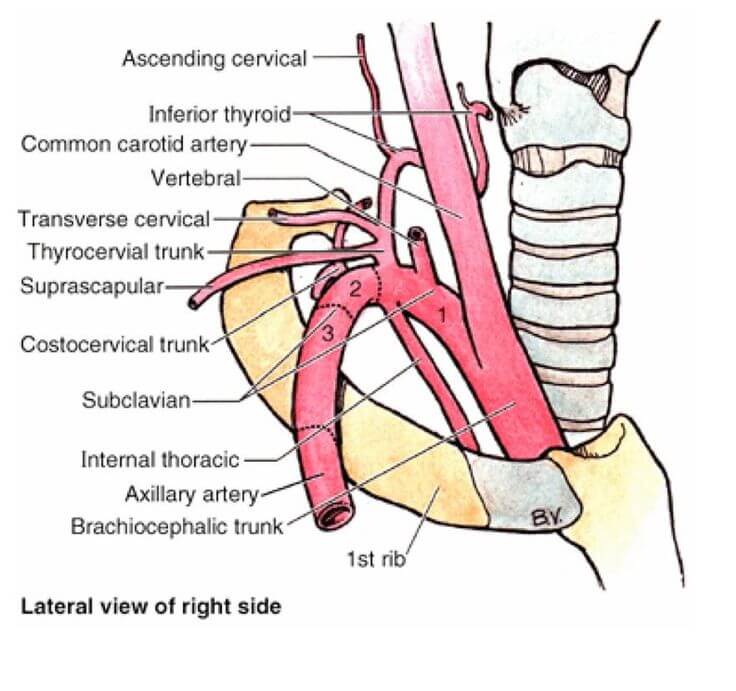
Branches of Subclavian artery : Mnemonic
Origin of Subclavian artery: Left: Arch of aorta Right: Brachiocephalic artery Extent of Subclavian artery: Arises posterior to sternoclavicular joint and ends at outer border of 1st rib by becoming acillary artery. Divisions of Subclavian artery: 3 parts in relation to Scalenus anterior muscle 1st part (medial to muscle) 2nd…

Fever and Rash : Mnemonic Based Approach
Seven Killer Causes of Fever and Rash Mnemonic: SMARTTT Sepsis Meningococcemia Acute endocarditis Rocky mountain spotted fever Toxic erythemas Toxic epidermal necrolysis Travel-related infections Onset of Rash with “X” Days of Fever Mnemonic: Very Sick Person Must Take Double Eggs Varicella (Chicken pox): 1st day (rash is often 1st sign…
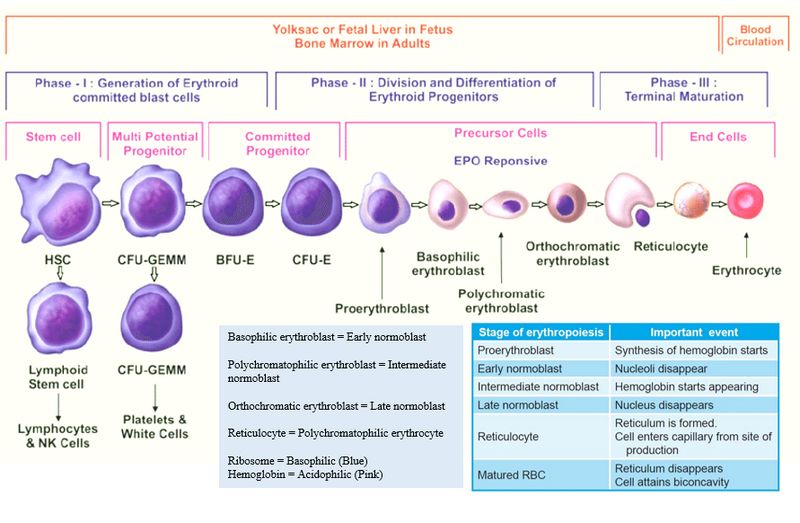
Erythropoiesis Simplified
Hemoglobin Switching mnemonics 1st to appear: Embryonic hemoglobin (Gower and Portland) Switch from fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin: “Gamma goes, Beta becomes, Alpha always” Fetal hemoglobin: α2γ2 Adult hemoglobin: α2β2 ζ chain α chain ε chain HbE Gower 1 HbE Gower 2 γ chain HbE Portland I HbF β chain HbE Portland II…
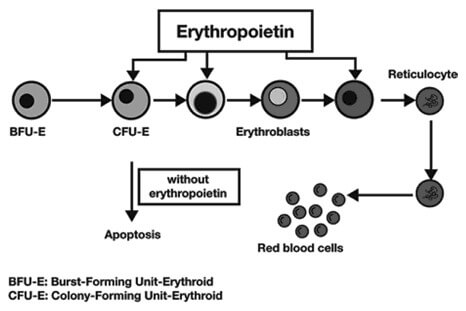
Erythropoietin (EPO) Physiology
Structure of erythropoietin (EPO) Glycoprotein hormone 165 amino acids Molecular mass – 30 kDa Site of production/synthesis of erythropoietin (EPO) Kidneys (75-90%): Peritubular interstitial cells Liver (15%; chief source in fetus and neonates): Centrilobular hepatocytes After birth, erythropoietin is not detectable until 8-12 weeks after birth leading to physiological anaemia…
Medical Significance of Bedbugs
Two species of bedbugs bite people: the common bedbug (Cimex lenticularis) and the tropical bedbug (Cimex hemipterous). These bugs are called udus (उडुस) in Nepali and khatmal (खटमल) in Hindi language. The adult bedbug is the approximate size, shape, and color of an apple seed. They are more commonly associated…

How to talk to your kids about drugs ?
Many communities around the country are faced with the reality that an alarming number of young people are trying tobacco, alcohol and other dangerous drugs. Many others are using them regularly. The numbers can be startling. The National Institute on Drug Abuse reports that by the 8th grade, 30% of…

An Unforgettable Night During Gyne/Obs Rotations
That night, I reported to the L&D floor just like any other night that week. It started off normally with the usual sign out with the residents and then checking the OR board to see if there were any cases to cover. I noticed a D&C up for grabs, so…