Mnemonic: ABCD(CD)E(CDE) – 4P
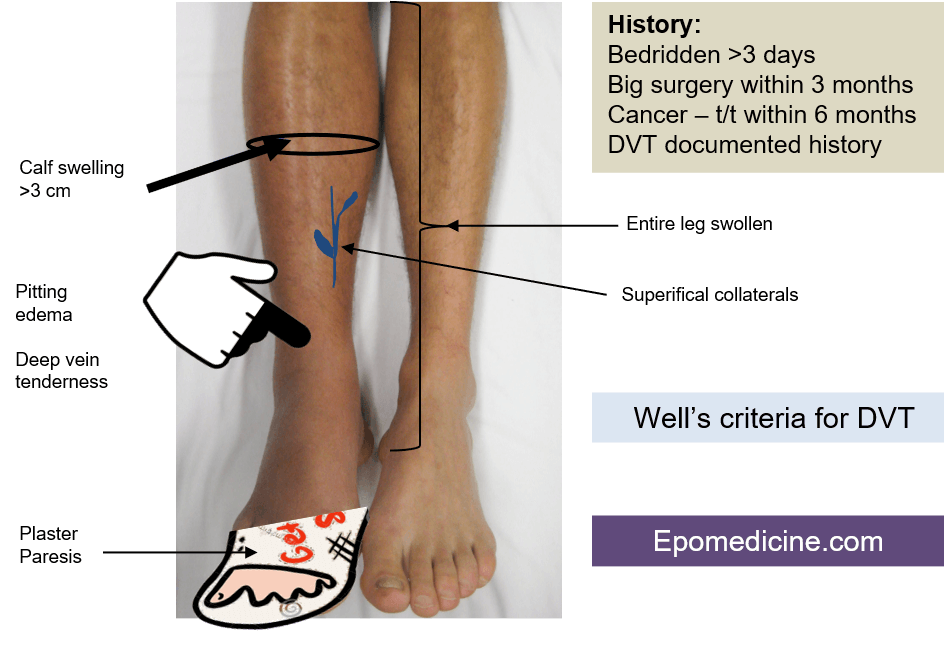
A: Alternate diagnosis of DVT more likely (-2)
B: Bedridden recently >3 days or Big (major) surgery within 3 months (+1)
C: Cancer – treatment or palliation within 6 months (+1)
D: Deep venous involvement:
Mnemonic – CD
- Collateral (non-varicose) superficial veins present (+1)
- Deep venous system tenderness (+1)
E: Edema:
Mnemonic – CDE
- Calf swelling > 3cm compared to other leg – measured 10 cm below tibial tuberosity (+1)
- Denting (pitting) edema of involved leg (+1)
- Entire leg swollen (+1)
4 P:
- Paralysis, Palsy or Plaster immobilization (+1)
- Previous documented DVT (+1)
Rule of 3 – Note the 3 sets of 3:
1. Bedridden for >3 days in 1 month
2. Major surgery in last 3 months
3. More than 3 cm calf enlargement
Pregnant and postpartum women should not be assessed with these criteria and should generally have ultrasonography if DVT suspected.
Interpretation and Applicable algorithm:
1. Score 0 or lower (low risk): 5% risk
2. Score 1-2 (intermediate risk): 17% risk
3. Score 3 or higher (high risk): 17-53% risk
Wells score is low or intermediate – check D-dimer
- D-dimer is normal – send home
- D-dimer is elevated – obtain ultrasound
Wells score is high – obtain ultrasound
- Ultrasound is positive – treat
- Ultrasound is negative – obtain D-dimer
- D-dimer is low – send home
- D-dimer is elevated – repeat ultrasound 1 week
Sensitivity: 77-98%
Specificity: 38-58%
References:
Wells PS, Anderson DR, Bormanis J, et al. Value of assessment of pretrest probability of deep-vein thrombosis in clinical management. Lancet. 1997;350:1795-1798.
Diagnosis of DVT with D-dimer testing and the Wells score (acutecaretesting.org)
Wells’ Criteria for DVT – MDCalc

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.