Course of Trigeminal Nerve and Trigeminothalamic Pathway
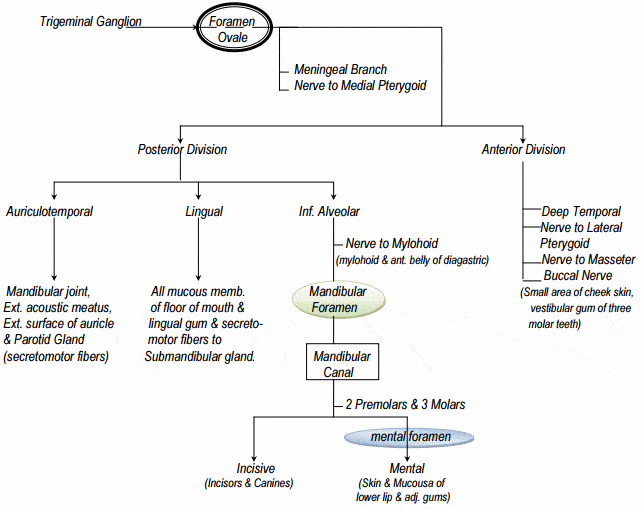
Mandibular (CN V3) Division of Trigeminal Nerve
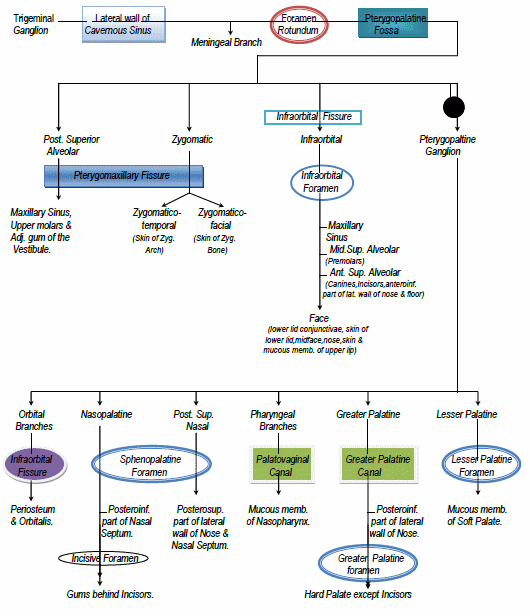
Maxillary (CN V2) Division of Trigeminal Nerve
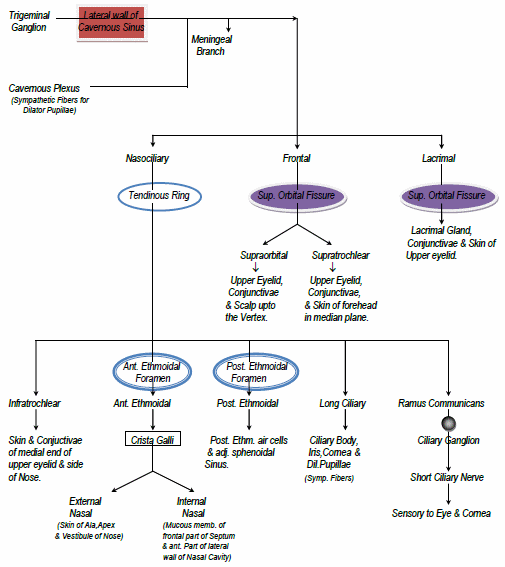
Ophthalmic (CN V1) Division of Trigeminal Nerve
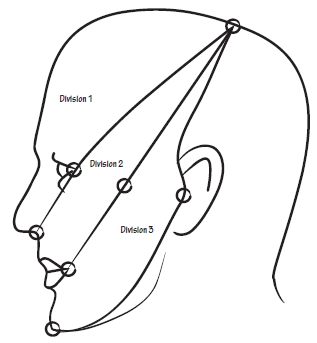
Sensory Map Of Trigeminal Nerve on Face
Area of Ophthalmic division: Line joining –
- Just behind the top of head
- Corner of eyes
- Tip of nose
Area of Maxillary division: Line joining –
- Same point as above in head
- Maxilla
- Angle of mouth
Area of Mandibular division: Line joining –
- Same point as above in head
- Tragus of ear
- Mentum
Important point to note:
Mandibular division neither covers the angle of mandible, nor the outer ear. These areas are often tested to differentiate neurologic and functional (non-neurologic symptoms) as Trigeminal nerve doesn’t have sensory supply to these regions. These regions are supplied by:
- Outer ear: Cranial nerve VII, IX and X
- Angle of Mandible: C2, C3
Lateral Pterygoids
While the other muscles of mastication closes the jaw, the lateral pterygoids open the jaw. Like, genioglossus of tongue, the fibers crosses and inserts to the angle of jaw on the opposite side. Hence, dysfunction of lateral pterygoid at one side leads to deviation of jaw in the same side due to the action of opposite lateral pterygoid.
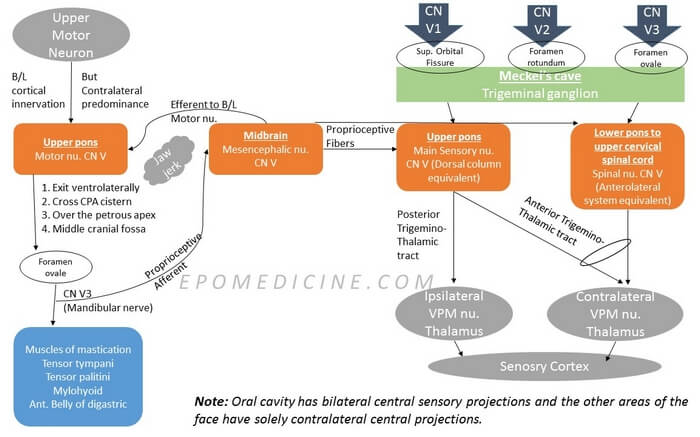
In Upper Motor Neuron lesion:
- They have bilateral cortical innervation with contralateral predominance.
- Hence, there may be no visible deviation of jaw during clinical examination.
- If deviation is seen: Deviation of jaw to the side contralateral to the UMN lesion
- Deviation at one side → Dysfunction of lateral pterygoid in same side → Contralateral UMN lesion
In Lower Motor Neuron lesion:
- Deviation of the jaw to the side ipsilateral to the LMN lesion.
Jaw Jerk
- Stimuli: Stretch applied by reflex hammer on relaxed jaw
- Sensory receptors: Muscle spindles of muscles of mastications
- Afferent: Proprioceptive fibers from CN V3
- Center: Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve (Not the trigeminal ganglion)
- Efferent: Bilateral innervation to the motor nucleus of facial nerve
- Response: Closure of jaw