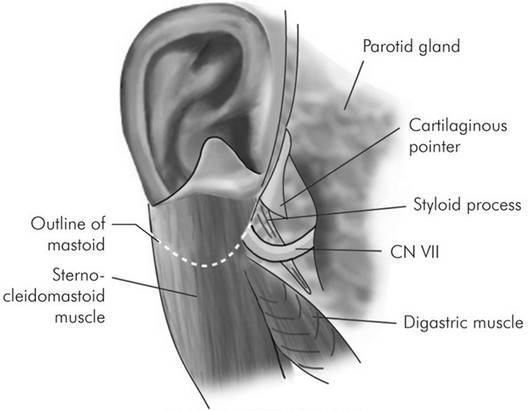
The facial nerve (CN VII) exits the skull base through the stylomastoid foramen situated posterolaterally to the styloid process and anteromedially to the mastoid process and enters the parotid gland to divide it into a large superficial lobe and a small deep lobe. The main trunk of facial nerve enters the parotid gland and divides into zygomaticotemporal and cervicofacial divisions at pes anserinus situated approximately 1.3 cm from stylomastoid foramen. Facial nerve paralysis is a daunting potential complication of parotid surgery and is widely reported. Knowledge of the key landmarks of the facial nerve trunk is essential for safe and effective surgical intervention in the region of the parotid gland.
Surgical landmarks to identify main trunk of facial nerve:
1. Tragal “pointer” (of Conley): facial nerve lies approximately 1 cm deep and slightly anterior and inferior to this “pointer”.
- As the tragal cartilage is dissected free from the parotid fascia, it takses bluntlu pointed shape in its medial aspect, which is called the “pointer”.
- It is regarded as the most important landmark.
2. Tendon of posterior belly of digastric muscle: facial nerve lies approximately 1 cm deep to the media attachment of the posterior belly of digastric muscle to the digastric groove of mastoid bone.
- During surgery, the tail of parotid gland is separated from the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the deep underlying posterior belly of digastric muscle, and then the gland is elevated and rotated off of the muscle.
3. Tympanomastoid suture/fissure: facial nerve lies 6-8 mm deep to this suture
- The tympanomastoid suture is situated at the apex of vagino-mastoid angle or valley of nerve where the mastoid and the vaginal portion of tympanic ring of external ear canal (temporal bone) meets.
4. Styloid process: lateral to styloid process
Note:
a. If the proximal segment of facial nerve is obscured, retrograde dissection of 1 or more of the peripheral branches may be necessary to identify the main trunk.
- Ramus frontalis is located by a line from tragus to lateral canthus.
- Ramus buccalis is located by a line from the tragus towards alae of the nose parallel to the zygoma but 1 cm below.
- Ramus mandibularis is near the angle of mandible at a point 4-4.5 cm from the attachment of the lobule of pinna.
b. When necessary, the facial nerve can be identified in the mastoid bone by mastoidectomy and followed peripherally.