The 2 commonly used criteria for diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis will be discussed here.
1987 ACR Criteria
Mnemonic: DMARDs if MADRAS
- Morning stiffness (>1 hour)
- Arthritis in >/= 3 joint areas
- Duration >6 weeks (of morning stiffness and other 3 features involving arthritis)
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Rheumatoid factor
- Radiographic changes (erosions)
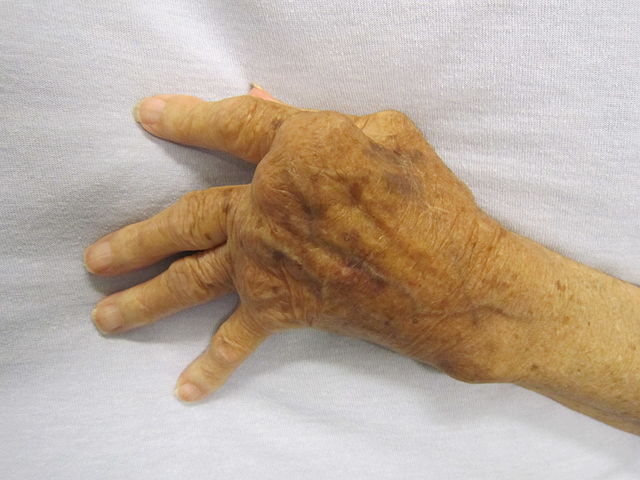
- Arthritis of hand joints (>/= 1 swollen joint)
- Symmetrical arthritis
Mnemonic: EARS
- Early morning stiffness
- Arthritis >/= 3 joints, hands involved
- Rheumatoid factor, Rheumatoid nodules, Radiographic changes
- Symmetrical arthritis, Six weeks
For diagnosis of RA: 4 out of 7 criteria must be present (except duration) and criteria listed above in number 1, 2, 7 and 8 must be present for >6 weeks to be established as criteria for RA.
Established RA: Sensitivity 79-80% and Specificity 90-93%
Early RA: Sensitivity 77-80% and Specificity 33-77%
2010 ACR/EULAR Criteria
Mnemonic: Three “A” and Two “6”
a. Arthritis (Joint involvement)
Large joints have smaller points and odd numbers of joint involvement get even numbered points.
- 1 Large joint: 0
- 2-10 Large joints: 1
- 1-3 Small joints: 2
- 4-10 Small joints: 3
- >10 Joints (atleast 1 small joint): 5
b. Autoantibodies (RF and ACPA)
- Both negative: 0
- Any one is low positive: 2
- Any one is high positive: 3
A weakly positive RF is defined as up to 3-fold higher and a strongly positive RF 3-fold higher than the upper normal range.
c. Acute phase reactants (CRP and ESR)
- Both normal: 0
- Any one is abnormal: 1
d. 6 weeks duation
- <6 weeks duration: 0
- >6 weeks duration: 1
e. >6/10 points = Definite RA
2010 Criteria increased the sensitivity for finding patients with early-stage disease who were destined eventually to develop full-blown RA over the next 6 years to 86% sensitivity, compared with 78% sensitivity for the 1987 criteria.