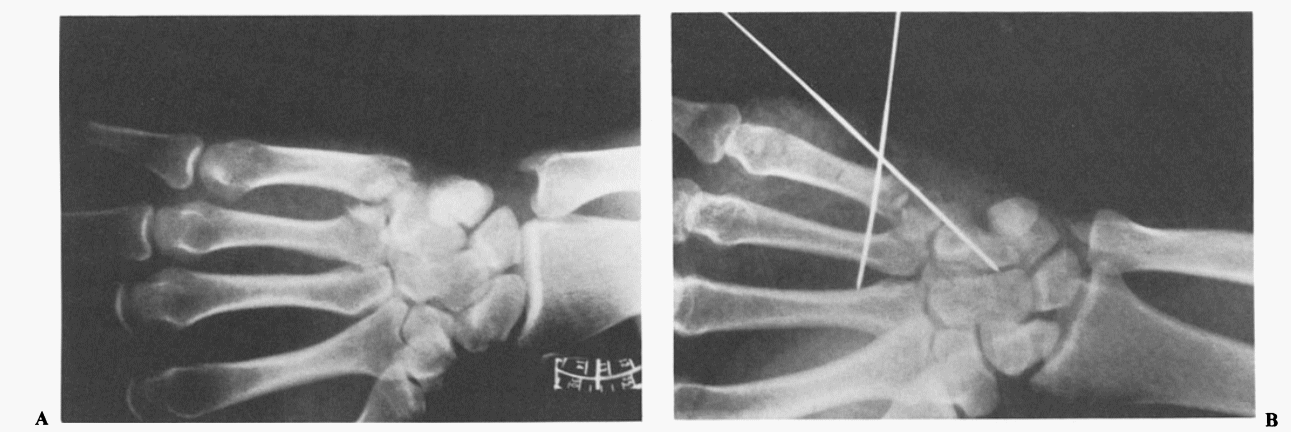
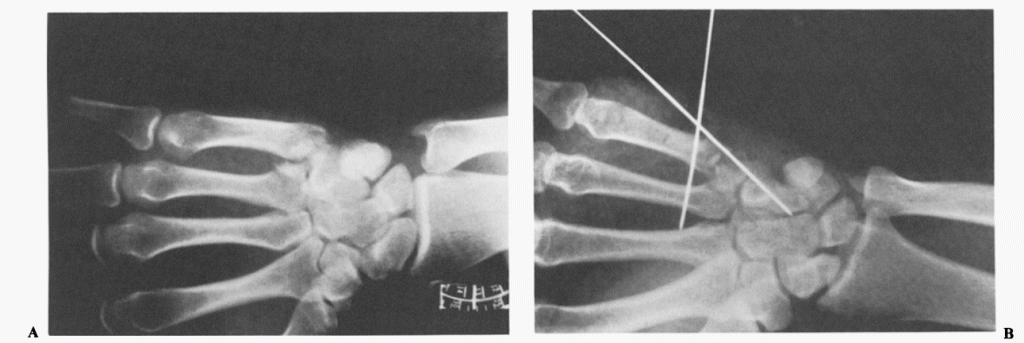
Definition: The fracture-dislocation at the base of the fifth metacarpal analogous to Bennett’s fracture of the thumb
Mechanism of injury:
- Axial loading of 5th metacarpal with ulnar directed vector causing a shear fracture
- Direct trauma
Muscle pull and displacement:
- Large ulnar fragment: Displaced ulnarly & proximally because of traction exerted by Extensor Carpi Ulnaris (ECU) tendon and thenar muscles
- Renders the fracture unstable
- Smaller radial fragment: Kept in place by intermetacarpal ligament between 4th & 5th metacarpal
Consequences of unreduced fracture-dislocation:
- Loss of grip strength
- Painful arthritis
Possible associations:
- Subluxation of 4th metacarpal base
- Hamate fracture
X-ray views:
- 30 degree pronated lateral view (key diagnostic view): clearly profiles metacarpal hamate joint
- Lateral view: fracture-dislocation may be seen
- Anteroposterior full supination view: more likely to expose fragment than in posteroanterior full pronation view
Treatment:
1. Closed reduction and internal fixation with K-wires
2. Open reduction and internal fixation with K-wires or lag screw (for large fragments)
- Dorsal or dorsal ulnar incision is used to approach the fracture
- Care must be taken to avoid the ulnar sensory nerve and its branches
References:
- Freeland, A. E., Jabaley, M. E., & Hughes, J. L. (1986). Reverse Bennett’s Fracture. Stable Fixation of the Hand and Wrist, 45–46. doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-8640-7_13
- Goedkoop, A. Y., van Onselen, E. B. H., Karim, R. B., & Hage, J. J. (2000). The “mirrored” Bennett fracture of the base of the fifth metacarpal. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, 120(10), 592–593. doi:10.1007/s004020000140

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.