Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA) cause non-anion gap metabolic acidosis.
Type 1: H+ excretion defect (A proton or 1st element of periodic table)
- This occurs in distal tubule (hence, distal defect)
- K+ is excreted instead of H+ causing Hypokalemia.
- Distal tubule H+ is non-functioning – urine pH >5.5.
- Chronic acidosis leads to decreased tubular calcium reabsorption leading to renal hypercalciuria.
- Acidosis and hypokalemia stimulate citrate reabsorption in proximal tubule and decrease urine excretion.
- Alkaline urine + Hypercalciuria + Hypocitraturia = Calcium phosphate stones and Nephrocalcinosis
Type 2: Bicarbonate reabsorption defect (Bi-carbonate or Two carbonates)
- Majority of bicarbonate reabsorption occurs in proximal tubule (hence, proximal defect)
- Since, it is a proximal defect – it has association with Fanconi’s syndrome
- H+ secreting mechanism in distal tubule is intact – hence, urine pH is <5.5 even though HCO3- is lost in urine (compensatory mechanism).
Type 3: Mixed (1 + 2) [Forget type 3 for now as it is not even mentioned in several textbooks]
Type 4: Aldosterone deficiency or resistance (A looks like 4 – 4ldosterone) leading to decreased Ammonia/NH4+ production (A looks like 4 – 4mmonia or NH4+ has a 4 in it)
- Aldosterone acts on distal tubule (hence, distal defect)
- Since, distal tubule H+ pump functions normally – urine pH <5.5.
- Due to impaired aldosterone action: Na+/K+-H+ exchange mechanism is impaired leading to defective excretion of K+ and H+ and defective reabsorption of Na+, i.e. hyperkalemia, acidosis and hyponatremia.
- Hyperkalemia inhibits ammoniagenesis.
Another rhyme mnemonic
Stone/Immune, Bone and Aldosterone.
RTA type 1: associated with Calcium Phosphate Stone, Autoimmune disorders like Sjogren’s syndrome and Lupus
RTA type 2: associated with Osteomalacia and Multiple myeloma
RTA type 4: associated with Aldosterone defect
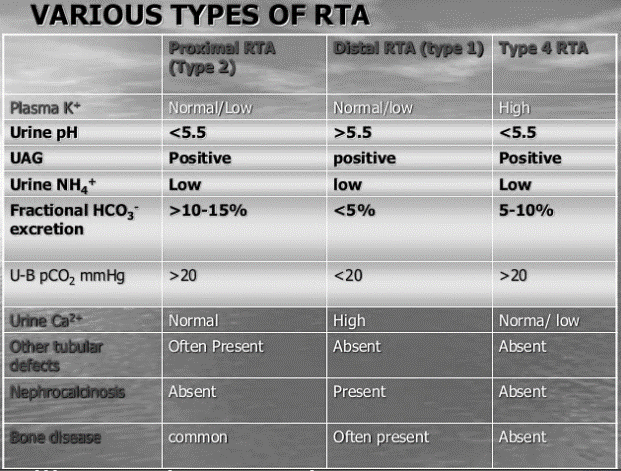
in Type 2, what happens to potassium not mentioned. Acidosis is always associated with hyperkalemia, except in RTA types 1 and 2