Postoperative fever is defined as a temperature >100°F (38°C) on 2 consecutive postoperative days, or >102.2°F (39°C) on any 1 postoperative day. The most common cause of fever within the first 48 hours is a pyretic response to surgery, which is self-limiting.
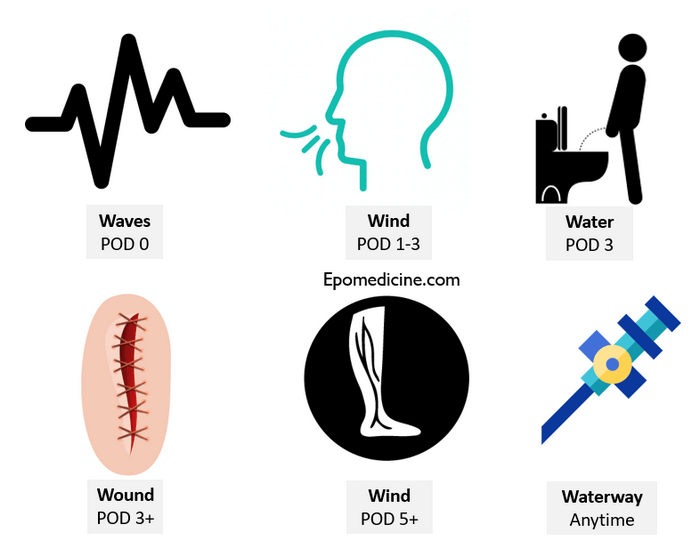
Textbooks have long listed the common causes of postoperative fever using the mnemonic of “W”s in the order of:
- Wind (atelectasis)
- Water (urinary tract infection)
- Wound (wound infection)
- Walking (venous thromboembolism)
- Wonder drug (drug fever)
We will add some more information and create a revised rule mnemonic of W’s with the evidence base for better clinical applicability. The study suggested to replace atelectasis with pneumonia for “Wind” as they found no clear association between fever and atelectasis.
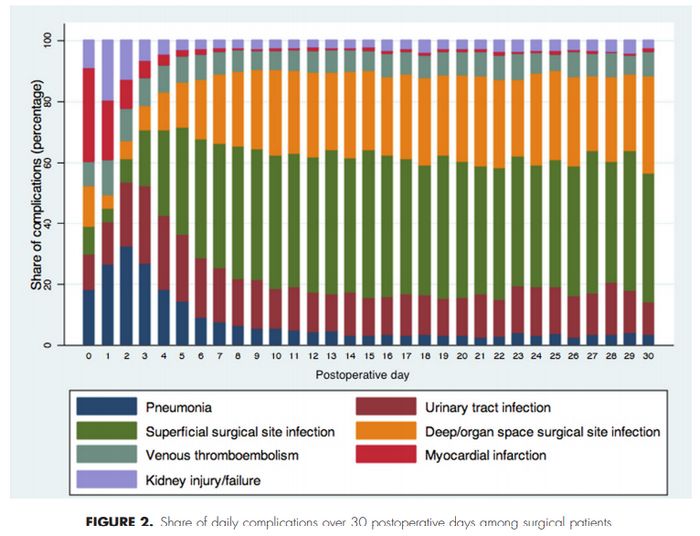
- Waves (ECG waves – Myocardial infarction)
- Most common cause in POD 0
- Wind (pneumonia)
- Most common cause in POD 1-3
- Water (UTI)
- Most common cause in POD 3 along with wind (pneumonia)
- Wound (superficial and deep SSI)
- Superifical SSI is the most common cause in POD 3+ upto a month
- Deep SSI or organ space infection is the second most common cause in POD 4+
- Walking (venous thromboembolism)
- Though not most common cause, it is common in POD 5+ and the risk continues even upto 3-4 weeks postoperatively
- The risk is 2 fold in homebound patients and patients with cancer
Malignant hyperthermia, Gas gangrene of wound, Bacteremia and Febrile non-hemolytic transfusion reactions are other immediate causes of fever in POD 0.
Some other additions to the revised mnemonic:
- Wonder drug (Drug fever): Though it was not evaluated in the study referenced, it is common cause of fever in POD 7+
- Wing/Waterway (Bloodstream infections or IV line related phlebitis/infections): These can cause fever anytime
- For postpartum fever: or puerperal pyrexia
- Womb (Endometritis): POD 2-3
- Walk (Septic pelvic thrombophlebitis): Day 5-6
- Weaning (Mastitis): Day 7-21
*POD: Postoperative Day or Postpartum day (where applicable)
Referene and Further reading: Hyder, J. A., Wakeam, E., Arora, V., Hevelone, N. D., Lipsitz, S. R., & Nguyen, L. L. (2015). Investigating the “Rule of W,” a Mnemonic for Teaching on Postoperative Complications. Journal of Surgical Education, 72(3), 430–437. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2014.11.004

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.