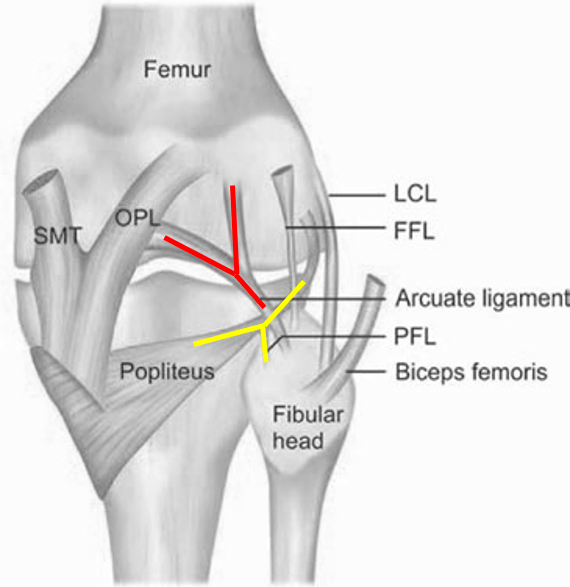
Anatomy of PLC
3 major static stabilizers of PLC
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Popliteus tendon
- Popliteofibular ligament
Other static stabilizers of PLC
- Lateral capsule thickening
- Arcuate ligament
- Fabellofibular ligament
Dynamic stabilizers of PLC
- Biceps femoris
- Popliteus muscle
- Iliotibial band (ITB)
- Lateral head of gastrocnemius
There are 2 “Y” shaped structures in the posterolateral corner of the knee.
1. Popliteus tendon, Popliteofibular ligament and Popliteus forms a “Y” shaped structure.
2. Arcuate ligament forms another “Y” shaped structure. Its medial limb attaches to oblique popliteal ligament and lateral limb is invariable and less distinct.
Biomechanics of PLC
1. Varus restraint: Primary (LCL) and Secondary (Other structures of PLC)
2. Tibial external rotation restraint (esp. at 30-40° flexion): Primary (LCL and popliteus complex) and Secondary (PCL)
Signs and Tests for PLC injury
1. Gait: Varus thrust or Hyperextension varus thrust (apparent tibia vara due to external rotation of tibia on full extension) or walking with slight knee flexion (to avoid instability and stresses on joint and capsule that occurs in hyperextension)
2. Increased external rotation: Dial test
3. External rotation recurvatum test
4. Posterolateral drawer test
5. Reverse pivot shift test
Modified Hughston Classification
| Grade | I (Mild) | II (Moderate) | III (Severe) |
| Varus stress – lateral opening at 30 degrees knee flexion | 0-5 mm | 6-10 mm | >10 mm |
| Dial test – rotational instability | 0-5 degrees | 6-10 degrees | >10 degrees |