What is Polymerase Chain Reaction ?
It is a process of artificial DNA replication (amplification of a selected part of DNA). As the name suggests:
- Polymerase: It requires DNA polymerase for extending the added primers to complete DNA replication.
- Chain Reaction: PCR is run in cycles. The number of molecules increase exponentially as the cycle is repeated. Example:
- We have 1 original molecule of DNA at the beginning
- After 1st cycle: We have 2 copies of the molecule
- After 2nd cycle: We have 4 copies of the molecule
- After 3rd cycle: We have 8 copies of the molecule and so on….
Components Needed for PCR
As PCR is also called as “molecular photocopying”, we use the analogy of a Photocopy to learn the role of components of PCR.
| Photocopier items | PCR components |
| The book | DNA template |
| The page | A portion of the genome (fragment) of interest |
| A bookmark | Primers that “mark” the specific fragment. It is not necessary to know the exact segment. Knowing flanking segments is enough. |
| Photocopier | DNA polymerase |
| Paper and toner | The 4 nucleotides |
A page to be photocopied is the Target Sequence – It contains important information of our interest among the whole book (DNA template). It may be containing a suspected mutation, short tandem repeat (STR), etc.
A bookmark identifies the specific page to photocopy out of a book – PCR primers identify the specific fragment to be copied from the entire genome.
To copy a page, the photocopier uses the paper and toner to make the copy – the DNA polymerase requires nucleotides to produce a replicate of the original DNA fragment.
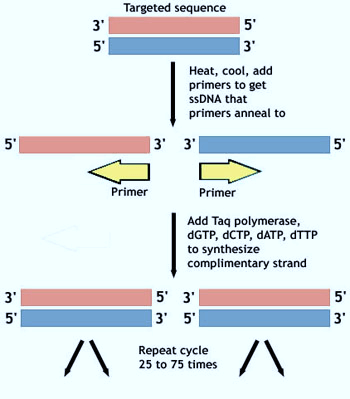
Steps of PCR
1. Solution containing components of PCR (explianed above) prepared.
2. Denaturation of dsDNA by heating to 95°c for few minutes (in vivo, this would be mediated by helicase).
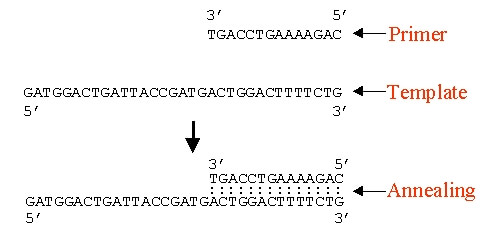
3. Annealing of DNA primer specific for region of interest and slowly cooling down the solution to 40°c (in vivo, primer would be synthesize by the enzyme primase – but in vitro as in PCR, we need to add them externally).
- The primers are 2 synthetic oligonucleiotides: one is complementary to a short sequence in one strand of the DNA to be amplified, and the other is complementary to a sequence in the other DNA strand.
- Primers provide 3′-OH end for extending the newly synthesized DNA strand.
- Example: To amplify the CAG repeat in …CTC AAG TCC TTC [CAG]n CAA CAG CCG CCA…
- This represents 5′ → 3′. Remember that it also has complementary bases running from 3′ → 5′.
- So the 2 sets of RNA primers required containes complementary bases to separated DNA template but runs in 5′ → 3′ direction starting from 3′ end of the template.
- So, the 2 sets of primers required in this case are:
- For DNA template running 5′ → 3′: TGGCGGTGTTG
- For complementary DNA template running 3′ → 5′: CTCAAGTCCTTC
4. Replication of DNA at primer by heat stable DNA polymerase (optimum temperature 72°c i.e. reheating to increase the activity of Taq DNA polymerase).
5. Repetition of process (chain reaction): Generally PCR is run for 20-30 cycles.
Clinical Uses of PCR
1. Diagnosis of viral infection and monitoring of antiviral therapy – HIV, Hepatitis B Virus, Human Cytomegalovirus, etc.
- PCR gives information on viral load.
- In HIV, PCR can be used when measurement of antibody is not reliable:
- Earlier diagnosis of disease
- Immune system not competent enough to make antibodies
- Neonate born to HIV positive mother – even non-infected newborns would have antibodies (transplacental)
2. Diagnosis of bacterial infection:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Chlamydia Trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrheae and Bordetella pertussis.
- Tests based on molecular methods have the advantage of avoiding days or weeks of delay and allow early recognition and treatment.
3. Forensic/Paternity testing:
- use of Variable Number (VNTR) or Short Tandem Repeats (STR) – these are unique copies of non-coding region of DNA between individuals.
- since they exist on both chromosomes, individuals have two copies at each locus – 1 paternal and 1 maternal.
- can only prove with certainty that the sample DOES NOT belong to the test subject – cannot prove with 100% certainty that DNA belongs to individual of interest because there is a small chance that someone shares the same VNTR or STR
4. Direct mutation testing:
- PCR can amplify the region for sequencing
Disadvantage of PCR
A potential problem for PCR is obtaining a pure sample of DNA to start with; any contaminant DNA will also be amplified.
RT-PCR
PCR can also be used to study pattern of gene expression by a process called reverse PCR.
- mRNA is converted into cDNA (copy DNA) by using reverse transcriptase (RNA dependent DNA polymerase)
- CDNA serves as a template for usual PCR procedure
- Clinical use: HIV viral load