- t(8;14): Burkitt’s lymphoma
- t(14;18): Follicular lymphoma
- t(11;14): Mantle cell lymphoma
- t(11,18): Marginal zone lymphoma (MALT lymphoma)
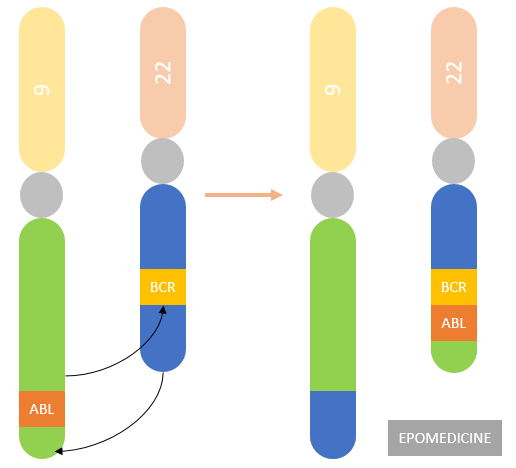
- t(9;22): CML (Philadelphia chromosome), Bad prognosis ALL
- t(8;21): AML M2
- t(15;17): AML M3 (Promyelocytic AML)
- t(X;18): Synovial cell sarcoma
- t(11;22): Ewing’s sarcoma
- t(12;21): Pre-B ALL (good prognosis ALL)
- t(4;11) and t(1;19): Bad prognosis ALL
Is it necessary to remember these? Are they high yield for exam? If yes, is there any way to remember these?
Here’s a mnemonic for the B cell non-hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL).
c-myc (8); cyclin-D (11); heavy-chain Ig (14); BCL-2 (18)
1. 14 is common in many transolactions
2. write small chromosomes 1st then larger
a. Burkitt’s lymphoma (B looks like 8): t(8;14)
b. Follicular lymphoma (F for fourteen and follicular): t(14;18)
c. Mantle cell lymphoma (M looks like 11): t(11;14)
d. Marginal zone lymphoma (outer margins of mantle cell and follicular lymphoma): t(11;18)
Superb
-It’s actually 18 letters in word for follicular lymphoma😅
F for follicur f for fourteen written first
-Burkitts lymphoma B for 8 (that is 8 in any translocation is for Burkitts) except t(8,21) for AML M2 that is one associated with chloroma. 🤢
– ewings e for eleven, e with wings for into 2 (X 2) t (11,22)
-Synovial sarcoma s for sex (X) SY FOR SHY AT 18 t (x,18)☺️
Thank you for the correction Akarsh. It is actually 18 letters in follicular lymphoma 😅
U r most welcome😊