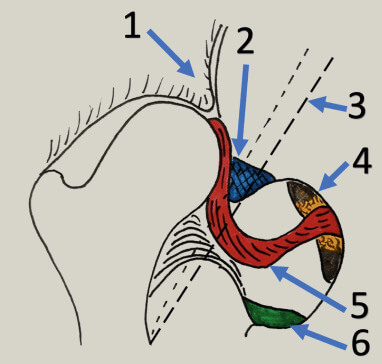
Extra-articular obstacles: Secondary muscle shortening due to hip in subluxed/dislocated position
- Contracted adductor longus
- Contracted iliopsoas
- Curves in front of the joint capsule
10.1016/j.mporth.2020.09.001
1. Anteromedial capsule; 2. Inverted limbus; 3. Iliopsoas tendon; 4. Pulvinar; 5. Ligamentum teres; 6. TAL
Intra-articular obstacles: Results in decreased volume of the acetabulum
- Thickened/elongated ligamentum teres
- Hypertrophied transverse acetabular ligament (TAL)
- In crawling or walking child, caused by constant pull of ligamentum teres on its attachment at the base of the acetabulum
- Constricted anteromedial joint capsule
- Most common and significant intra-articular obstacle
- Caused by overlying contracted iliopsoas tendon
- Inverted and hypertrophied labrum (limbus)
- Rare finding (seen only in teratologic dislocations and previously failed closed reductions)
- Pulvinar hypertrophy
Neo-limbus (acetabular roof hyaline cartilage): Neolimbus is a hypertrophied ridge of fibrocartilage in the superolateral region of the acetabulum caused by pressure from the dislocated hip on this region. While some authors consider it can be an obstacle to reduction of hip, others have made following considerations:
a. Unlike limbus, it can invert or evert and is not an obstacle to reduction.
b. Neolimbus is not a fixed deformity and will spontaneously resolve once the femoral head has been reduced.
c. Neolimbus contains acetabular cartilage, and therefore epiphyseal cartilage, which is involved in the growth and development of the older child’s acetabulum and hence, should never be removed.Further reading and references:
- Lovell and Winter’s Pediatric Orthopedics
- Landa J, Benke M, Feldman DS. The limbus and the neolimbus in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008 Apr;466(4):776-81. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0158-y. Epub 2008 Mar 12. PMID: 18335297; PMCID: PMC2504652.
- Studer K, Williams N, Studer P, et al. Obstacles to reduction in infantile developmental dysplasia of the hip. Journal of Children’s Orthopaedics. 2017;11(5):358-366. doi:10.1302/1863-2548.11.170031
Mnemonic: PLACE
- Pulvinar
- Labrum (limbus), Ligaments (TAL, Ligamentum teres)
- Acetabular roof cartilage hypertrophy (Neolimbus) – controversial
- Capsule (anteromedial)
- Extra-articular (iliopsoas and adductor longus tendon)

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.