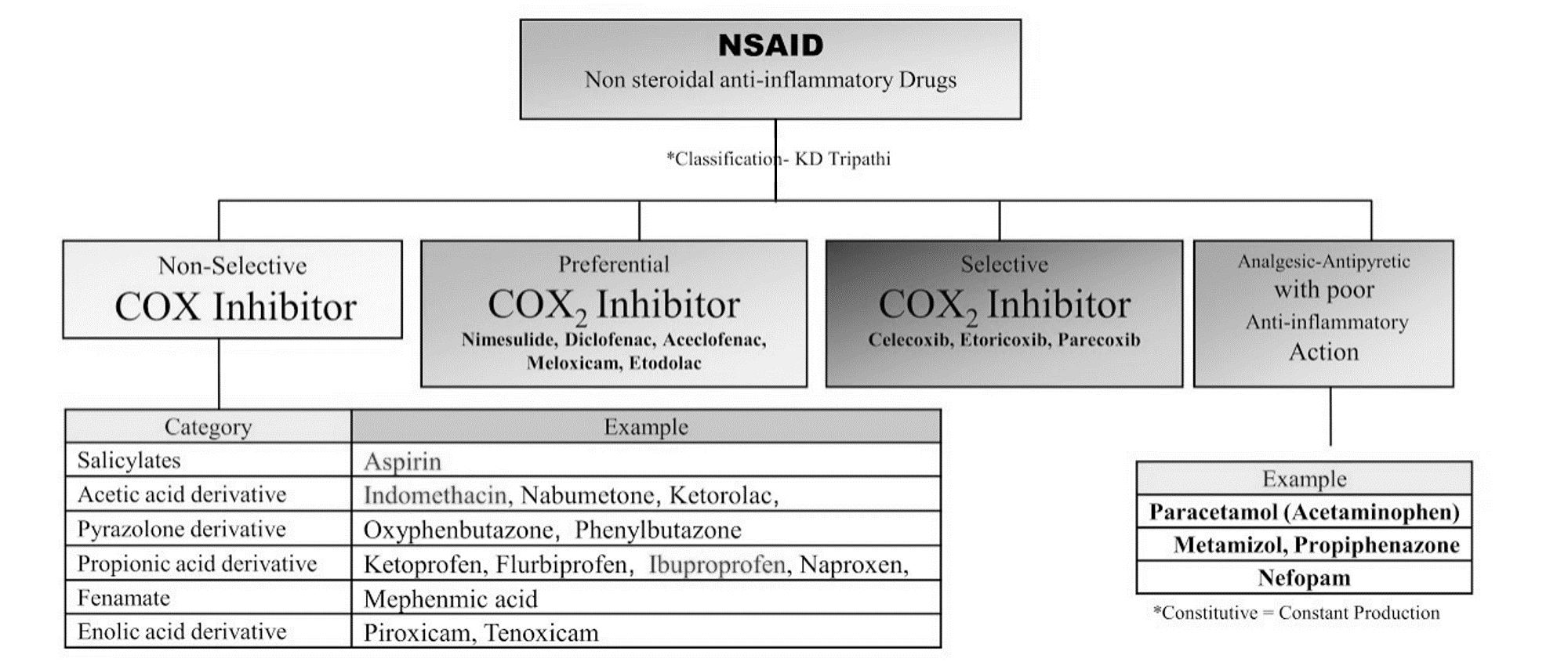
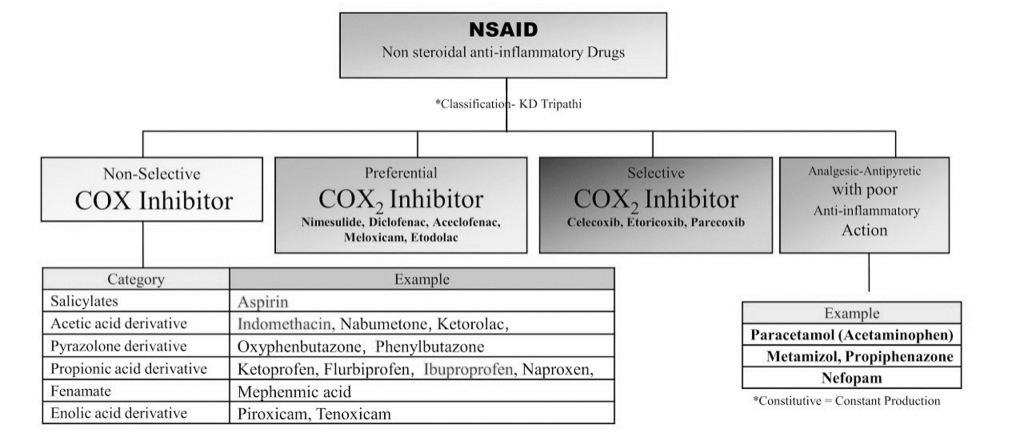
Classification
Mnemonic: Prescribed By SOFIA
- Propionic acid derivatives: Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Flurbiprofen, Naproxen
- Pyrrolo-pyrrole derivates: Ketoroloac
- Pyrazolone derivatives: Phenylbutazone, Oxybutazone
- Benzoxazocine derivatives: Nefopam
- Salicyaltes: Aspirin
- Selective COX-2 inhibitor: Celecoxib, Etoricoxib, Parecoxib
- Oxicam derivatives: Piroxicam, Tenoxicam
- Fenamic acid derivatives: Mefenamic acid (Anthranilic acid derivative)
- Indol derivatives: Indomethacin, Sulindac
- Aryl acetic acid derivatives: Diclofenac, Aceclofenac
Side effects and Contraindications
Mnemonic: BARS
- Bleeding
- Inhibit platelet cycloxygenase (COX), thereby blocking the formation of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and impairing TXA2 dependent platelet aggregation
- Asthma
- Inhibition of COX pathway shifts the arachidonic acid metabolism to Lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway leading to increased leukotriene synthesis
- Allergy
- Upto 2% prevalence
- Renal disease
- Inhibition of PGE2/PGI2 leads to constriction of afferent arteriole and pre-renal AKI
- Leads to sodium retention (peripheral edema, hypertension, heart failure)
- Stomach: Mucosal damage by –
- COX-1 inhibition: Reduced blood flow
- Topical irritation: Epithelial damage
- COX-2 inhibition: Leukocyte adherence
Beneficial effects
Mnemonic: Five “A”s
- Analgesic
- Antipyretic
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anti-thrombotic
- Arteriosus closure (PDA closure)