The basic clinical examination of the Cardiac System is by Auscultation (listening to the sounds made by the heart). As explained in the previous article physiological sounds made in each cardiac cycle viz. S1 and S2 due to the closure of the Atrio-Ventricular Valves and Outlet Valve in synchrony.
Please go through my other article before reading further:
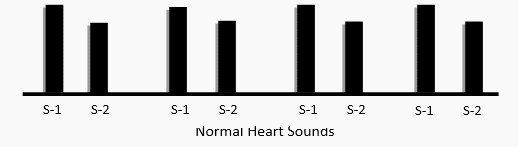
In pathological conditions of the heart few other sounds are heard as described below.
Types of abnormal Heart Sounds
- Change in the character of S-1 and S-2
- S-3 and S-4
- Clicks
- Snaps
- Rubs
- Murmurs
Patho-Physiology of the Abnormal Sounds:
- S3 – Due to PASSIVE VENTRICULAR FILLING
- S4 – Due to RAPID ACTIVE FILLING AGAINST STIFF VENTRICLE
- Clicks – Due to opening of valves in the Systolic Phase.
- Snaps – Due to opening of valves in the Diastolic Phase.
- Rubs – Due to rubbing of pericardial layers against each other.
- Murmurs – Due to flow of blood through narrowed orifice. They are of 2 types:
- Functional – Hyper-dynamic Circulation.
- Organic – Abnormalities of Valves or Chamber.
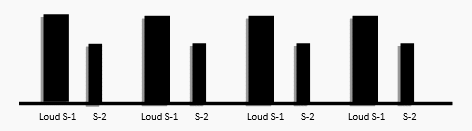
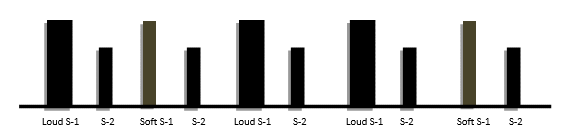
S – 1 (Abnormal):
- Heard due to closure of AV Valves – Mitral and Tricuspid.
- LOUD: Heard due to strong closure of AV valves in case of:
- Hyper-dynamic Circulation
- Thin Chest Wall
- Mitral Stenosis
- SOFT: Heard due to weak closure of AV valves in case of:
- Hypo-dynamic Circulation
- Thin Chest Wall
- Emphysema, Pericardial Effusion
- Fibrotic / Calcified Valves
- VARIABLE: Heard due to de-synchronization between atria and ventricles in case of –
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Complete Heart Block
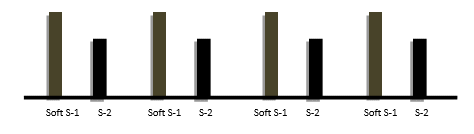
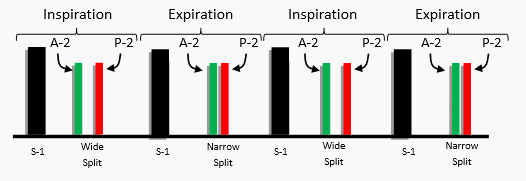
S-2 (Split) :
- S-2 is comprised of two sounds produced by closure of Aortic valve and Pulmonary Valve.
- Physiologically during Inspiration there is a gap between the components called SPLIT.
- Whereas during Expiration there is a FUSION of the components.
- WIDE & MOBILE: Heard due to delayed closure of pulmonary valve in case of :
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Right Bundle Branch Block
- Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Pulmonary hypertension
Split – WIDE – during inspiration
Split – NARROW – during expiration
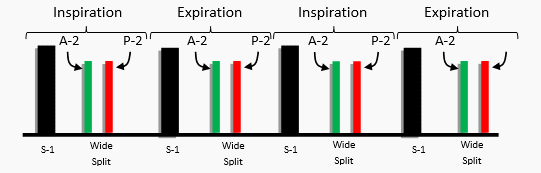
- WIDE AND FIXED: Heard in case of Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) due to equal filling of ventricles due to the shunt.
Split – WIDE – during inspiration and expiration
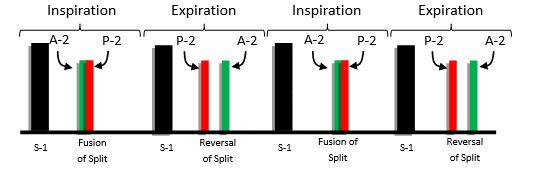
- REVERSE/PARADOXICAL: Heard due to delayed left ventricular contraction in case of –
- Aortic Stenosis
- Left Bundle Branch Block
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
FUSION of S2 is during INSPIRATION
SPLIT of S2 is during EXPIRATION (Pulmonary component followed by Aortic)
S – 3 (Ventricular Gallop)
- Heard soon after S-2 (as the Mitral valve opens and allows passive filling of Left Ventricle).
- Mechanism: When large amount of blood strikes a compliant ventricular wall.
- Character: Low Pitched sound, heard with the bell of the stethoscope better, at the apex in Left Lateral Position.
- Heard In: Children, Pregnant Women, Athletes and Ventricular Overload (as in Congestive Cardiac Failure, Aortic Regurgitation).
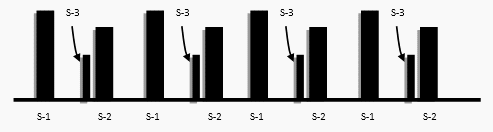
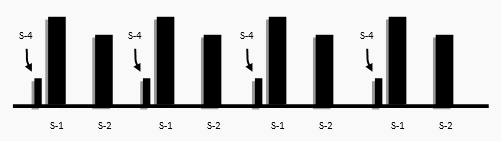
S – 4 (Atrial Gallop)
- Heard just before S-1 (as the Mitral valve is about to be closed when there is an active filling of the Left Ventricle)
- Mechanism: When the jet of blood strikes a noncompliant ventricular wall.
- Character: Low Pitched sound, heard with the bell of the stethoscope better, at the apex in Left Lateral Position.
- Heard In: Ventricular Hypertrophy and Cardiomyopathy.
Clicks and Snaps
- Opening of any valve usually does not produce a sound, but any pathology if developed in the valve causes a sound while opening.
- They are High Pitched sounds and may be heard even in the absence of any abnormal sounds, indicating a minute pathology.
- Clicks are usually heard during Systole and Snaps during Diastole.
- Conditions where they are heard:
- Early Systolic Click: Aortic and Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
- Mid Systolic Click: Mitral Valve Prolapse
- Early Diastolic Snap: Mitral Valve Stenosis
Rub
- Constant friction between the Visceral and Parietal Layers of the Pericardium.
- It is a High Pitched Scratchy sound, usually over the Left Sternal Border.
- Heard in case of Pericarditis and disappears as Effusion develops.
Summary
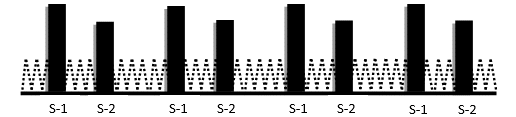
The primary Heart Sounds are S-1 and S-2.
Any pathology in the Heart causes additional sounds such as abnormal S-1, Splitting of S-2, presence of S-3 and S-4, Clicks, Snaps and Rubs.
Accurate identification of these sounds is helpful in the diagnosis of many Cardiac conditions.
References
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th Edition.
- Bates’ Guide to Physical Examination and History Taking, 10th Edition.
- Hutchinson’s Clinical Methods, 23rd Edition.

Graduated from one of the famous institutions in Telangana, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences. He has always been fond of writing articles in Medicine. Since the undergraduate years was interested in making creative Presentations and taking seminars.