Porta hepatis
Mnemonic: DAVE
From anterior to posterior:
- Ducts (right and left hepatic duct branches)
- Arteries (right and left hepatic artery branches)
- Vein (portal vein)
- Epiploic foramen (foramen of Winslow)
Femoral triangle or Scarpa’s triangle
Mnemonic: NAVEL
From lateral to medial
- Nerve (femoral nerve and femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve)
- Artery (femoral artery)
- Vein (femoral vein and it’s tributary – great saphenous vein)
- Empty space (femoral canal)
- Lymph node of Cloquet/Rosenmuller and Lymphatics (within femoral canal)
All are contents of the femoral sheath except the femoral nerve.
Tarsal Tunnel (Within Flexor Retinaculum, Posterior to Medial malleolus)
Mnemonic: Tom, Dick And Very Nervous Harry
From anterior to posterior
- Tibialis (tibialis posterior)
- Digitorum (flexor digitorum longus)
- Artery (posterior tibial artery)
- Vein (posterior tibial vein)
- Nerve (tibial nerve)
- Hallucis (flexor hallucis longus)
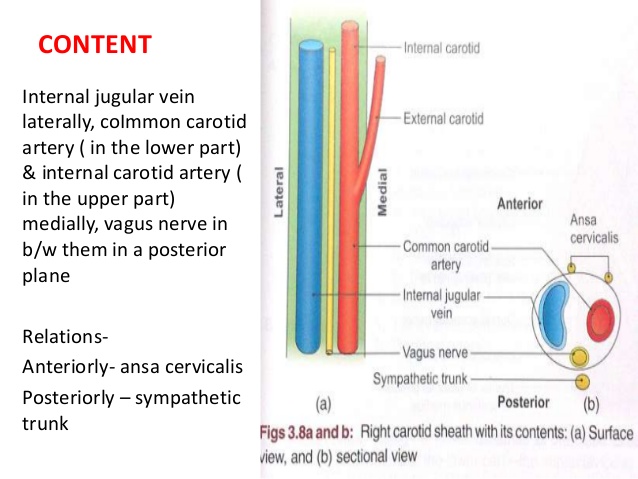
Carotid Sheath
Mnemonic: VNA – AS
From lateral to medial
- Vein (internal jugular vein)
- Nerve (vagus nerve)
- Artery (internal carotid artery in upper part and common carotid artery in lower part)
Outside carotid sheath:
- Anterior: Ansa cervicalis
- Posterior: Sympathetic chain
Cubital Fossa
Contents from lateral to medial
Mnemonic: R-TAN
- Radial nerve (not always strictly considered as part of cubital fossa)
- Tendon (Biceps tendon)
- Artery (Brachial artery)
- Nerve (Median nerve)
Cubital tunnel is a space through which ulnar nerve passes posterior to the medial epicondyle of humerus, under the cubital tunnel retinaculum (ligament or band of Osborne)
Subcutanoeus structures from lateral to medial
Mnemonic: CMB
- Cephalic vein
- Median cubital vein (preferred site of venipuncture
- Basilic vein
Popliteal fossa
Mnemonic: PeN TiN VAN
From lateral to medial
- Peroneal Nerve
- Tibial Nerve
- Vein (Popliteal vein)
- Artery (Popliteal artery)
- Nerve (Genicular branch of obturator nerve – descends upon popliteal artery)
Intercostal space
Superior to inferior along the inferior border of the rib
Mnemonic: VAN
- Vein (intercostal vein)
- Artery (intercostal artery)
- Nerve (intercostal nerve)
Collateral neurovascular bundle runs along the superior border of the rib in the lower part of intercostal space in reverse order, i.e. NAV
- Nerve
- Artery
- Vein