Mnemonic: FOOL
a. Fat pads
b. Overt findings and outlines
c. Ossification centers
d. Lines
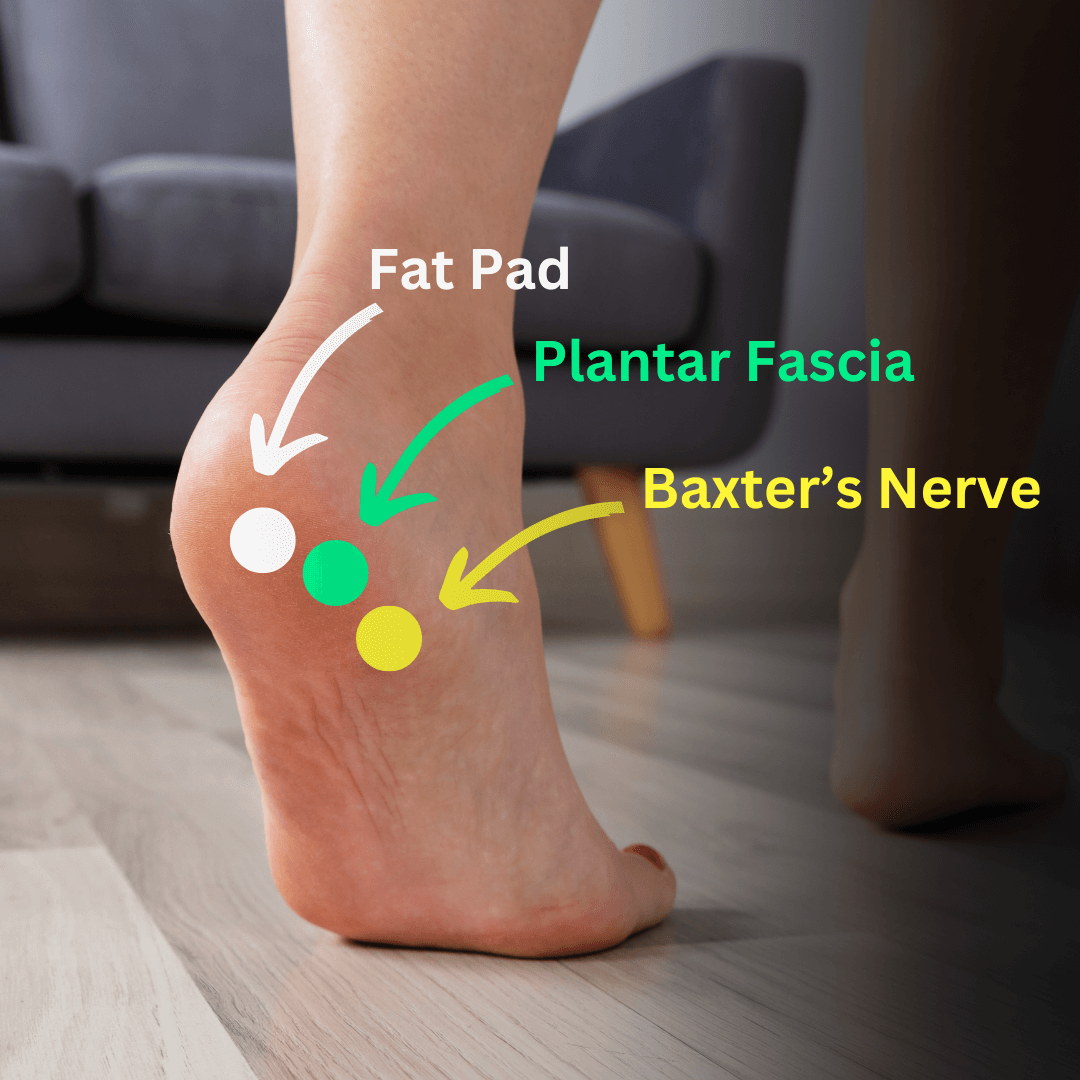
Fat pads
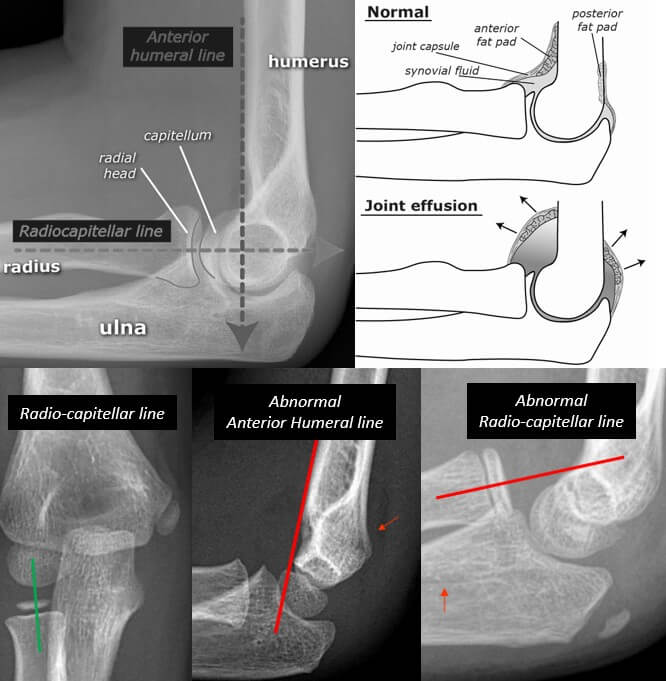
The elbow joint has anterior and posterior fat pads which are extra-synovial but within the articular capsule. These are present as a radiolucent (black) line (compared to bone and surrounding soft tissues) in lateral X-rays.
Normal finding: Straight radiolucent line immediately anterior to the distal humerus (anterior fat pad).
Abnormal findings: Joint effusion or synovitis leads to displacement of the fat pads away from the bone.
- Visible posterior fat pad (normally contained in olecranon fossa) ALWAYS indicates joint effusion.
- In setting of trauma – think of intra-articular fracture particularly in adults
- In children – soft tissue damage may also be associated with joint effusion
- Raised anterior fat pad (Sail sign) indicates elbow effusion – should arise suspicion of undisplaced radial head facture if a fracture cannot be identified.
Fractures may be present without fat pads, e.g. Radial neck, Medial epicondyle or Olecranon tip.
b. Overt findings and Outlines
Evaluate for obvious soft tissue injuries, obvious fractures and/or dislocations.
Trace outlines (cortex) of each bone (distal humerus, proximal radius and olecranon) to detect subtle injuries
c. Ossification centers
The age of appearane of 6 centers of secondary ossification centers can be remembered with a mneamonic.
Mnemonic – CRITOE
- Capitulum: 2 years
- Radial head: 4 years
- Internal (medial) epicondyle: 6 years
- Trochlea: 8 years
- Olecranon: 10years
- External (lateral) epicondyle: 12 years
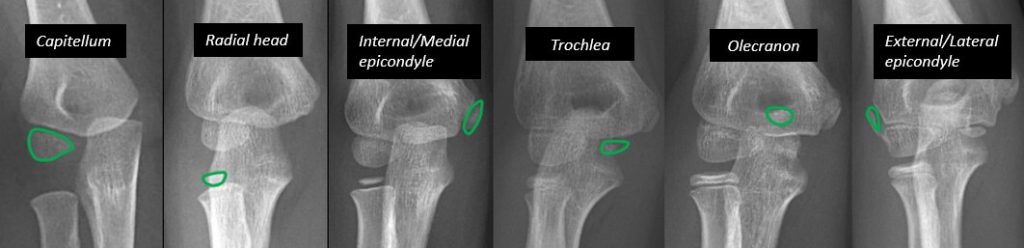
Trochlear and olecranon centres are often multicentric and should not be mistaken for fracture fragments. Although the CRITOE order is the most common sequence, individual variation can occur. But, the internal epicondyle always ossifies before the trochlea. Possible normal variants are CIRTOE or CRIOTE.
Unlike fractures, ossification centers are smooth and well-corticated.
d. Lines
i. Anterior humeral line: A vertical running drawn on the anterior surface of humerus must run down to intersect middle 1/3rd of CAPITELLUM (on lateral x-rays). It is less reliable in children <5 years old.
- Abnormal: Think of DISTAL HUMERUS fracture
When axial force is applied down the radius (such as after a fall onto an outstretched hand), the radial head impacts the capitellum. The narrowest and weakest part of the distal humerus is placed under stress resulting in supracondylar fracture and posterior dislacement of the capitellum.
ii. Radio-capitellar (Mclaughlin or Storen’s line) line: A line through the center of radius runs vertically (on AP x-rays) or horizontally (lateral x-rays) and passes the central CAPITELLUM. In 16% of normal radiographs in children, radiocapitellar line can be abnormal due to following reasons – small epiphyses & eccentric ossification or metaphyseal surface of the proximal radius may not be parallel to articular surface of capitellum.
- Abnormal: Think of RADIAL HEAD dislocation or subluxation (don’t forget to look for monteggia fracture dislocation).
iii. Lateral humeral line (LHL): Radiocapitellar line can miss the capitellum in 16% normal pediatric elbow radiographs in children <5 years. In an AP xray, the line runs parallel to the long axis of the humerus at the most lateral extent of the ossified distal humerus. When extended distally, this line should lie lateral to the radial neck to demonstrate a congruent radiocapitellar joint.