It is the region in thoracic cavity between the pulmonary cavities (covered by mediastinal pleura and excludes the lungs).
Extent: Thoracic outlet (1st rib) to Diaphragm (T12)
Superior mediastinum:
| Upper extent | Thoracic outlet |
| Contents (superficial to deep) | 1. Glands (Thymus and Lymph nodes) 2. 3 Veins (Brachiocephalic Lt. and Rt. and SVC) 3. 4 Arteries (Arch of aorta and it’s 3 branches) 4. 3 Nerves (Vagus, Phrenic and Left recurrent laryngeal) 5. 2 Tubes (Trachea and Esophagus) 7. 1 duct (Thoracic duct) |
| Lower extent | Line through angle of Louis (manubriosternal joint to T4/5) |
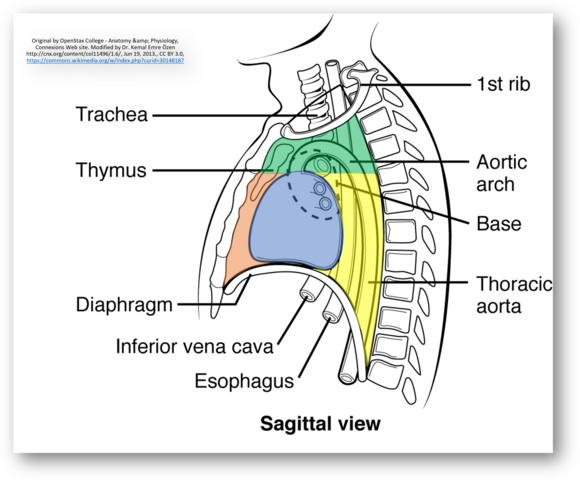
Green (Superior mediastinum); Orange (Anterior mediastinum); Blue (Middle mediastinum); Yellow (Posterior mediastinum)
Inferior mediastinum:
| Anterior mediastinum | Middle mediastinum | Posterior mediastinum | |
| Upper extent | T4/5 | T4/5 | T4/5 |
| Contents | 1. Thymic remnants 2. Lymph nodes 3. Fat | 1. Phrenic nerve 2. Pericardium 3. Heart 4. Ascending aorta 5. Pulmonary trunk 6. SVC 7. Lymph nodes | Remember esophageal and aortic openings of diaphragm: 3 gooses And A Duck. 1. Esophagoose 2. Right vagoose 3. Left vagoose 4. Aorta (descending) 5. Azygous vein 6. throacic Duct 7. Sympathetic and Splanchnic nerves |
| Lower extentn | T9 | T9 | T12 |
Mediastinal masses
Anterior mediastinum: Mnemonic – 4 Ts
- Thymic neoplasm
- Teratoma
- Thyroid
- Terrible lymphoma
Middle mediastinum:
- Bronchogenic and pericardial cysts
- Esophageal tumors
- Vascular masses
- Lymphoma and lymph nodes
Posterior mediastinum: Mnemonic – MNOP
- Meningocele
- Neurogenic tumors
- Osseous tumors (Chordoma, Chondrosarcoma, Ewings)
- Paraspinal abscess