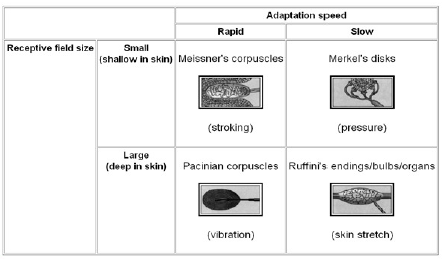
Adaptation of Mechanoreceptors
Mnemonic: Life is fast for MPs (Member of Parliament) and slow for MRs. In alphabetical order, meIssner’s come becore meRkel. Hence, Meissner’s corpuscle are the quicker among two.
1. Fast adapting receptors: MP
- Meissner’s corpuscle
- Pacinian corpuscle
2. Slowly adapting receptors: MR
- Merkel disc
- Ruffini corpuscle/ending
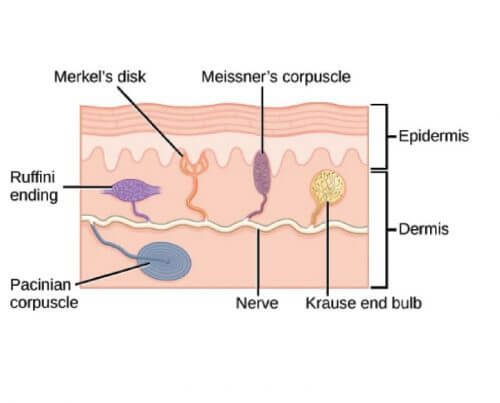
Location of Mechanoreceptors
Mnemonic: Both starting with “M” are superficial and have small receptive field. Other 2 are deeply located.
- Superficial (Epidermis): Meissner’s corpuscle and Merkel’s disc
- Deep (Dermis): Ruffini’s ending and Pacinian corpuscle
Mnemonic: MeiSSner has SS which stands for hairleSS or Smooth Surface.
- Found in hairless (glaborous skin) only: Meissner corpuscle
- Found in both hairless and hairy skin: Others
Functions of Mechanoreceptors
Mnemonic:
The superficial receptors detect touch and the deep receptors detect pressure.
- Meissner is smooth to pronounce – found on smooth skin and detects smooth (fine) touch.
- Merkel is harder to pronounce – found also on hairy skin and detects crude touch.
- ViP STaR or PV = nRT
- Vibtation: Pacinian corpuscle
- Stretch and Temperature (warm): Ruffini endings
- Krause bulb = Kelvin = Kold (Cold)
- Meissner corpuscle: Light/fine touch and Moving 2 point discrimination
- Merkel disc: Crude touch and Static 2 point discrimination
- Ruffini endings: Stretch (prolonged pressure) and warmth
- Pacinian corpuscle: Vibration
- Krause bulb: Cold
They are also classified as: Fast Adapting (FA) or Slow Adapting (SA) followed by 1 (superficial) or 2 (deep)
- FA1 – Meissner corpuscle
- FA2 – Pacinian corpuscle
- SA1 – Merkel disc
- SA2 – Ruffini endings

I would say more than amazing! Its fantastic.
Awesome mnemonic 👍👍 helped me a lot to remember them 👌👌
lovely, From Thailand 😀