Definition of ATT induced hepatitis
- ALT > 3 X Normal + Symptoms OR
- ALT > 5 X Normal without Symptoms
Management of ATT induced hepatitis
1. Hold all TB drugs for 7-10 days. Wait before restarting ATT until:
- Symptoms: Resolve
- ALT <2.5 X Normal
For severe TB, patients should be started on SEQ (Streptomycin, Ethambutol and Quinolone) until first line drugs can be re-introduced.
2. Re-introduce first line ATT in a stepwise manner:
- Start full dose Ethambutol (it is non-hepatotoxic) from Day 1
- Day 1-3: E + H (1/3rd-full dose)
- Start Isoniazid and increase the dose in subsequent days, i.e. 1/3rd, 2/3rd then full dose
- Perform LFT at Day 3
- Day 4-6: E + H + R (1/3rd-full dose)
- Start Rifampicin and increase the dose in subsequent days, i.e. 1/3rd, 2/3rd then full dose
- Perform LFT at Day 6
- Day 7-9 (only if patient has no liver disorder): E + H + R + Z (1/3rd-full dose)
- Start Pyrazinamide and increase the dose in subsequent days, i.e. 1/3rd, 2/3rd then full dose
- Perform LFT at Day 9
- If patient is symptomatic or LFT is deranged at any stage, offending drug must be stopped.
3. Duration of treatment depends on the number of drugs given.
Reference: National-Tuberculosis-Management-Guidelines-2019_Nepal.pdf (nepalntp.gov.np)
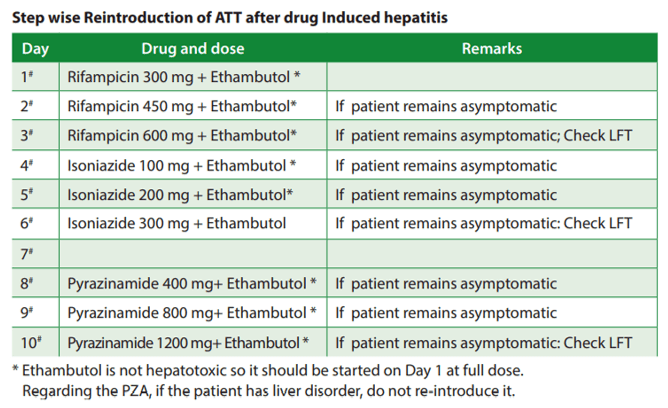
The table for “reintroduction of TB drugs in sequence of Rifampicin–>Isoniazid—> Pyrazinamide” doesn’t well correlate to what is written in explanation. Must be a typo only but it makes the matter most confusing!