The severity of alcoholic hepatitis can be assessed using a number of simple quantitative indices (Maddrey score, Meld score, Combined clinical and laboratory index). Of these, the Maddrey Discriminant Function (MDF) is the simplest.
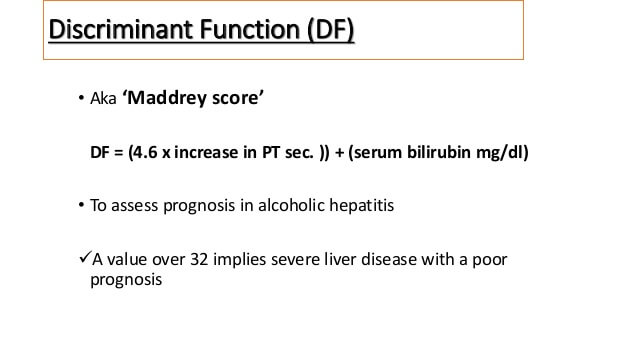
Maddrey score = 4.6 X (prolongation of prothrombin time above control in seconds) + Total bilirubin in mg/dl
To calculate Maddrey discriminant function using SI units – micromol/l (i.e. not US) divide bilirubin value by 17.
Interpretation:
Maddrey score >32 characterizes severe alcoholic hepatitis associated with a short-term mortality (within 30 days) of 30-50%, and has been used to determine the need for corticosteroid therapy.
Example: Patient prothrombin time 16 s, bilirubin 150 micromole/L, lab control prothrombin time 12 s
Maddrey score = 4.6 (16-12) + 150/7 = 26 (Maddrey score <32 is associated with a low likelihood of mortality during the current admission)
Lillie model
In patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis who have been treated with glucocorticoids, a prognostic scoring system (the Lillie model) has been proposed for predicting mortality. The model combines 6 variables:
- Age
- Renal insufficiency (Creatinine >1.3 pr creatinine clearance <40)
- Albumin
- PT
- Bilirubin
- Evolution of bilirubin at Day 7
The authors concluded that the term “nonresponder” can now be extended to patients with a Lille score above 0.45, which corresponds to 40% of cases.
References:
- A Practical Approach to the Spectrum of Alcoholic Liver Disease, An Issue of Clinics in Liver Disease – By David Bernstein
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology: A Clinical Handbook edited by Nicholas Joseph Talley, Isidor Segal, Martin D. Weltman
- Louvet A, Naveau S, Abdelnour M, Ramond MJ, Diaz E, Fartoux L, Dharancy S, Texier F, Hollebecque A, Serfaty L, Boleslawski E, Deltenre P, Canva V, Pruvot FR, Mathurin P. The Lille model: a new tool for therapeutic strategy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids. Hepatology. 2007 Jun;45(6):1348-54. PubMed PMID: 17518367.