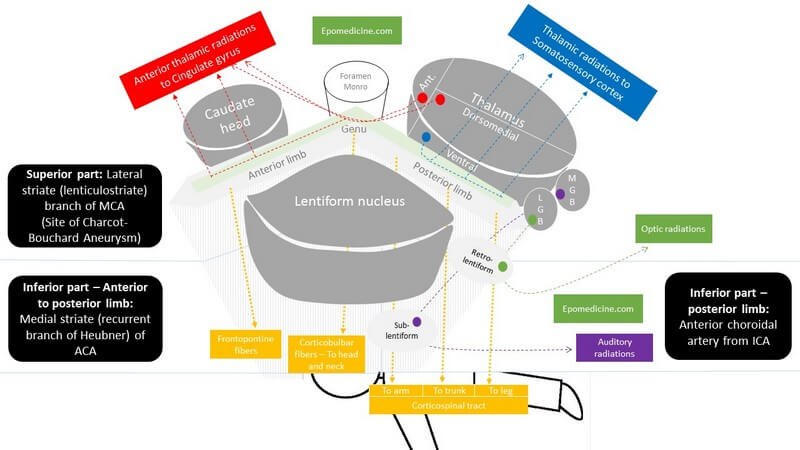
There are 2 major triangles in the neck, containing other smaller triangles.
1. Anterior triangle: Midline of neck – Mandible – Anterior border of SCM
- Submental triangle: IA (Submental LN)
- Submandibular or Digastric triangle: IB (Submandibular LN), Submandibular gland, CN XII
- Carotid triangle: II + III, Carotid sheath (CCA, IJV, XN X)
- Muscular triangle: IV, Infrahyoid muscles, Thyroid and Parathyroid glands
Posterior triangle: Posterior border of SCM – Trapezius – Clavicle (level V); 2 triangles inside separated by inferior belly of omohyoid
- Occipital triangle: OT GLASS
- Occipital artery
- Transverse cervical artery and vein
- Greater auricular nerve (C2, C3)
- Lesser occipital nerve (C2)
- Accessory spinal nerve (CN XI)
- Supraclavicular nerve (C3, C4)
- Small muscular branches: Levator scapulae (C3, C4), Trapezius (C3, C4), Rhomboideus (C5)
- Supraclavicular or Subclavian triangle:
- 3 trunks of brachial plexus
- Nerves arising from roots and trunks of brachial plexus:
- Long thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7) – serratus anterior
- Nerve to subclavius (C5, C6)
- Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6)
- Subclavian artery (3rd part) and Subclavian vein
- Suprascapular artery and vein
- External jugular vein (lower part)
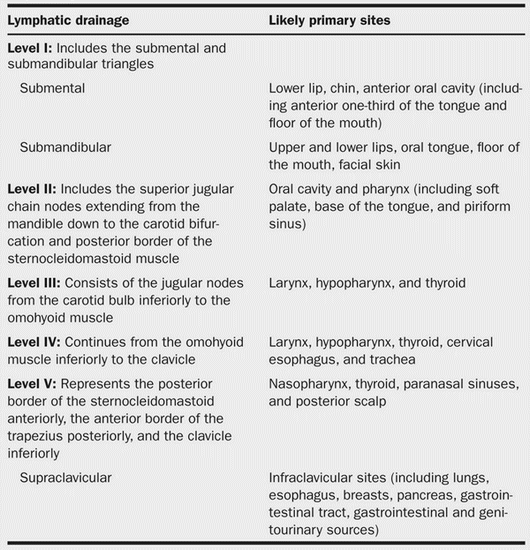
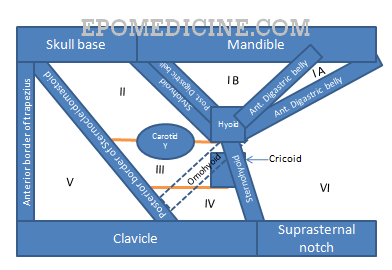
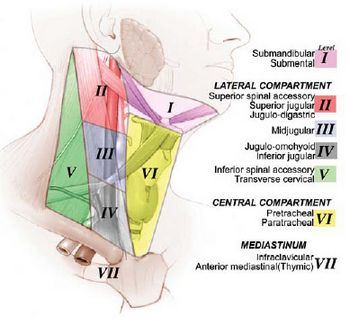
Surgically, cervical lymph nodes are divided into 6-7 levels (only 6 according to many authors who exclude the level VII nodes) for staging of carcinoma which would also be the basis for selective neck dissection. There are 5 levels in the lateral compartment and 2 in the central compartment. Nodes not included in these system of levels are retropharyngeal group, periparotid group, buccinator group, post auricular group and suboccipital group of nodes.
| Level | Lymph nodes | Boundaries | |
| I | A | Submental nodes | Bilaterally: Anterior belly of digastrics Inferiorly: Hyoid bone |
| B | Submandibular nodes | Superiorly: Mandible Posteroinferiorly: Posterior belly of digastrics Anteroinferiorly: Anterior belly of digastrics | |
| II | A (Anterior to the vertical line in relation to spinal accessory nerve) | Upper internal jugular (deep cervical) nodes | Superiorly: Skull base Inferiorly: Inferior border of hyoid bone and Carotid bifurcation Posteriorly: Posterior border of Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) Anteriorly: Lateral border of Sternohyoid and Stylohyoid |
| B (Posterior to the vertical line in relation to spinal accessory nerve) | |||
| III | Mid internal jugular (deep cervical) nodes | Superiorly: Inferior border of hyoid bone and Carotid bifurcation Inferiorly: Inferior border of cricoid cartilage and Junction of omohyoid muscle and IJV Posteriorly: Posterior border of SCM Anteriorly: Lateral border of sternohyoid | |
| IV | Lower internal jugular (deep cervical nodes) | Superiorly: Inferior border of cricoids cartilage and Junction of omohyoid and IJV Inferiorly: Clavicle Posteriorly: Posterior border of SCM Anteriorly: Lateral border of sternohyoid | |
| V | A (Above the horizontal plane marking the inferior border of arch of cricoids cartilage) | Posterior triangle (spinal accessory) nodes | Superiorly: Convergence of SCM and trapezius Inferiorly: Clavicle Posteriorly: Anterior border of trapezius Anteriorly: Posterior border of SCM |
| B (Below the horizontal plane marking the inferior border of arch of cricoids cartilage) | |||
| VI (Prelaryngeal or Delphian, Pretracheal, Paratracheal, Prethyroidal) | Anterior compartment (midline) nodes | Superiorly: Hyoid bone Inferiorly: Suprasternal notch Bilaterally: Carotid arteries | |
| VII | Upper mediastinal nodes | Below suprasternal notch | |
The highest jugular digastric node near the angle of the mandible is called the “sentinel” node.
The “signal” node is the lowest along the internal jugular chain called the virchow nodes.
Probable source of Nodal metastasis:
- Level 1: Oral cavity, submandibular gland
- Level 2: Nasopharynx, oropharynx, parotid, supraglottic larynx
- Level 3: Oropharynx, hypopharynx, supraglottic larynx
- Level 4: Subglottic larynx, hypopharynx, esophagus, thyroid
- Level 5: Nasopharynx, oropharynx
- Level 6 & 7: Thyroid, larynx, lung
Note: Bilateral nodes are common with cancers of soft palate, tongue, epiglottis, and nasopharynx.
Selective Neck dissection involves:
- Supraomohyoid/Anterolateral: Level I to III
- Extended Supraomohyoid: Level I to IV
- Lateral: Level II to IV
- Posterolateral: Level II to V
- Anterior or Central: Level VI
- Superior mediastinal: Level VII
Comprehensive Neck dissection inolves:
- Radical and Modified Radical Neck Dissection: Level I to V