Ligaments
Mnemonic: TV TFCL
1. True ligaments:
- ligamentum Teres hepatis/round ligament (obliterated umbilical vein remnant)
- ligamentum Venosum (ductus venosus remnant)
2. False ligaments (Peritoneal folds):
- Triangular ligaments (right and left): connects respective liver lobes to diaphragm
- Falciform ligament: connects anterior surface of liver to anterior abdominal wall
- it’s free edge contains ligamentum teres
- Coronary ligament: encloses bare area of liver
- anterior and posterior folds on each side unites to form triangular ligament
- Lesser omentum:
- Hepatogastric ligament
- Hepatoduodenal ligament (surrounds portal triad)
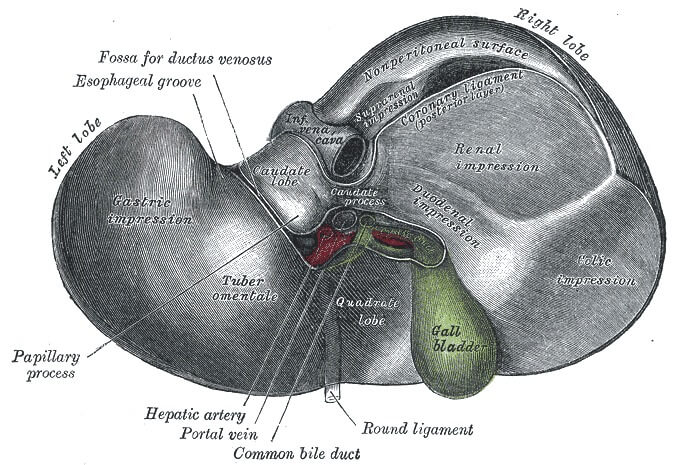
Posteroinferior (Visceral) Surface of Liver
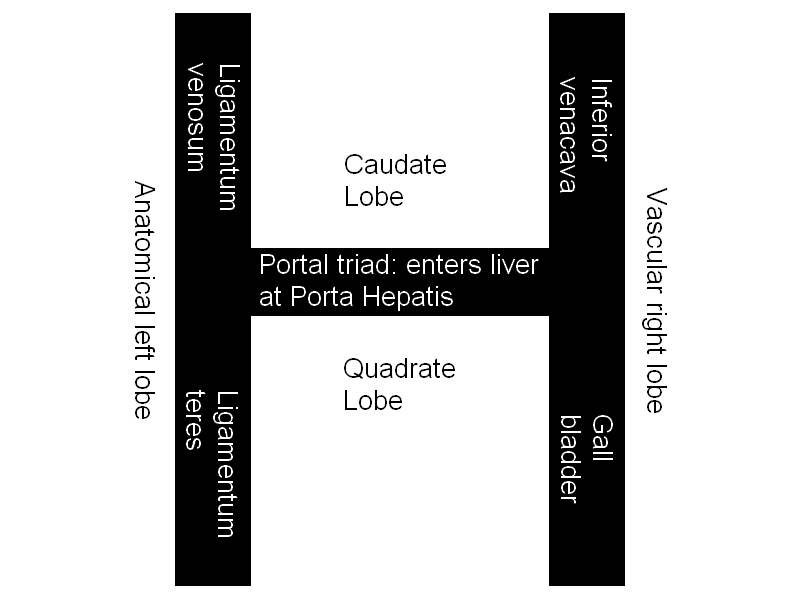
Anatomical halves are separated by Ligamentum venosum and Ligamentum teres.
Vascular halves are separated by IVC and Gall bladder.
Caudate lobe and Quadrate lobe:
- Anatomically: Right lobe
- Functionally (Vascular): Left lobe
Mnemonic: IVC are in one line
- Inferior venacava (IVC)
- ligamentum Venosum
- Caudate lobe
Mnemonic: LGBTQ are in one line
- Ligamentum Teres
- Gall Bladder
- Quadrate lobe
Porta hepatis separates the caudate and quadrate lobes. It transmits all the vessels, nerves and ducts entering or leaving the liver with the exception of the hepatic veins. The order of the structures in the porta hepatis from anterior to posterior can be remembered using the mnemonic “DAVE”:
- Ducts (right and left hepatic duct branches)
- Arteries (right and left hepatic artery branches)
- Vein (portal vein; NOT hepatic vein)
- Epiploic foramen (of Winlsow)
Hepatic Segmentation
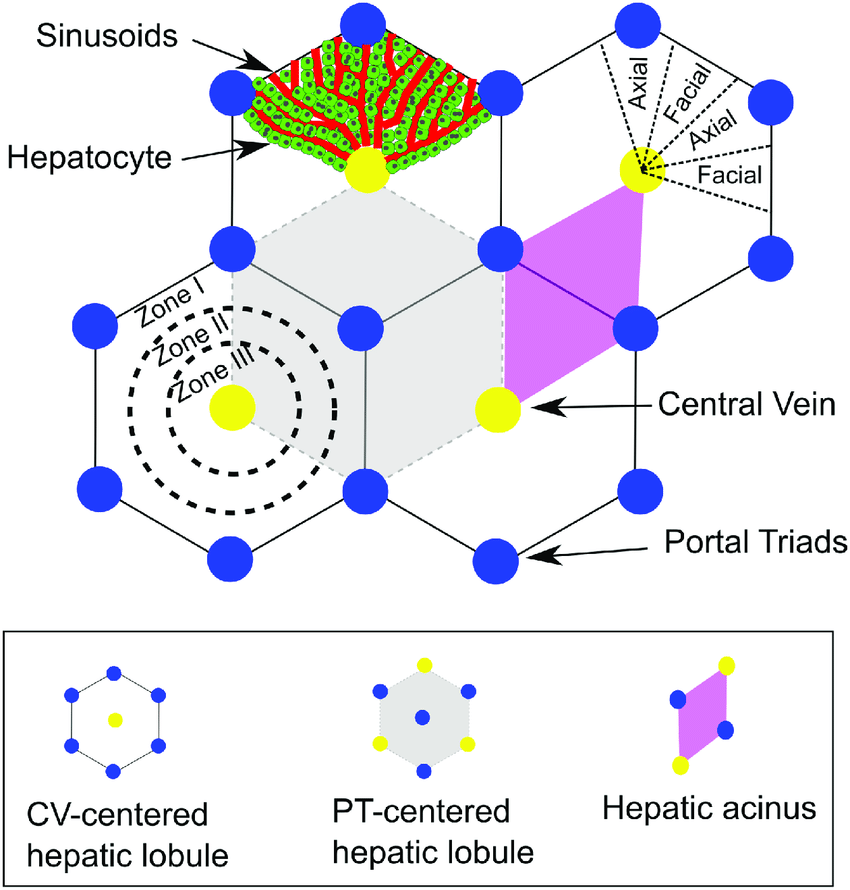
Liver Zonation
Mnemonic: Cen-three-lobular zone
Functionally, liver can be divided into 3 zones, based upon oxygen supply.
- Zone 1: Periportal zone
- Predominantly involved in autoimmune and viral hepatitis (ALT > AST)
- Zone 2: Transitional zone
- Zone 3: Centrilobular zone
- Predominantly involved in ischemic and toxic events, heart failure and Budd-chiari syndrome (AST > ALT)
Blood and Nerve Supply of Liver
1. Arteries:
- Hepatic artery (30%) – branch of celiac trunk
- Portal vein (70%)
2. Veins: IVC via right and left hepatic veins
3. Lymphatics: Celiac nodes
4. Nerves:
- Sympathetic: Celiac plexus
- Parasympathetic: Anterior vagal trunk