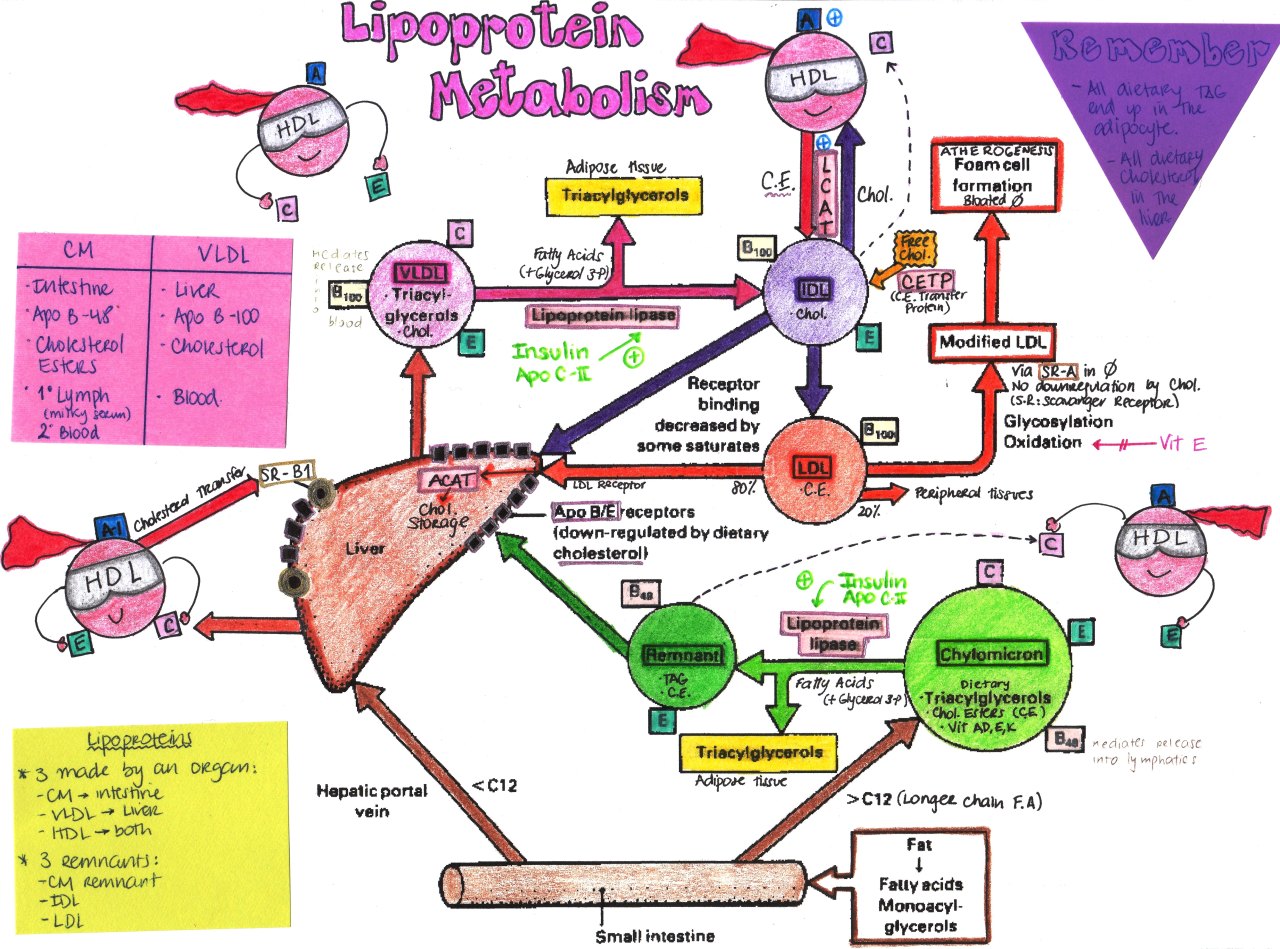
Lipoproteins
Composition of Lipoproteins:
- Non-polar core – mainly triglycerides and cholesteryl esters
- Single surface layer – amphipathic phospholipids and cholesterol
- Apoprotein or Apolipoprotein
| Class | Abbreviation | Density | Protein | Lipid content | Electrophoretic mobility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chylomicrons | CM | lowest | lowest | highest (exogenous triacylglycerol) | don’t migrate |
| Very low density lipoproteins | VLDL | .. | .. | .. (endogenous triacylglycerol) | pre-β globulin region |
| Intermediate density lipoproteins | IDL | .. | .. | .. | .. |
| Low density lipoproteins | LDL | .. | .. | .. (highest cholesterol and cholesterol esters) | β-globulin region |
| High density lipoproteins | HDL | highest | highest | lowest | α-globulin region |
Size of lipoprotein α 1/density (CM are largest and HDL are smallest in size).
Apoproteins
- Apo-A1: Found in HDL and Chylomicrons. It activates LCAT (Lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase), which in turn promotes breakdown of cholesterol-containing lipoproteins.
- LCAT converts cholesterol to cholesterol esters.
- Apo-B100: Very large. Found in LDL and VLDL and serves as a receptor for uptake of these particles by target cells. Also plays structural role.
- Apo-B48: 48% the size of Apo-B100. Structural protein in chylomicrons.
- Apo-CII: Serves as a cofactor for lipoprotein lipase (induced by insulin) – to aid in breakdown of lipoproteins. Found in HDL2, VLDL, and Chylomicrons.
- lipoprotein lipase hydrolyzes triacylglycerols (TAG) into fatty acids and glycerol.
- extracellular enzyme located on capillary endothelium (absent in adult liver and predominantly present in adipose tissue, cardiac and skeletal muscles and lactating mammary glands; highest concentration in cardiac muscle).
- Heart lipoprotein lipase has low Km and adipose lipoprotein lipase has high Km – heart can continuously use fatty acid as fuel (0xidation) even at low lipoprotein concentration and adipocytes can remove fatty acids from circulating lipoprotein and store them as TAG (re-esterification of fatty acid) only when lipoprotein concentrations are elevated. This also enables delivery of fatty acids to be redirected from adipose tissue to heart in starved state.
- Apo-CII and phospholipids are cofactors and Apo-CIII and Apo-AII are inhibitors.
- Apo-E: Serves as a receptor-ligand for LDL and chylomicron remnants.
- Also found on ApoE-Rich HDL, a special form of HDL.
- The presence of different alleles of this protein in brain cells has related to Alzheimer’s Disease, in recent research.
Apo C and Apo E are donated by HDL to chylomicrons and VLDL.
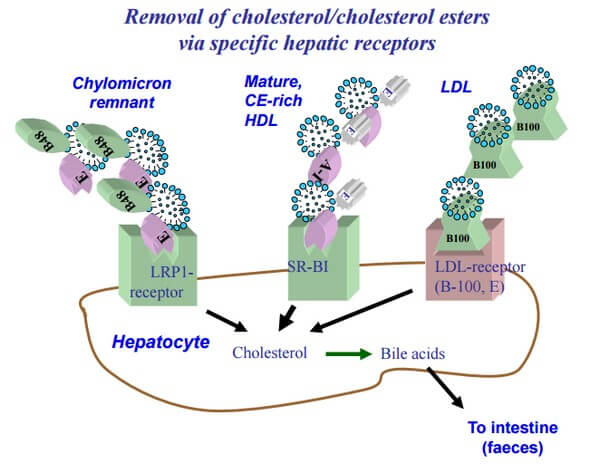
Lipoprotein Receptors
1. LDL receptor (Apo-B100, E Receptor)
- Specific for Apo-B100 but not B-48
- Also takes up lipoproteins rich in apo-E
- Takes up LDL, VLDL remnant (IDL) and chylomicron remnant (all have lost triglycerides but are still rich in cholesterol) by endocytosis
- Widely distributed throughout different tissues
- Regulation: The delivery of the cholesterol to the cell inhibits receptor synthesis and cholesterol synthesis (negative feedback). Cholesterol influx stimulates ACAT (liver enzyme) activity leading to esterification of cholesterol.
2. Remnant receptor (Apo-E)
- Found in the liver only.
- Recognizes Chylomicron Remnants and Apo-E Rich HDL receptors.
- Delivers cholesterol to liver and it is not regulated.
3. Scavenger receptor
- Uptake of oxidized or chemically modified LDL-Particles by Monocytes in circulation or Macrophages in tissues (these are not recognised by LDL receptor).
- It is not downregulated by negative feedback like LDL receptor.
Physiology of Lipoprotein Metabolism in Molecular level
- Dietary fats (exogenous triglycerides) are carried by nascent chylomicrons (B-48) – synthesized by intestine.
- Liver fatty acid (endogenous triglycerides) are carried by nascent VLDL (B-100) – synthesized by liver.
- HDL acts as reservoir for different apoproteins and exchange them with other lipoproteins.
- Provides Apo CII and E to nascent chylomicron and VLDL to form chylomicron (B-48, CII, E) and VLDL (B-100, CII, E).
- Lipoprotein lipase hydrolyzes TAG in chylomicron and VLDL to fatty acid. In muscle, fatty acids are oxidized for energy; in adipose tissue, they are re-esterized as TAGs for storage.
- Apo CII is taken back by HDL and remaining is: Chylomicron remnamnt (B-48, E) and VLDL remnant/IDL (B-100,E) which have lost triglyceride but are rich in cholesterol.
- Chylomicron remnant (B-48, E) enter liver through LDL receptor (Apo B-100, E) and Remnant receptor/LDL receptor related protein or LRP (Apo E).
- IDL or VLDL remnant (B-100, E) has 2 fates:
- Major: Loses Apo-E and is converted to LDL (B-100)
- Minor: Taken up by liver via LDL receptor
- LDL (B-100) has 2 fates:
- Major (80%): Enter liver through LDL receptor (ApoB-100, E)
- Minor (20%): Extrahepatic tissues through LDL receptor (ApoE)
- Oxidized LDL: Taken up by scavenger receptor
- Role of HDL: Besides being a reservoir for apoproteins, it serves function of reverse cholesterol transport.
- Other lipoproteins deliver cholesterol to extrahepatic tissues
- HDL takes cholesterol from extrahepatic tissues through ABC-1 (ATP binding cassette) transporter.
- LCAT in HDL (stimulated by A-1) converts cholesterol to cholesterol ester (forms HDL3 rich in CE)
- CETP (Cholesterol ester transport protein) mediates exchange of cholesterol ester for triglyceride from HDL3 with other lipoproteins (HDL3 transfers CE and receives TGs) forming TG rich HDL2 (mature HDL).
- HDL2 have 2 fates:
- TGs hydrolyzed by hepatic lipase: converted back to HDL3
- Taken up in liver by SR-1 receptor.
- What happens after uptake of Cholesterol in tissues:
- Downregulates LDL receptor
- Downregulates HMG-CoA reductase (Cholesterol synthesis)
- Upregulates ACAT (Cholesterol esterified and stored as cholesterol ester)
- Synthesis of cell membrane, steroidal hormones, bile acids
- Repackaging in HDL and VLDL (in liver)
Defects in Components of Lipoprotein Metabolism
1. Lipoprotein Lipase (Type I hyperlipidemia): Increased chylomicrons and VLDL (triglycerides) with decrease in LDL and HDL – cholesterol is normal
- Deficienct lipoportein lipase
- Defective Apo-CII leading to inadequate activation of lipoprotein lipase
Other features of type I hyperlipidemia:
- Red-orange eruptive xanthomas
- Fatty liver
- Acute pancreatitis
- Abdominal pain after fatty meal
- No atherosclerosis (LDL is not raised)
2. LDL receptor (Type II hyperlipidemia): Increased LDL (cholesterol)
- Type IIa hyperlipidemia: Familial hypercholesterolemia (Autosomal dominant)
- Type IIb hyperlipidemia: Familial combined hyperlipidemia
- Increased LDL (cholesterol) + Increased VLDL (triglycerides)
- Excessive free fatty acid production by various tissues leads to increased VLDL synthesis by the liver. Initially, most VLDL is converted into LDL until this mechanism is saturated, after which VLDL levels elevate.
- Metabolic syndrome (Syndrome ‘X’) is a form of acquired combined hyperlipidemia
Other features of Type IIa hyperlipidemia:
- Xanthomas of achilles tendon
- Subcutaneous tuberous xanthomas over the elbows
- Xanthelasmas (lipid in the eyelid)
- Corneal arcus
- High risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease
- No pancreatitis
3. Apo E (Type III hyperlipidemia or familial dysbetalipoporteinemia or remnant hyperlipidemia):
- Increased remnants – chylomicron remnant and IDL/VLDL remnant (rich in cholesterol)
- Palmar xanthomas
- Similar to type II hyperlipidemia
4. Unknown defect leading to overproduction or under-clearance of VLDL (Type IV hyperlipidemia):
- Increased VLDL leading to Hypertriglyceridemia with normal cholesterol levels
- Eruptive xanthomas and Coronary artery disease
Type V Hyperlipidemia (Mixed hyperlipidemia): Type I + Type IV hyperlipidemia
- Remember: 1 + 4 = 5
5. B-100 and B-48: Abetalipoproteinemia
- Low chylomicrons (very low triglycerides) and VLDL (low cholesterol)
- Low chylomicrons = fat accumulates in enterocytes and hepatocytes
- Essential fatty acids and vitamins A and E are not well absorbed
- Steatorrhea, Cerebellar ataxia, Pigmentary degeneration in retina, Acanthocytes (thorny appearing RBCs), Loss of night vision
6. ABCA-1: Tangier disease
- Reduced HDL concentration
- Tendency to hypertriglyceridemia; some elevation in VLDLs; hypertrophic tonsils with orange appearance
7. Defect in Lysosomal Hydrolysis of cholesterol: Cholesteryl Ester Storage Disease (Wolman’s Disease).
All are inherited in autosomal recessive pattern except type II hyperlipidemia (receptor defect) and type IV hyperlipidemia which are autosomal dominant. To learn the technique of guessing the inheritance pattern of genetic diseases – use this mnemonic.