Etiology
Mnemonic: RSTUV
- Radial inclination – decreased
- Shape of lunate (Type 1 has more proximal apex; Type 2 & 3 are more rectangular)
- Type 1 lunate is seen with negative ulnar variance and possess highest risk of Kienbock’s disease
- Trauma (repetitive micro-fractures or single fracture)
- Ulnar variance – negative (increased radial-lunate contact stress)
- Vascular anatomy (3 patterns – X, Y, I)
- “I” pattern (single vessel to lunate) – highest risk of avascular necrosis
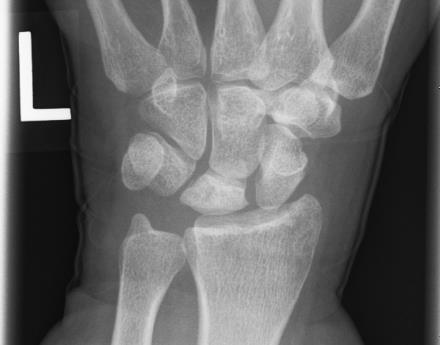
Muzichick, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
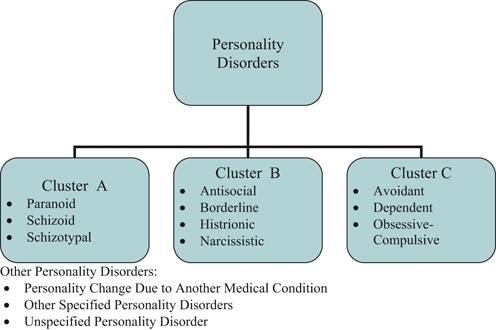
Lichtman Classification and Management
| Stage | Description | Treatment |
| Mnemonic: ABCD | Mnemonic: ABCD | |
| I | Abnormal MRI (decreased T1 intensity; variable T2 intensity) or scintigraphy | Analgesics + immobilization |
| II | Bone sclerosis ± Bone breaks (fracture lines) | Bony procedures: 1. Negative or Neutral ulnar variance: Joint levelling procedure (Radius shortening osteotomy; Ulnar lengthening) 2. Positive ulnar variance: Revascularization procedures (pedicled vascularized bone graft from dorsal distal radius), Distal radius core decompression, Radial wedge osteotomy |
| III | Collapse of wrist with: | |
| A | Normal carpal alignment | Same as stage II |
| B | Fixed scaphoid rotation | Carpal fusion (STT or SC) Carpectomy (PRC) |
| IV | Degenerative changes of wrist | Deliverance (Salvage) 1. Proximal row carpectomy (PRC – allows capitate to articulate into lunate fossa) 2. Wrist arthrodesis 3. Wrist denervation 4. Total wrist arthroplasty |

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.