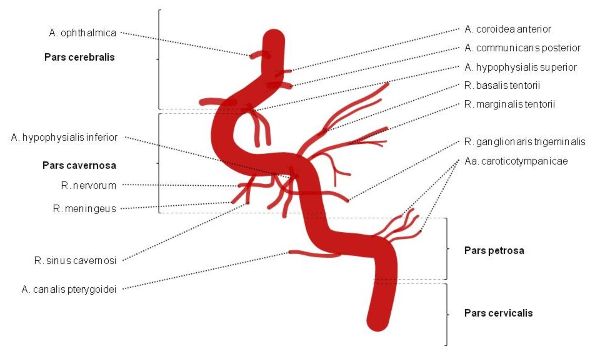
7 segments of Internal Carotid Artery
We have already discussed a mnemonic to remember the course of Internal Carotid Artery with the help of 2 horizontal “S” under the topic of Circle of Willis.
- C1 – Cervical segment
- C2 – Petrous (horizontal) segment
- C3 – Lacerum segment
- C4 – Cavernous segment
- C5 – Clinoid segment
- C6 – Ophthalmic (supraclinoid) segment
- C7 – Communicating (terminal) segment
Mnemonic: Except for the C7, odd numbered segments do not have branches.
Branches of Internal Carotid Artery
Segment C2
These supply the nose and ear.
- Vidian artery
- Caroticotympanic artery
Segment C4
These supply the trigeminal ganglion, pituitary and meninges.
- Inferolateral trunk: supplies trigeminal ganglion
- Meningohypophyseal trunk: supplies meninges and pituitary (through inferior hypophyseal artery)
Segment C6
These supply the pituitary, eye, orbit and nose.
- Superior hypophyseal artery
- Ophthalmic artery
Segment C7
These supply brain as a part of circle of willis.
- Posterior communicating artery
- Anterior choroidal artery
- Terminal branches: Middle cerebral artery and Anterior cerebral artery
Mnemonic:
- 1st supplies the parts of head – nose and ear.
- Then supplies the covering of brain and pituitary.
- Then supplies the eyes.
- At last supplies the brain.
Mnemonic for branches: A VIP’S COMMA
- A: Anterior choroidal artery (C7)
- V: Vidian artery (C2)
- I: Inferolateral trunk (C4)
- P: Posterior communicating artery (C7)
- S: Superior hypophyseal artery (C6)
- C: Caroticotympanic artery (C2)
- O: Ophthalmic artery (C6)
- M: Meningohypophyseal trunk (C4)
- M: Middle cerebral artery (C7)
- A: Anterior cerebral artery (C7)
Brain structures supplied by Internal Carotid Artery
1. Cerebral hemispheres
2. Eye, optic nerve, optic chiasma and optic tract
3. Midbrain through anterior choroidal artery
4. Thalamus and internal capsule through posterior communicating artery
5. Pituitary gland and hypothalamus
6. Meninges of the skull base