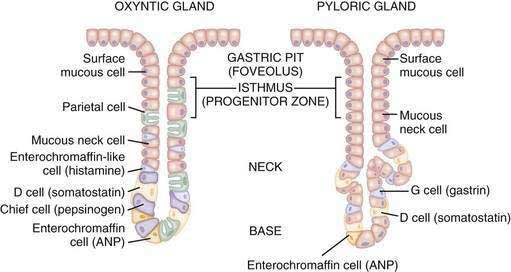
Anatomically, stomach can be divided into 3 parts from above to below:
- Cardiac
- Fundus and body/corpus
- Pyloric/Antral
Gastric pits deepen as we move below from cardiac to pyloric glands.
Mucus secreting cells: Present in all 3 glands – cardiac, fundic and pyloric but predominate in cardiac and pyloric glands.
Pyloric glands have 1 more cell – G cells which secrete Gastrin.
Fundic glands (gastric glands of fundus and body) can be divided into 3 parts from above (towards gastric pit) to downwards:
- Isthmus (Outer zone) – Mucus cells and Stem cells
- Neck (Middle zone) – Parietal (Oxyntic) cells
- Fundus (Basal zone) – Chief (Zymogen) cells and Enteroendocrine cells (Mnemonic: ECF)
Parietal (Oxyntic) cells secrete:
- Hydrochloric acid
- Intrinsic factor
- Ghrelin
Mnemonic: Parietal cells are Pink (Eosinophilic).
Chief (Zymogen/Peptic) cells secrete:
- Pepsin
- Gastric lipase
Mnemonic: Basal cheif cells are Blue (Basophilic). These have a lot of rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER).
Enteroendocrine cells:
- G cells = Gastrin
- D cells = Somatostatin
- ECL cells = Histamine