Enzymes:
- Fatty acid synthase (6 enzymes and 1 Acyl carrier protein molecule)
- Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (rate-limiting enzyme)
Starting material:
- For palmitate synthesis: Acetyl-CoA
- For odd number carbon long chain fatty acid synthesis: Propionyl-CoA
2 Carbon donor: Malonyl-CoA (donates 2 C and 1 C is thrown out as CO2)
Site: Cytosol
Citrate shuttle transfers acetyl-CoA from mitochondria to cytosol.
- OAA + Acetyl-CoA = Citrate (Mitochondria)
- Citrate (Mitochondria) = Citrate (Cytosol)
- Citrate = OAA + Acetyl-CoA (Cytosol)
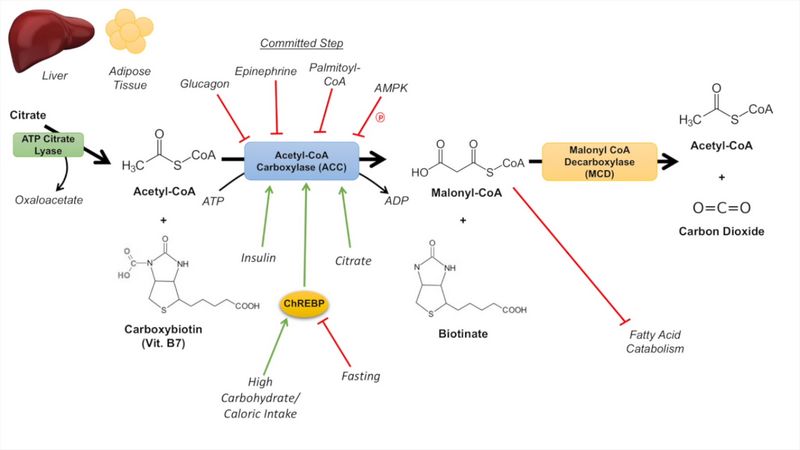
1st and Rate limitng step
Formation of Malonyl-CoA (3C) from Acetyl-CoA (2C) by Acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
- 1 ATP used
- Requires Biotin and Bicarbonate (source of CO2)
- Stimulated by: Insulin, Citrate, ChREBP (induced by high carbohydrate diet/caloric intake)
- Inhibited by: Glucagon, Epinephrine (AMP dependent kinase), Palmitoyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA inhibits carnitine acyltransferase to prevent fatty acids from being taken into the mitochondrial matrix to be beta oxidized at times when fatty acids are being synthesized, thus preventing a futile cycle.
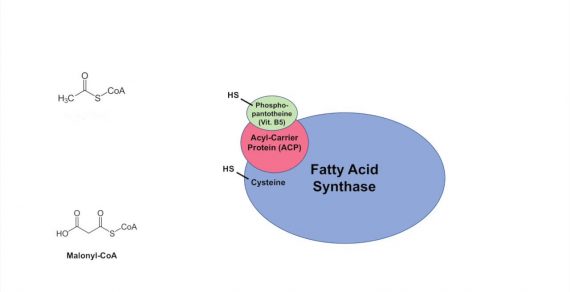
Fatty Acid Synthase
It is a multimeric complex, but the 2 important domains are:
1. Ketoacyl synthase (KAS) end:
- has Cysteine-SH active site
- accepts Acetyl-CoA and Acyl chain extended by 2 C on each cycle
2. Acyl carrier protein (ACP) end:
- has Pantothenic-SH active site
- accepts Malonyl-CoA
Fatty Acid Synthesis
NADPH donors:
- HMP shunt pathway
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- Malic enzyme
Mnemonic: HIM donates NADPH.
1. Loading of precursors to KAS and ACP end of FA synthase.
2. Condensation: Addition of 2 C atoms derived from Malonyl-CoA (Malonyl-CoA at ACP end takes precursor at KAS end and KAS end is free)
3. Reduction: 1 NADPH used
4. Dehydration
5. Reduction: 1 NADPH used
6. Acyl chain extended by 2 C atom (donated by Malonyl-CoA) is transferred to KAS end and ACP end is free to receive Malonyl-C0A.
- Precursor loaded on KAS end is transferred to ACP end with Malonyl-CoA (KAS end is free).
- Acyl chain elongated with 2 C atom is transferred from ACP end to KAS end (ACP end is free).
- Malonyl-CoA is loaded on ACP end.
- Cycle repeats.
7. Cycle of precursor loading, condensation, reduction, dehydration and reduction (Chain elongation) occurs unless 16 C Palmitate is formed which is released from FA synthase enzyme complex by Thioesterase.
Humans make palmitic acid (16:0) as stored fat (only de novo fat possible).
- End-product: Palmitate (C16:0)
- Total of 7 cycles:
- Starts with 2 carbon acetyl-CoA
- Malonyl-CoA acts as a 2 carbon donor
- 7 Malonyl-CoA utilized (14 carbons)
- 2 NADPH (2 reduction reactions) X 7 cycles = 14 NADPH utilized
- 1 ATP (acetyl-CoA carboxylase reaction) X 7 cycles = 7 ATP utilized (+1 ATP to transport acetyl-CoA from mitochondria to cytosol)
- 1 CO2 (released when malonyl-CoA donates 2 C acyl chain) X 7 cycles = 7 CO2 released
- 1 Acetyl-CoA (to make malonyl-CoA) X 7 cylces + 1 Acetyl-CoA (precursor in KAS end) = 8 Acetyl-CoA utilized
From palmitate, we have elongases which add additional carbons and desaturases which introduce double bonds. Beyond oleate (18:1Δ9), mammals cannot go any further – we can’t introduce double bonds beyond C9, yet we do need some of those. These are essential fatty acids which can be synthesized only by plants and must be obtained in our diet. They are essential for instance for making arachidonate.
Elongation, starting with stearate (18:0), is performed mainly in the ER (microsomal system requiring oxygen i.e. aerobic process) by several membrane-bound enzymes. The enzymatic steps involved in the elongation process are principally the same as those carried out by FA Synthase.
Mitochondrial fatty acid elongation (anaerobic pathway) is essentially a reversal of beta-oxidation, except that one NADPH and one NADH are required (beta-oxidation yields two NADH). Mitochondrial fatty acid elongation acts primarily on fatty acyl CoA substrates shorter than 16 carbons. Pyridoxal-phosphate is required as a coenzyme. It is favored by high NADH/NAD ratio.