Course
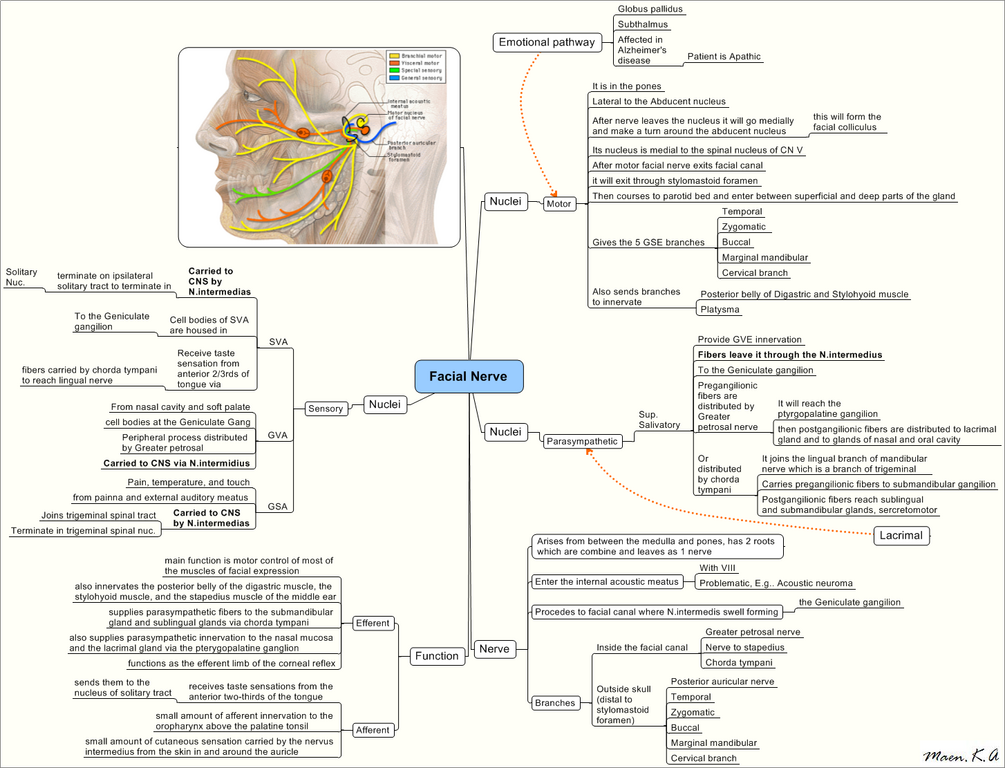
Origin: Ponto-medullary junction (Nucleus solitarius, Facial nucleus and Superior salivatory nucleus)
Internal acoustic meatus: 7 up, Coke down
- 7th (Facial nerve) up
- Cochlear nerve (CN VIII) down
- Superior and inferior vestibular nerve (CN VIII) posteriorly
Facial canal:
- Forms Geniculate ganglion
- Gives 3 branches: GSC
- Greater petrosal nerve (first branch; forms nerve of pterygopalatine ganglion with Deep Petrosal Nerve)
- Nerve to Stapedius
- Chorda tympani (taste sensation from anterior 2/3 tongue, sublingular and submandibular gland)
After exiting skull from stylomastoid foramen:
- 3 branches before entering the parotid gland: PDS
- Posterior auricular nerve
- Digastric branch (Posterior belly of digastric)
- Stylohyoid branch
- 5 branches within the parotid gland (most superficial structure passing through parotid): Tum Zyada Bakbak Mat Karo (innervates the muscles of facial expression)
- Tympanic
- Zygomatic
- Buccal
- Marginal mandibular
- Cervical (least important branch – supplies platysma)
Further reading:
Facial nerve lesions
1. Supranuclear lesion: Contralateral lower 1/2 face paralyzed; forehead wrinkling spared (Bilateral cortical innervation)
2. Infranuclear lesion: Entire face paralyzed on same size
- At or just above stylomastoid foramen: Bell’s palsy
- Above origin of chorda tympani: Bell’s palsy + Reduced salivation and loss of taste from anterior 2/3 tongue
- Above origin of nerve to stapedius: Above + Hyperacusis
- At geniculate ganglion: Above + Reduced lacrimation

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.