Second week is the week of twos. In third week trilaminal germ disc is formed. And now, here I have attempted to fit the fourth week in development of embryo as the week of fours.
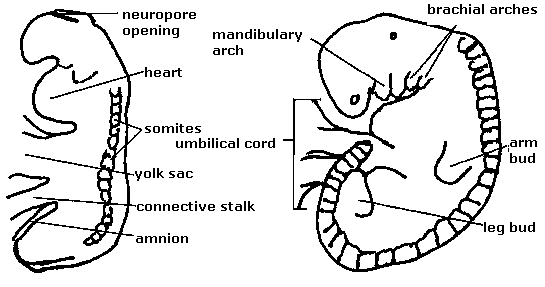
Four folds of the embryo
The embryo undergoes:
- Lateral folding
- Cranio-caudal folding
It forms four folds: 2 lateral, cranial and a caudal fold.
- Due to lateral folding several embryonic structures fuse in the midline including the heart tubes.
- Due to cranio-caudal folding cranial embryonic structures descend caudally and ventrally including the heart tubes and septum transversum.
Four subdivision of neural tube
As discussed earlier, by the end of 3rd week – neural plate forms neural folds and neural groove.
Day 22: Middle portion of neural fold closes first at the region of 4th-5th somite
Day 25: Closure of rostral neuropore
- Failure to close: Anencephaly
Day 28: Closure of caudal neuropore
- Failure to close: Spina bifida
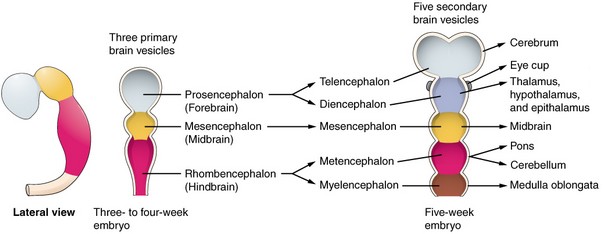
The closure of the caudal neuropore marks the completion of neurulation and divides neuropore into 4 divisions:
- Prosencephalon (Forebrain)
- Mesencephalon (Midbrain)
- Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain)
- Spinal cord
Sulcus limitans divides the neural tube into the dorsal (alar) plate, i.e. sensory and ventral (basal) plate, i.e. motor.
Optical vesicle (future optic nerve, retina, and iris) forms at the basal plate of the prosencephalon.
Neural crest cells: The neuroectodermal cells from lateral part of neural plate detaches and are called neural crest cells. These cells form crests above the neural tube (remember the crest of feathers in the logo of World Health Organization).
Neural crest cells give rise to Parasympathetic nervous system and Ganglia.
Four pharyngeal arches are visible
- Four pharyngeal arches are visible by the end of 4th week – 1st arch (mandibular arch) is prominent.
- 5th and 6th pharyngeal arch haven’t yet developed (5th arch later completely regresses).
For more details: Branchial apparatus made easy
Four limb buds begin to grow
- Upper limb buds become recognizabe during week 4 (Day 26-27).
- Lower limb bud becomes present by the end of 4th week.
Four prominences begin development of face
- Stomodeum (primitive mouth) – other prominences grow around the stomodeum
- Frontonasal prominence
- Maxillary prominences
- Mandibular prominences
The embryology of face and falate has already been discussed in: Embryology of face and palate made easy
Four chambered aseptate heart forms and beats
The embryology of heart has already been discussed in: Simplified embryology of heart
Foregut (four-gut) gives respiratory diverticulum
The primitive gut is formed in the 4th week by the incorporation of endoderm of dorsal yolk sac into the developing embryo. It extends from stomodeum to cloaca and consists of 3 parts: foregut, midgut and hindgut.
During the 4th week of gestation of the respiratory diverticulum, appear as a ventral outgrowth of the foregut endoderm.
Four compartmented somites
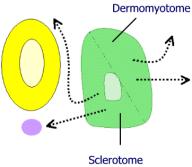 Somites are mesodermal mass around the neural tube that arises from the paraxial mesoder. It hast 4 compartments:
Somites are mesodermal mass around the neural tube that arises from the paraxial mesoder. It hast 4 compartments:
- Sclerotome: Vertebrae and rib cartilages
- Myotome: Skeletal muscles of back, ribs and limbs
- Dermatome: Dermis on the back
- Syndetome: Tendons and some blood vessels
They begin to be formed at the end of 3rd week and becomes prominent in 4th and 5th week. After day 25, about 3-4 somite pairs grow per day to a total of 42-44 in humas.
- 3 week embryo: 6-7 pairs of somites
- 4 week embryo: 27-29 paris of somites