Mnemonic: Remember 4 D common to all + 3 D for C-spine and 1 D for L-spine
Diagnosis requires: Score >4
Denis column disruption:
- Anterior column destroyed or unable to function (2 points)
- Posterior column destroyed or unable to function (2 points)
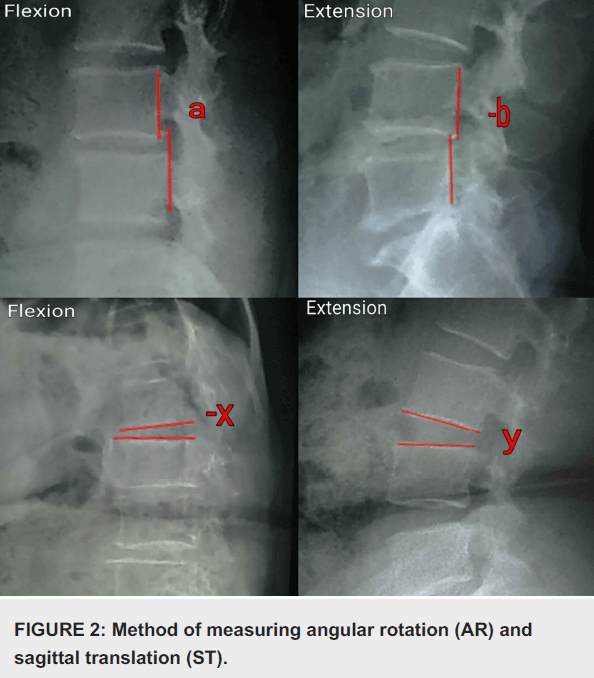
Deformity: Will have a maximum score of 4 points (2 points assigned for ART – angulation, rotation and translation each)
- Sagittal plane translation/displacement: 2 points
- C-spine: >3.5 mm or 20% in flexion-extension or resting x-rays
- T-spine: >2.5 mm
- L-spine: >4.5 mm or 15% in flexion-extension or resting x-rays
- Mnemonic: Remember C/T/L – 3.5/2.5/4.5
- Sagittal plane rotation in flexion-extension X-rays: 2 points
- C-spine: >20 degrees
- L-spine:
- >15 degrees at L1-L2, L2-L3 and L3-L4
- >20 degrees at L4-L5
- >25 degrees at L5-S1
- Mnemonic: Multiply by 5 (L3: 3X5 = 15; L4: 4X5 = 20; L5: 5X5 = 25)
- Sagittal plane angulation (relative) in resting X-rays: 2 points
- C-spine: >11 degrees
- T-spine: >5 degrees
- L-spine: >22 degrees
Damage of spinal cord/nerve root:
- C-spine: Spinal cord damage (2 points) and Nerve root damage (1 point)
- T-spine: Spinal cord damage (2 points)
- L-spine: Cauda equina syndrome (3 points)
Dangerous loading anticipated: 1 point
Other elements specific to C-spine:
- Distraction test (Stretch test) positive: 2 points
- Lateral view X-ray or C-arm with crutchfield tong traction or head-halter traction with 5 pounds of weight increment every 5 minutes (upto 1/3 of body weight) until test is positive (neurologic deficit or abnormal separation of anterior and posterior elements)
- Developmentally narrow spinal canal (Sagittal diameter <13 mm or Pavlov’s ratio <0.8): 1 points
- Disc narrowing (abnormal): 1 points
Other elements specific to T-spine:
- Disarticulation of costovertebral articulation: 1 point
Reference: Kim, C. W., Perry, A., & Garfin, S. R. (2005). Spinal Instability: The Orthopedic Approach. Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology, 09(01), 77–87. doi:10.1055/s-2005-867098