Interstitium is the scaffolding that supports the alveolar walls and surrounds both the alveoli and the terminal bronchioles. Neither alveoli nor interstitium is visible on a chest X-ray when normal. It is necessary to analyze whether the pattern of diffuse opacification in the lung field is alveolar or interstitial.
Terms:
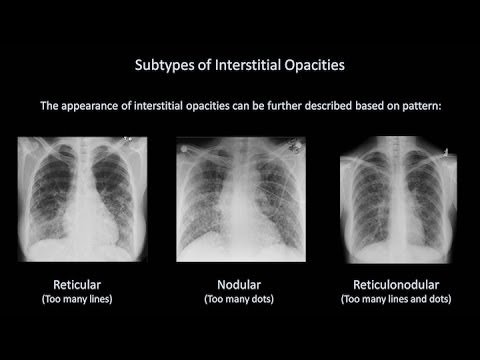
- Fine or small nodules: tiny opacities
- Reticular: mesh or basket-like – fine or coarse lines.
- Reticulo-nodular: a combination of both reticular and nodular pattern
- Septal lines: fine thread-like lines produced by fluid or thickening of the septa between the lobules of the lung. Kerley B lines are one of the commonest septal lines mentioned around in the rounds and textbooks.
- Kerley B lines: fine horizontal lines approximately 1 cm long, situated perpendicular to the lateral pleural surface – commonly seen just above the costophrenic angles on a frontal CXR
- Air bronchogram: air-filled bronchi (dark) being made visible by the opacification of surrounding alveoli (grey/white)
Difference between alveolar vs interstitial shadow:
| Alveolar pattern | Interstitial pattern | |
| Usual shadows | Fluffy or blobby | Small nodules |
| Ill-defined margins | Linear/reticular | |
| Coalescing/merging | Linear/reticular with septal lines | |
| Segmental/lobar | Reticulo-nodular | |
| Additional features | Air bronchogram | Reduced lung volume (extensive disease) |
| Honey-comb pattern (end-stage disease) |
Differential diagnosis:
These two entities may be present simultaneously but generally, one of them is present dominantly.
Dominant alveolar pattern
1. Adults:
- Pulmonary edema
- Lobar pneumonia
- Hemorrhage
- Lymphoma
- Bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma
- Adult respiratory distress syndrome (early)
- Aspiration pneumonia
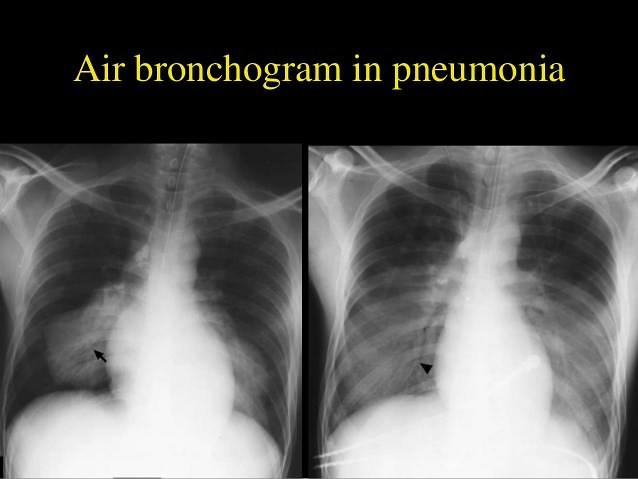
2. Infants:
- Hyaline membrane disease
- Transient tachypnoea of the newborn
Dominant Interstitial pattern:
- Pulmonary oedema
- Pneumonia: viral or Pneumocystis carinii (early)
- Tuberculosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Rheumatoid lung
- Sclerodema
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa
- Crack smoking
Hey, thanks for the forum topic.Much thanks again. Great. Sulivan