A) GLUCOSE LEVEL
1. Post-prandial:
- 140-200 mg/dl: Impaired glucose tolerance (Pre-diabetes)
- Diabetes prevented with: weight loss, exercise, metformin (in high risk)
- ≥200 mg/dl (+ Clinical symptoms): Diabetes confirmed
2. Fasting:
- 100-126 mg/dl: Impaired fasting glucose (Pre-diabetes)
- ≥126 mg/dl (+ Clinical symptoms): Diabetes confirmed
B) CONFIRMATION OF DIABETES MELLITUS
1. Postpranial glucose ≥200 mg/dl or Fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dl + Clinical Symptoms
2. ≥200 mg/dl glucose level after 2 hours of 75 gm glucose load (Oral glucose tolerance test)
3. HbA1c ≥ 6.5% (not recommended)
C) SECONDARY DIABETES MELLITUS
1. Drugs: Steroids, Thiazides, Diazoxide, Protease inhibitors
2. Genetic: Down’s syndrome, Turner’s syndrome, Klinefelter’s syndrome
3. Endocrinopathies: Cushing’s syndrome, Acromegaly, Hyperthyroidism, Pheochromocytoma
4. Exocrine pancreatic diseases: Hemochromatosis, pancreatitis, malignancy, cystic fibrosis
Management of secondary diabetes: Investigate and treat accordingly
D) TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
Absolute insulin deficiency; characterized by low level of insulin and C-peptide
Insulin:
Method of delivery: subcutaneous injection
Administration: 90 degrees to skin on anterior abdominal wall, upper arms, thighs or buttocks
Delivery devices: glass syringe, plastic syringe, pen device, infusion pump
Regimens:
a. Twice daily administration: Soluble + Isophane (1:2)
- Before breakfast: 2/3rd dose
- Before dinner: 1/3rd dose
b. Multiple injection regimen:
- Before each meal: short-acting insulin
- Basal bolus: intermediate or long-acting insulin X 1-2/day
c. Alternate: Continuous subcutaneous infusion (CSI)
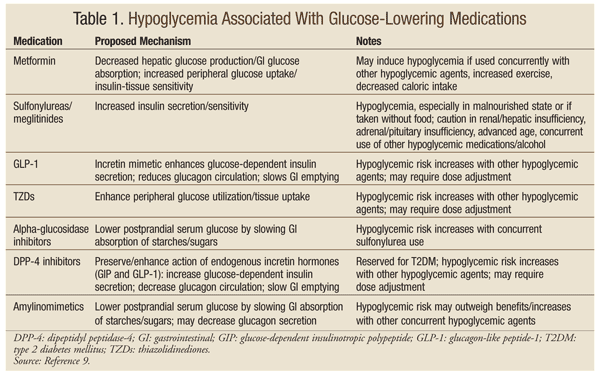
Adverse effects of insulin:
- Hypoglycemia
- Weight gain
- Peripheral edema
- Local allergy
- Lipohypothrophu/atrophy
Patient is taught to count carbohydrate and to calculate both correction and prandial dosing.
If ESRD: Consider transplantation of isolated pancreatic islets
E) Type 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Relative insulin deficiency; characterized by normal or high level of C-peptide
Aim: Target HbA1c <7%
1. Diet control:
a. Carbohydrate (45-60%): Sucrose upto 10%
b. Fat (<35%):
- n-6 PUFA: <10%
- n-3 PUFA: 1 portion oily fish X 1-2/wk
- Monounsaturated fatty acid: 10-20%
- Saturated fatty acid: <10%
c. Protein (10-15%): <1 gm/kg/day
d. Salt: <6 gm/day
2. Weight loss: ~ 10%
3. Exercise: ≥30 min/day
4. Vaccinations
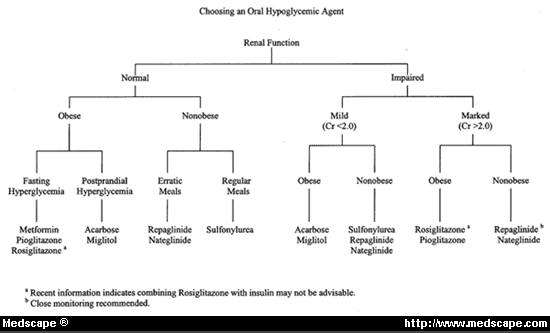
5. Anti-Diabetics:
a. 1st line:
- Metformin (Contraindicated if Creatinine >1.5 mg/dl) OR
- Sulfonylureas (If metformin intolerance or with weight loss/osmotic symptoms)
b. 2nd line:
- Sulfonylureas OR
- Thiazolidinediones (If hypoglycemia is concern and no congestive heart failure) OR
- DPP-4 inhibitor (If hypoglycemia is concern or weight gain is concern)
c. 3rd line:
- Continue Metformin or Sulfonylureas if tolerated and Add –
- Thiazolidinediones or DDP-4 inhibitor OR
- Insulin (Initial basal; add prandial if required; start 0.3 U/kg) OR
- GLP-1 agonist (if obese and <10 years from diagnosis)
Aim: BP <130/80 mmHg
- ACE inhibitor +/- CCBs or Diuretics
Aim: Urinary microalbuminuria (>30 mg/g creatinine)
- ACE inhibitor or ARBs
Aim: LDL <100 mg/dl
- Statins
Aim: HDL >40 mg/dl
- Fibrate or nicotinic acid
- Exercise
Other:
- Aspirin: If >40 years
- Yearly dilated eye examination