Understand the conducting system of heart, cardiac action potential and pacemaker action potential.
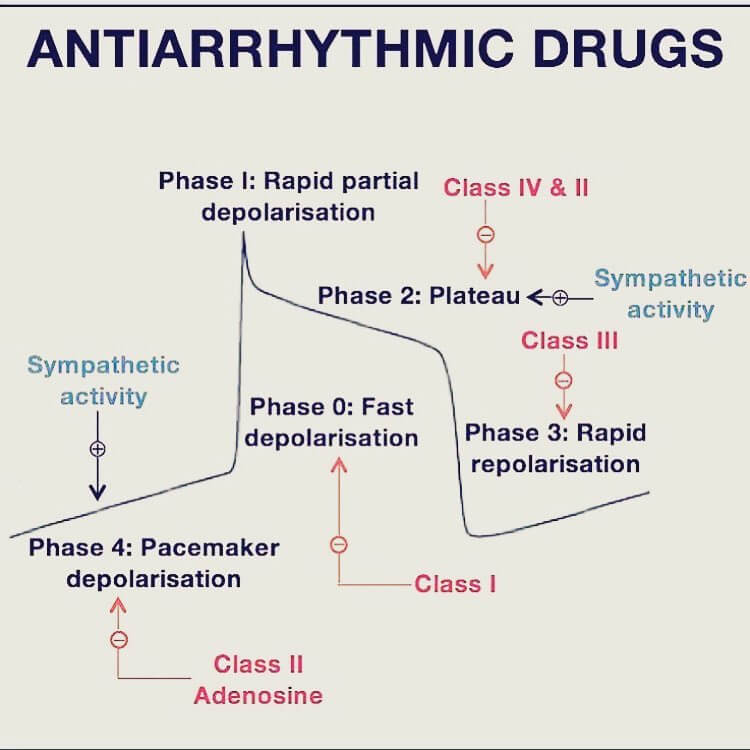
Mnemonic to remember Vaughan Williams classification for anti-arrhythmic – Some Block Potassium Channel DAAM!
| Mnemonic | Class | Mechanism of action | Comments | Example | Use |
| Some | IA | Sodium channel blocker (moderate) Intermediate action | Moderate ↓ phase 0 slope ↑ EFR & AP duration Additional class III action | Quinidine, Procainamide, Disopyramide | Ventricular arrhythmias, WPW (procainamide) |
| IB | Sodium channel blocker (weak) Fast action | Small ↓ phase 0 slope ↓ EFR & AP duration | Lidocaine, Mexiletine | VT | |
| IC | Sodium channel blocker (strong) Slow action | Pronounced ↓ phase 0 slope = EFR & AP duration | Flecainide, Propafenone | Paroxysmal AF, recurrent SVT | |
| Block | II | Beta blocker | ↓ phase 4 slope in nodes (pacemaker potential) Prolong AV node repolarization | Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Carvedilol, Esmolol, Metoprolol, Propranolol, Sotalol | Recurrent tachyarrhythmias |
| Potassium | III | Potassium channel blocker | Delay phase 3 (repolarization) | Amiodarone (also class I, II & IV action), Sotalol (also class II action), Dofetilide, Ibutilide | Atrial fibrillation & flutter, Ventricular tachycardia |
| Channel | IV | Calcium channel blocker | Prolongs phase 2 ↓ slope phase 0 & 4 in node (pacemaker potential) Prolong AV node repolarization | Verapamil, Diltiazem | Paroxysmal SVT, AF with RVR |
| DAAM | V/Others | Direct nodal inhibition | Digoxin Atropine Adenosine Magensium sulphate | SVT (Adenosine), Torsades de pointes (Magnesium), Rate control in AF (Digoxin) |