Diagnosis (Berlin Criteria)
| Mnemonic | A | R | D | S |
| Acute Lung Injury (ALI) | Acute onset (<7 days) | Ratio PaO2/FiO2 ≤300 mmHg or 40 kPa | Diffuse bilateral pulmonary infiltrates on CXR | Swan-Ganz pulmonary wedge pressure ≤18 mmHg or No evidence of Left atrial hypertension |
| Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) | Acute onset (<7 days) | Ratio PaO2/FiO2 ≤200 mmHg or 26.6 kPa | Diffuse bilateral pulmonary infiltrates on CXR | Swan-Ganz pulmonary wedge pressure ≤18 mmHg or No evidence of Left atrial hypertension |
Causes of ALI and ARDS
Mnemonic: ARDS
- A
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Air embolism
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- R
- Radiation-Trauma-Burns
- D
- DIC
- Drugs (chemotherapy, heroin)
- near Drowning
- Dialysis
- Dysregulation of metabolic pathways (pancreatitis, uremia, ingestion of paraquat)
- S
- Shock
- Sepsis
- Smoke inhalation
Phases of ALI and ARDS
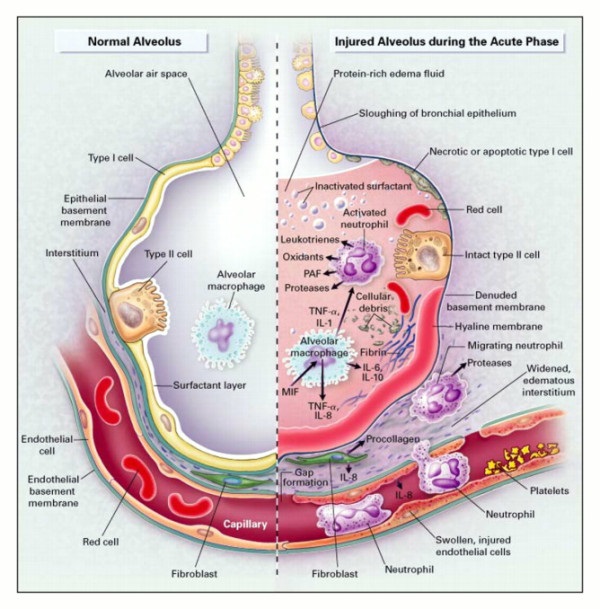
| Phase (Mnemonic: EPF) | Onset | Event | Pathology | Treatment principles |
| 1. Exudative | <1 week | IL-1 & other inflammatory mediators | Interstitial alveolar edema Hyaline membrane | 1. Primarily supportive 2. Treatment of cause 3. PEEP ventilation 4. Inverse ventilation (Inspiration : Expiration ratio = 2:1) 5. Prone ventilation |
| 2. Proliferative | 1-3 weeks | Type II pneumocyte + myofibroblast proliferation | Alveolar exudate resolves or organizes | Inhaled NO (Vasodilation may improve V/Q at ventilated areas) |
| 3. Fibrotic | >3 weeks | Collagen III to I conversion | Alveolar ducts & spaces undergo fibrosis | Steroids |