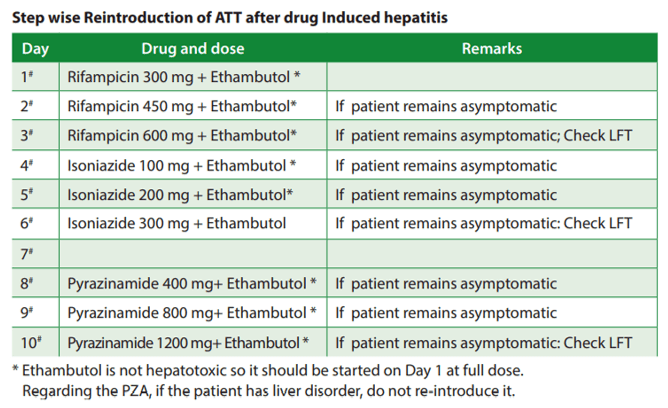
Normal values
- pH: 7.35-7.45
- PaCO2: 35-45 mmHg (4.7-6 kPa)
- PaO2: 75-100 mmHg
- HCO3-: 22-26 mEq/L
- SaO2: 94-100%
- Base excess: -2 to +2 mmol/L
Step 1: pH
- >7.45 = Alkalemia
- <7.35 = Acidemia
- 7.35-7.45 = Normal or Complete compensation
Step 2: pCO2
- Increased = Respiratory acidosis or compensation of metabolic alkalosis
- Determine chronicity by looking at metabolic compensation:
- Acute: 10 Δ pCO2 = 0.08 Δ pH (opposite direction)
- Chronic: 10 Δ pCO2 = 0.03 Δ pH
- Determine chronicity by looking at metabolic compensation:
- Decreased = Respiratory alkalosis or compensation of metabolic acidosis
Step 3: HCO3-
- Increased = Metabolic alkalosis (VOMED) or compensation of respiratory acidosis
- Decreased = Metabolic acidosis or compensation of respiratory alkalosis
- Determine anion-gap (AG): Normal = 5-12 (or 2.5 X Albumin)
- AG = Na – [Cl – HCO3]
- AG increased = Anion gap acidosis (MUDPILES/GOLDMARK)
- AG decreased = Non-anion gap (hyperchloremic) acidosis (GUT/HARDUP)
- AG = Na – [Cl – HCO3]
- Determine anion-gap (AG): Normal = 5-12 (or 2.5 X Albumin)
Step 4: Determine compensation
If there is metabolic acidosis or alkalosis, determine if there is appropriate respiratory compensation:
- Expected pCO2 = 1.5 X [HCO3] + 8 +/- 2 (Winter’s formula) OR
- Expected pCO2 = last 2 digits of pH
No respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 = Measured pCO2
Respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 ≠ Measure pCO2
Step 5: Delta ratio
ΔAG / ΔHCO3
- 1 = No other derangements
- >1.5 = Superimposed metabolic alkalosis
- <0.8 = Superimposed non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
Mnemonics
MUDPILES:
- Methanol/Metformin
- Uremia
- DKA
- Paraldehyde
- INH
- Lactic acidosis
- Ethylene glycol
- Salicylates
GOLDMARK:
- Glycols
- Oxoproline
- L-lactate (standard lactate seen in lactic acidosis)
- D-lactate (exogenous lactate produced by gut bacteria)
- Methanol
- Aspirin
- Renal failure
- Ketones (diabetic, alcoholic, starvation)
GUT:
- Gastrointestinal losses (diarrhea, pancreatic fistula)
- Urinary losses
- Total parenteral nutrition
HARDCUP:
- Hyperchloremia
- Acetazolamide, Addison’s disease
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Diarrhea, iliostomies, fistula
- Cholestyramine
- Ureteroenterostomies
- Pancreatoenterostomies
VOMED:
- Vomiting or aspiration
- Overcorrection of chronic hypercarbia or any acidosis
- Mineralocorticoid excess
- Ethylene glycol poisoning/Early sepsis
- Diuretics/Diarrhea