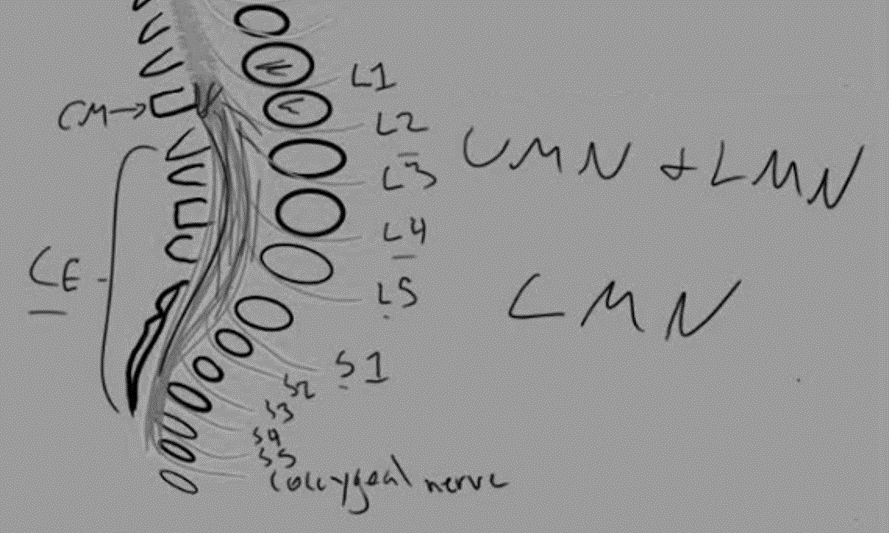Definitions
| Condition | Vertebral level of injury | Neurological level of injury | ISNCI level of injury |
| Conus Medullaris Syndrome (CMS) | T12-L2 | T12-S5 | T11 |
| Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) | L3-L5 | L3-S5 | L2 |
Anatomy
The spinal cord ends as a tapered structure called the conus medullaris at the level of L2–L3 disc in the neonate and the L1–L2 disc or cephalad at 1 year and older. It consists of the sacral (S2-S5) and coccygeal spinal cord segments.
The rest of the caudad spinal canal only houses nerve roots that are collectively known as cauda equina. The nerves in the cauda equina region include lower lumbar and all of the sacral nerve roots.
The pelvic splanchnic nerves carry preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from S2-S4 to innervate the detrusor muscle of the urinary bladder. Conversely, somatic lower motor neurons from S2-S4 innervate the voluntary muscles of the external anal sphincter and the urethral sphincter via the inferior rectal and the perineal branches of the pudendal nerve, respectively.
Pathophysiology
Some important points to note:
1. Conus medullaris comprises of a spinal cord and is in proximity to the nerve roots. Hence, conus medullaris syndrome is a combination of upper motor neuron (UMN) and lower motor neuron (LMN) lesion.
2. Cauda equina comprises of nerve roots only. Hence, cauda equina syndrome is a lower motor neuron (LMN) lesion.
3. Nerve roots in cauda equina have poorly developed epineurium making it susceptible to injury.
4. Not only the magnitude but also the length and the speed of obstruction are important in damaging the cauda equina region.
5. With fractures located above the L2 level – the conus medullaris and spinal cord occupy the spinal canal in this location, and these neural elements are more prone to neurologic injury than the nerve roots of the cauda equina.
Conus medullaris vs Cauda equina syndrome
| Conus medullaris syndrome | Cauda equina syndrome | |
| Presentation | Sudden and bilateral (predominantly symmetric) | Gradual and unilateral (often asymmetric) |
| Reflexes | Knee jerks preserved but ankle jerks affected | Both ankle and knee jerks affected |
| Radicular pain | Less severe | More severe |
| Low back pain | More | Less |
| Sensory symptoms and signs | More localized to perianal region; sensory dissociation occurs | More localized to saddle area; no sensory disscoiation |
| Motor strength | Hyper-reflexic distal paresis | Areflexic paraplegia |
| Impotence | Frequent | Less frequent |
| Sphincter dysfunction | Early; both urinary and fecal incontinence | Late; urinary incontinence |
Mnemonic: Conus rhymes with ANUS
1. periAnal localized
2. Nimble (fast and early involvement)
3. Upper motor neuron involvement
4. Symmetric involvement