Rule of 150 and 4
a. Begin treatment if: Paracetamol is ingested at a dose >150 mg/kg
Threshold to begin treatment is half the dose (75 mg/kg) in high risk cases:
1. Regular ethanol consumption: >21 Units/week in male and >14 Units/week in female
2. Regular use of enzyme inducing drugs: carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbitone, rifampicin
3. Conditions causing glutathion depletion: malnutrition, HIV, eating disorder, cystic fibrosis
Remember the 3 E – Ethanol, Enzyme inducer, Eating disorder
b. Within 4 hours of ingestion: Oral/NG/OG Activated Charcol (1/50, i.e. 1 gm/kg or 50 gm)
c. Send Serum APAP level after 4 hours post-ingestion and Start NAC if: Serum APAP level >150 microgram/ml at 4 hours post-ingestion (or use Rumack-Matthew normogram for acute ingestion upto 24 hours) OR Ingested dose >150 mg/kg and Serum APAP level cannot be obtained within 8 hours post-ingestion or patient presents after 8 hours or if the dosing is staggered
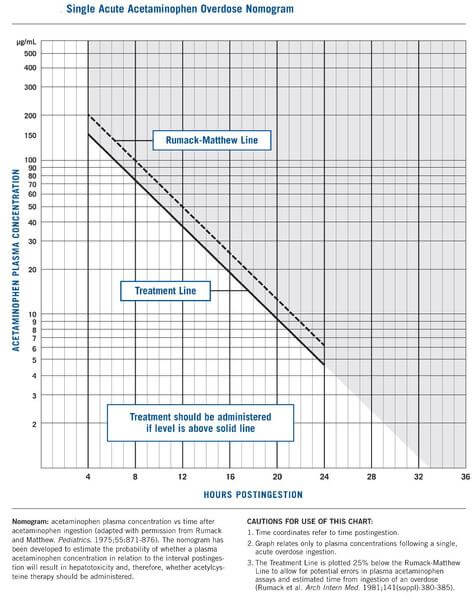
d. NAC dosing:
- Loading: 150 mg/kg IV in 200 ml (3 ml/kg) 5%DW over 1 hour
- Maintenance: 150 mg/kg IV in (21 ml/kg) 1500 ml 5%DW over 20 hours.
- 1/3rd in 1st 4 hours
- 2/3rd in later 16 hours
Oral dose of NAC:
1. Loading: 140 mg/kg
2. Maintenance: 70 mg/kg every 4 hours for 17 doses
Rechecking serum APAP level:
1. IV NAC dosing: at 20 hours
2. Oral NAC dosing: at 24 hours
NAC can be started empirically if serum APAP level is not obtained within 8 hours and it can be stopped prior to completion of total regimen if:
a. APAP level returns to 0
b. INR <2
c. AST normalizes
King’s college Criteria
It is used for predicting fulminant hepatic failure and referral to the transplant center.
Mnemonic: A or B, C and D
a. Acidosis: Arterial pH <7.3 or lactate >3 OR
b. All of the following:
- Bleeding risk: PT >100s or INR >6.5
- Creatinine: >3.4 mg/dl
- Drowsiness: Hepatic Encephalopathy Grade III or IV
References:
- Wallace CI, Dargan PI, Jones ALParacetamol overdose: an evidence based flowchart to guide managementEmergency Medicine Journal 2002;19:202-205.
- The Washington Manual of Medical Therapeutics – By Hemant Godara

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.